* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electricity 6
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
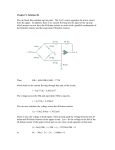
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
2016-17 Electricity 6 1. 4V 2Ω A. As drawn right now, is the above an open or closed circuit? B. With the switch is closed, what is the current in the circuit? 4V 2. Work the circuit at the right and answer the following questions. E D A. Calculate the current flowing thru the circuit. C. If a third battery is added to the circuit, how will the current change? 10Ω C B. If one of the resistors is removed, how will the current change? F 6V B 6Ω D. How much current is flowing thru the 6Ω resistor? 3V G E. How much voltage is used by the 6Ω resistor? A F. 2Ω How much power is used by the 6Ω resistor? G. Calculate how much voltage is left at point E. I H H. How much power does the whole circuit use? 3. Series or parallel? A. ___ Only one path for the electricity to flow. E. ____ If one light turns off, the others stay on. B. ___ Paths are dependent on each other (one affects the other). F. ____ If you turn off one light, all the lights turn off. C. ___ How your house is wired. D. ___ Paths are independent of each other. Small pipe Big pipe 6. G.____ Has more than one path for the electricity to flow. H.____ Two devices have the same current. I. ____ Two devices have the same voltage. 4. The four holes at the left are pipes coming out of the page. A. Are the four holes in parallel or series, as shown? B. Together is there a bigger hole or a smaller hole for water to flow thru? C. Each pipe can allow 2 gal/sec, how much can flow thru them together? D. So, is the resistance increasing or decreasing? This is why 4 equal resistors in parallel are the same as a single resistor that is 1/4th as big. 5. A. B. C. D. Which pipe allows current to flow through it: big pipe, small pipe, or both? Which pipe allows the most current through it: big pipe, small pipe, or both? Which pipe is the bigger resistor: big pipe, small pipe, or both? When the two pipes are put together is the total current more or less than that of the big pipe alone? E. So, when the two pipes are put together, does the total resistance increase or decrease? This is why resistors in parallel decrease the total resistance Five 100Ω resistors are placed in a circuit. A. What is the total resistance if they are in series? B. What is the total resistance if they are in parallel? cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2017, C. Stephen Murray 2016-17 Electricity and Magnetism 6—p2 7. Decide if the following are in parallel or series and find the total voltage or total resistance. A. Parallel or series? B. Parallel or series? C. Parallel or series? 3V 3Ω 8V 8V 3V 8. Rt = ______ 12Ω 12Ω 3V 6Ω Vt = ______ D. Parallel or series? Vt = ______ After working the diagram, answer the following. C 12Ω Rt = ______ D E F A. If the 6Ω resistor is disconnected, how will it affect the 2Ω resistor? B. What is the voltage at point H? 3V B C. What is the voltage at point F? D. What is the voltage from point E to point H? 2Ω 6Ω 1Ω 3V E. Calculate the current in each branch. F. Which resistor has the most voltage across it? G. Which resistor has the most current running thru it? A H I G H. What is the current flowing from H to I? I. What is the total current of the circuit? J. How much power is used by the 6Ω resistor? K. How much power is used by the entire circuit? 9. Two magnets are placed inside a graduated cylinder. The top magnet is suspended above the bottom magnet by magnetic repulsion. This is known as “MagLev”, magnetic levitation. It is the same concept that allows bullet trains to move so fast due to a lack of contact friction, since the train doesn’t actually touch the track. ___ ___ A. In the given spaces label the poles of the suspended magnet. B. Since 1000 g = 1 kg, what is the mass of the upper magnet? 600 g C. What is the weight of the upper magnet? N D. So how much magnetic force is the lower magnet exerting on the upper magnet? S 8 cm E. By Newton’s 3rd Law, what force must the upper magnet exert on the lower magnet? F. What is the height of the upper magnet in meters? G. What is the potential energy of the upper magnet? H. If the lower magnet were removed, what would the speed of the upper magnet be when it hits the bottom of the cylinder? cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2017, C. Stephen Murray cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2017, C. Stephen Murray cstephenmurray.com Copyright © 2017, C. Stephen Murray