* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes on 6.5 Rhombi
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
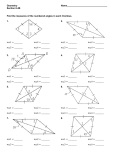
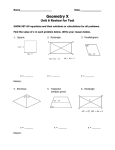
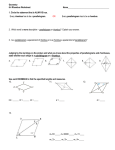
Geometry Honors/Theory: Notes on Rhombi Name_________________________ A rhombus is a quadrilateral in which all four sides are congruent. In other words, all sides have a rhombus have the same length. Examples of rhombuses --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------A rhombus is a type of parallelogram. This means that opposite sides of a rhombus are parallel. To prove this is true, try to make a rhombus in which both pairs of opposite sides are not parallel. For example, in the above diagram, the "hopeful beginning" of a rhombus that is not a parallelogram is given. Note how opposite sides are not parallel, but they are the same length. Now, if you form the left and right side of this shape, you can clearly see that the left side will be longer than the right side. This is a problem, because a rhombus must have four congruent sides. Therefore, since a rhombus that's not a parallelogram cannot be made, the original statement is true: a rhombus is a type of parallelogram. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Since a rhombus is a parallelogram, it possesses every Characteristics of Parallelograms Opposite sides are parallel. characteristic of parallelograms. These characteristics are given in the box to the right: Opposite sides are congruent. Opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. The diagonals bisect each other. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------One other important characteristic about rhombuses is the following: The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular. In other words, the diagonals of a rhombus intersect at 90 angles. For the rhombus to the left, the diagonals are drawn, and one can clearly see that the diagonals intersect to form right angles. Of even greater importance, note how four right triangles have been formed. This allows for the use of the Pythagorean Theorem. Pythagorean Theorem: a 2 b2 c2 1 The variables a, b, and c do not represent random sides of the right triangle. Remember a and b are the lengths of the legs, and c is the length of the hypotenuse. Remember that the two legs are the two sides which form the right angle in the right triangle. a c a The hypotenuse is the longest side, and it is located across from the right angle. b c b b a c In each of the diagrams to the right, note how c is the side across from the right angle. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------For the triangle to the right, find the value of x. x 3 Since x is located across from the right angle, it is c in the equation: a 2 b2 c2 4 32 42 x 2 9 16 x 2 25 x 2 x5 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Note how the right triangle pictured above was actually taken from x 3 the rhombus pictured to the right. 4 So, once again, because right triangles are formed after drawing the diagonals of a rhombus, one should expect to use the Pythagorean Theorem to find lengths of segments and sides. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------A 1. ABCD, pictured to the left, is a rhombus. D What is the value of y? 12 16 B y C --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------M What is MR in the figure to the left if MHEG is a rhombus? a 2 b2 c2 15 H G 9 R E Since MR is one of the legs, it could be noted as a: a 2 92 152 a 2 81 225 a2 So, MR = 12 . 144 a 12 2 In the figure to the right, VQMC is a rhombus. If CJ 7 , and CM 25 , what is JM? Q V J M C --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Classwork/Homework 1. For all parallelograms, _________________ sides are congruent, while in rhombuses, _________ sides are congruent. 2. The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is ___________. 3. The diagonals of a rhombus are ____________________. 4. What does the word perpendicular mean? --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------For Questions 5-8, the quadrilaterals pictured below are all rhombuses. 5. What is the value of x? 6. What is the value of y? 5x + 11 S y 32 8 T R Q 6 U 7. mM 5z 10 , and mP 8z 14 8. mT 6a 29 , and mR 4a 3 M S 5z + 10 P T 6a - 29 N 8z + 14 4a - 3 O R U --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------9. A parallelogram has one interior angle that measures 50 degrees. What are the measures of the other three interior angles? 3 I For Questions 11-12, consider rhombus XSIN to the left. In the figure, SW 5 units . 11. What is WN? S W N X If XS 13 units , what is XW? 12. --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------S 13. T R U Given: RSTU is a rhombus. Prove: RSU TUS Fill in all of the blanks for the two-column proof. Statements 1. RSTU is a rhombus. Reasons 1. RU ST 2. 3. R T 3. 4. RUS TSU 4. 5. RSU TUS 5. 2. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- --------------- Find the sum of measures of the interior angles of each convex polygon. 14. 20-gon 15. Decagon 16. Hexagon ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Find the measure of each interior angle of each regular polygon. 17. Pentagon 18. Nonagon 19. 30-gon ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------20. The measure of an interior angle of a regular polygon is 60. Find the number of sides. ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------21. What is the sum of the exterior angles of a 30-gon? ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------22. What is the measure of each exterior angle of a regular heptagon? 4