* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ASSIGNMENT TWO
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
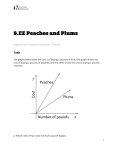
Assignment two HCS 112 Fundamentals of economics Section A 1) State three changes causing the demand curve of a consumer to shift to the right. [4] 2) A consumer buys 100 units of a good at a price of Rs. 5 per unit. When price changes he buys 140 units. What is the new price if price elasticity of demand is - 2 ? [4] 3) Assume that a consumer has an income of $400 per week, the price of a compact disk is $20 per CD, and the price of overcoats is $80. Draw a budget line representing the combinations of CDs and overcoats a consumer can buy in a week. Assume the price of overcoats falls to $50. Draw a new budget line reflecting the drop in price. [6] 4) The table below represents a consumer’s preferences for strawberries and peaches. Assume the price of strawberries is $4 per quart, the price of peaches is $2 per pound, and the consumer has an income of $10. If the consumer is buying 2 quarts of strawberries and 1 pound of peaches is she maximizing her utility? Explain your answer. [6] Quarts of Strawberries 1 2 3 4 MU of Strawberries 20 16 8 4 Pounds of Peaches 1 2 3 4 MU of Peaches 18 14 10 6 Section B Question One Adam Smith in The Wealth of Nations (1776) wrote of a factory that made pins. He claimed that labor' s marginal physical product would be increasing due to specialization. As more people (laborers) are added to production, each can specialize on a smaller part of the pin production process. With many workers, a firm will be able to take advantage of each worker' s specific talents by letting them do what they are best at. By each worker doing only one specific task, tasks will be simplified and work will become less stressful. Tasks will be easier to learn and master. Consider the production function for pins given below where P is output of pins, T is tools used in the production process and L is laborers: P = F(L,T) = TL 2. a) Fill in the following chart using the production function given above. The chart represents a short run situation where labor is a variable input but tools are fixed.[8] Labor Tools 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 Total Product Average Product Marginal Product b) Is the marginal physical product of labor increasing as Adam Smith asserts? Show your answer by first graphing the total production curve that corresponds to Smith' s pin production function. Then graph the average and marginal product curves derived from your total product curve. [4] c) In the long run both inputs are variable. Does the pin production function given above exhibit increasing, decreasing or constant returns to scale? Describe what ' returns to scale'means intuitively and show how you arrived at your answer below. [4] Question Two Consider the market for peaches, which is reputed to be perfectly competitive. The production of peaches requires two inputs – labor, which is variable, and land, which is fixed in the short run. The following figure represents the cost structure for a typical peach farmer in the short run with a marginal cost curve (MC) and an average total cost curve (ATC) for three scales: small (S), medium (M), and large (L). (Values between tick marks are odd numbers). Price per Peach (in cents) The Market for Peaches 50 48 46 44 42 40 38 36 34 32 30 28 26 24 22 20 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 ATC(S) ATC(M) ATC(L) MC(S) MC(M) MC(L) 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Peaches a) The market price for peaches is 46 cents and farmers are on the small scale in the short run. i. How many peaches should the farmer produce? ii. What is the average cost of production? iii. What is the total cost of production? iv. What are profits? [8] b) Assume that the only farm sizes available are small (S), medium (M), and large (L). i. What scale of production would be efficient if the farmer were to produce 7 peaches? ii. What would then be the average cost of production? [4] c) Continue assuming the price of peaches is 46 cents in the short run. i. What will be the long run equilibrium price of peaches? ii. What is the profit-maximizing quantity at the equilibrium price? iii. Characterize profits at this price and quantity. [6] Question three One of the world’s most successful cartels has been the Central Selling Organization (CSO), which controls about three-quarters of the world’s diamonds. This collusive oligopoly has kept diamond prices high by restricting supply. The CSO has also promoted the general consumption of diamonds through advertising and marketing. New supplies of diamonds have been found in Zimbabwe and Mozambique. These new mines, which are outside the direct control of the CSO, want to sell their diamonds on the open market. a. What would you predict will happen in the market for diamonds if these new mines do not cooperate with the cartel? [4] b. What do you think will happen to CSO diamond advertising? Good Luck [2]