* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What Does “Rail-to-Rail” Operation Really Mean?
Survey
Document related concepts
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
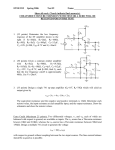
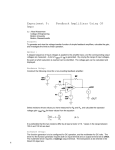
What Does “Rail-to-Rail” Operation Really Mean? © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 1 Agenda O What does “Rail-to-Rail” output operation mean Amplifier Output Stage O Distortion O O O Techniques to Compare Rail-to-Rail Op Amps Microchip Op Amps and References © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 2 Rail-to-Rail Operation O Rail means supply voltage (VDD and VSS) Rail-to-Rail output of amplifier O In reality: O O O Output can not reach the rails The difference from the rail is called Headroom © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 3 Amplifier Output Stage VIN+ VDD VOH VOL VOUT O Push-Pull output O Headroom O Transistor junction drop VIN— VSS Headroom O When VOUT → VDD : VDD – VOUT = VOH © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. O When VOUT → VSS : VOUT – VSS = VOL What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 4 Amplifier Output Stage O Headroom increases with increasing output current Output Voltage Headroom (mV typ.) 1,000 T A = 25°C 100 VOH VOL 10 1 10µ 1. E - 0 5 1. E - 0 4 1. E - 0 3 100µ 1m Output Current Magnitude (A) © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. 1. E - 0 2 10m What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 5 Output Distortion Voltage O O time Signal distortion (clipping) Approaching the rail distorts the output 5.5 RL = 10kΩ TA = 25°C VOUT (V typ.) 5.0 VDD = 5V 4.5 VOUT 4.0 3.5 Time © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 6 Amplifier Non-Linearity O Non-linearity when VOUT → the rails Input Offset Voltage (µV typ.) 200 150 RL = 10kΩ VDD = 5.5 V TA = 25°C 100 50 0 -50 O -100 -150 -200 -1.0 VCM = VSS 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 Non-linear Regions 6.0 Output Voltage (V) © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 7 Amplifier Linearity O Open Loop Gain (AVOL) measurement range O provides the clue to determine the linear region O AVOL = ∆VOS/∆VOUT O Input Offset Voltage (µV typ.) 200 150 100 50 0 -50 -100 VDD = 5.5 V VCM = VSS -150 two point measurement: VOS → VOUT = 300mV VOS → VOUT = VDD - 300mV © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. TA = 25°C RL = 10kΩ -200 -1.0 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 Output Voltage (V) (300mV for MCP6001) What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 8 Amplifier Linearity O What causes the distortion? O O transistors no longer in linear operation Linear Region O O O Specified in measurement conditions Recommended headroom for MCP6001 O 300mV with 10kΩ load to VDD/2 sink/source current dependent © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 9 Rail-to-Rail Output Amplifiers Comparison Techniques O O O Compare headroom vs. sink/source current Compare the AVOL measurement range Do bench verification O Compare expected vs. measured output voltage © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 10 Microchip Op Amps Part number MCP6271 MCP6281 MCP6291 MCP6S21 MCP6241 MCP6001 MCP6140 MCP6041 MCP6021 TC1034 MCP606 I/O Range R/R I/O R/R I/O R/R I/O R/R I/O R/R I/O R/R I/O R/R I/O R/R I/O R/R I/O R/R I/O R/R O VDD (V) Range 2.0-5.5 2.2-5.5 2.4-5.5 2.5-5.5 1.8-5.5 1.8-5.5 1.4-5.4 1.4-5.5 2.5-5.5 1.8-5.5 2.5-5.5 IQ (µA) max 240 570 1300 1300 50 100 1 1 1400 8µA 25µA MCP616 MCP601 R/R O R/R O 2.3-5.6 2.7-5.5 25µA 325µA R/R I/O → Rail-to-Rail Input/Output © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 11 Conclusion O O O O Amplifier output can not reach the rails Headroom is dependent on sink/source current Approaching the rails introduces distortion Bench test device to determine linear region © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 12 References O Application Notes O O O O O O O O O O ADN009, What Does “Rail-to-Rail” Operation Really Mean? ADN003, Select the Right Operational Amplifier for your Filtering Circuits AN699, Anti-Aliasing, Analog Filters for Data Acquisition Systems AN722, Operational Amplifier Topologies and DC Specifications AN723, Operational Amplifier AC Specifications and Applications AN695, Interfacing Pressure Sensors to Microchip’s Analog Peripherals AN737, Using Digital Potentiometers to Design Low Pass Adjustable Filters AN246, Driving the Analog Inputs of a SAR A/D Converter AN688, Layout Tips for 12-Bit A/D Converter Application AN884, Driving Capacitive Loads With Op Amps © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 13 WebSeminar: April 21, 2004 What Does “Rail-to-Rail” Operation Really Mean? © 2004 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. What does “Rail-to-Rail Operation” really mean? 14