* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 11 and 14 LTs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
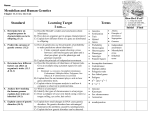
GENETICS (CHAPTERS 11 +14) At the end of this unit, you should be able to give thorough answers to the following questions: How does biological information pass from one generation to the next? How does genetics affect all other fields of biology? How is meiosis an essential component for maintaining life? Learning Targets 1. I know when a dominant or recessive allele will be expressed. (Section 11.1) o I can distinguish between a gene, allele and trait. o I can identify when a dominant or recessive allele will be expressed. o I know how the terms P, F1 and F2 are used to show different generations 2. I know that Punnett squares can be used to predict offspring. (Page 268) o I can predict the probability of a particular outcome, based on a Punnett square. o I can construct a Punnett square of a one-factor cross (monohybrid), given parental information. o I can interpret the results of a monohybrid Punnett square. o I know the rules of probability and how these rules relate to a phenotype of an offspring 3. I know how to determine the phenotype of an organism given its genotype. (Section 11.2) o I can identify a homozygous genotype. o I can identify a heterozygous genotype. o I can explain the difference between a homozygous and heterozygous genotype. o I can distinguish between a male and female genotype. I have no idea! 0 I might need some help 1 I feel good about this 2 I got it! What if I need help? # of Written test Questions # of M.C. test Questions 3 Pages 262-265 C.U. pg 265 BrainPop Heredity Mendel’s Peas Notes 3 2 7 6 5 2 0 1 2 3 0 1 2 3 Page 266-268 WKST Monohybrid practice problems and homework problems Probability Lab Spongebob WKST YouTube Video Page 267 Monohybrid WKSTs Genetics Vocab intro WKST Learning Targets I know that Dihybrid Punnett squares can be used to predict offspring. (Page 268) o I can complete a Punnett square of a two-factor cross (dihybrid), given parental information. o I can interpret the results of a Punnett square. o I know how the rule of independent assortment applies to the formation of gametes. (Section 11.2) o I can list the gametes produced by an individual, when given their genotype 5. I know the inheritance patterns of sex-linked disorders, codominance, incomplete dominance, and multiple alleles. (Section 11.3) o I can explain how sex-linked disorders are inherited. o I can identify other types of inheritance such as codominance, incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, and polygenic traits. o I can identify other types of inheritance such as codominance, incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, and polygenic traits. I have no idea! I might need some help I feel good about this I got it! What if I need help? # of Written test Questions 8 8 5 8 # of M.C. test Questions 4. 0 1 2 3 Page 264-265 & 268 Dihybrid practice problems and Homework WKSTs, A few more dihybrid problems 0 1 2 3 Pages 335-336 Dihybrid Worksheet Notes Learning Targets 6. I know how to analyze a karyotype. (Section 14.1) o I can identify a karyotype. o I can write the genetic notation for an individual, based on a karyotype. o I can determine the disorder of an individual, based on a karyotype. o I can describe the difference between autosomes and sex chromosomes. o I can analyze a karyotype to determine sex. 7. I know humans have different blood types due to multiple alleles o I can determine possible blood donors for each blood type o I can predict a baby’s blood type if I know the parent’s blood type o I know which blood types are dominant, recessive, and codominant o I can determine a person’s blood type if I know their genotype 8. I know how to analyze a pedigree. (Section 14.1) o I can state the genotype of an individual based on their information on a pedigree. o I can predict the probability that a particular individual will have a disorder, using my knowledge of sex-linked traits. o I can identify males and females in a pedigree. o I can determine whether an individual has a disorder, does not have a disorder or is a carrier for a disorder, based on a pedigree. I have no idea! 0 0 0 I might need some help 1 1 1 I feel good about this 2 2 2 # of Written test Questions # of M.C. test Questions I got it! What if I need help? 3 Page 334 Karyotype smartboard Ladybug Activity Computer Lab activity 3 Page 274 Blood Cell smartboard Computer Lab activity Blood Typing Lab 6 6 3 Page 336-337 Pedigree practice problems and homework WKSTs 6 6 3 NEXT GENERATION SCIENCE STANDARDS During this unit we will address and assess the following NGSS standard(s): LS3-1 Ask questions to clarify relationships about the role of DNA and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits passed from parents to offspring. [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the phases of meiosis or the biochemical mechanism of specific steps in the process.] LS3-3 Apply concepts of statistics and probability to explain the variation and distribution of expressed traits in a population. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on the use of mathematics to describe the probability of traits as it relates to genetic and environmental factors in the expression of traits.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include Hardy-Weinberg calculations.]