* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DWDM
STANAG 3910 wikipedia , lookup
History of telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
Optical disc drive wikipedia , lookup
Analog television wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
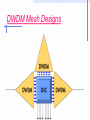
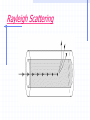
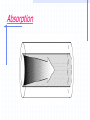
DENSE WAVELENGTH DIVISION MULTIPLEXING PRESENTED TO DR.SAPNA GAMBHIR ASSOCIATE PROF. CSE DEPTT. YMCAUST.FBD. PRESENTED BY PRITI RANI MNW-891-2K11 MTECH(CN) YMCAUST.FBD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION VARIETIES OF WDM DWDM TECHNOLOGY HISTORY OF DWDM DWDM SYSTEM AND COMPONENTS TOPOLOGY CONT… TRANSMISSION CHALLENGES MARKET DYNAMIC FUTURE APPLICATIONS BENEFITS REFERNCES INTRODUCTION One of the major issues in the networking industry today is tremendous demand for more and more bandwidth. With the development of Optical network and the use Dense Wavelength Division Technology, a new and probably, a very crucial milestone is being reached network evaluation. OPTICAL NETWORKING Optical networks are high-capacity telecommunications networks based on optical technologies. The origin of optical networks is linked to Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) which arose to provide additional capacity on existing fibers. CLASSIFICATION OF OPTICAL NETWORK FIRST GENERATION: Networks use microwave technology based. SECOND GENERATION: Networks use microwave links with optical fibers. THIRD GENERATION: Networks employ Wavelength Division Multiplexing technology. What is DWDM? Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) is a fiber-optic transmission technique. It involves the process of multiplexing many different wavelength signals onto a single fiber. So each fiber has a set of parallel optical channels each using slightly different light wavelengths. CONT.. It employs light wavelengths to transmit data parallel-by-bit or serial-by-character. DWDM is a very crucial component of optical networks that will allow the transmission of data: voice, video over the optical layer. CONT.. It transmits multiple data signals using different wavelengths of light through a single fiber. Incoming optical signals are assigned to specific frequencies within a designated frequency band. The capacity of fiber is increased when these signals are multiplexed onto one fiber CONT.. Transmission capabilities is 4-8 times of TDM Systems with the help of Erbium doped optical amplifier. EDFA’s : increase the optical signal and don’t have to regenerate signal to boost it strength. It lengthens the distances of transmission to more than 300 km before regeneration . Why DWDM? Unlimited Transmission Capacity Transparency Scalability Dynamic Provisioning Is DWDM Flexible? DWDM is a protocol and bit rate independent hence, data signals such as ATM, SONET and IP can be transmitted through same stream regardless their speed difference. The signals are never terminated within the optical layer allows the independence of bit rate and protocols,allowing DWDM technology to be integrated with existing equipment in network. Hence, there’s a flexibility to expand capacity within any portion of their networks. Is DWDM Expandable? “ DWDM technology gives us the ability to expand out fiber network rapidly to meet growing demands of our customer”, said Mike Flynn, group President for ALLTEL’s communications operations. DWDM coupled with ATM simplifies the network, reduce network costs and provide new services. They can add current and new TDM systems to their existing technology to create a system with virtually endless capacity DISADVANTAGES Not cost effective for low channel numbers Sonet/sdh network management system Are not well equipped to handle dwdm topologies DWDM SYSTEM Comparison of TDM, WDM, and DWDM multiplexing capabilities Multiple x Scalable Protoco Bit rate l indepen indepen dent dent Chann els per optical fiber Optical Equival system ent DScapacity 3 connect ions TDM No No No 1 2.5 Gbit/s 48 WDM Yes Yes Yes 2 5 Gbit/s 96 DWDM Yes Yes Yes 16 N/A at publicati on N/A at publicati on EVOLUTION OF DWDM A picture representing the really cool analogy Before After TDM (cars go faster) After DWDM (all the lanes are used) Example of Speeds Currently Lucent DWDM systems support transmissions of 160 separate wavelengths. Each wavelength is capable of supporting a signal of up to 10 Gbps. The total combined bandwidth is 1.6 trillion bits per second. This is greater than the speed of one million T-1 connections. How DWDM saves $$ In addition to saving money on fiber cables, DWDM also saves money on optical repeating equipment Because one fiber is used instead of many, one repeater can be used in place of many For example: you need 16 OC-3 carrier lines to go 1000 miles and repeaters are needed every 100 miles… If you didn’t use DWDM, you would need 16 thousand miles of fiber and 160 repeaters With DWDM, you need only 1 thousand miles of fiber and 10 repeaters A picture of How DWDM saves $$ Before DWDM After DWDM Signal Quality Optical Signal to Noise Ratio Optical Spectrum Analyzer Optical Signal Noise Floor DWDM Components Transmitter : - Changes electrical bits to optical pulses - Is frequency specific - Uses a narrowband laser to generate the optical pulse 5.2 Multiplexer/ Demultiplexer: - Combines/separates discrete wavelengths 5.3 Amplifier: - Pre-amplifier boosts signal pulses at the receive side - Post-amplifier boosts signal pulses at the transmit side CONT… 5.5 Receiver (receive transponder) - Changes optical pulses back to electrical bits - Uses wideband laser to provide the optical pulse DWDM Mesh Designs Advantages of DWDM Point to Point Systems The DWDM point-to-point architecture is simple to build and troubleshoot . It enables protocol transparency, increme-ntal growth, and capacity expansion over time, while dramatically reducing start-up costs. Point-to-point solutions are also extremely efficient. No amplifiers or additional equipment required. Transmission Challenges Attenuation Attenuation is caused by : - intrinsic factors primarily scattering and absorption - extrinsic factors, including stress from the manufacturing process, the environment, and physical bending Rayleigh scattering - is an issue at shorter wavelengths Rayleigh Scattering CONT… Attenuation due to absorption - is an issue at longer wavelengths - the intrinsic properties of the material - impurities in the glass, and any atomic defects in the glass. These impurities absorb the optical energy, causing the light to become dimmer. Absorption Dispersion Dispersion is the spreading of light pulses as they travel down optical fiber. Dispersion results in distortion of the signal, which limits the bandwidth of the fiber. Two general types of dispersion Chromatic Dispersion - is linear Chromatic dispersion occurs because different wavelengths propagate at different speeds. Increases as the square of the bit rate. Polarization Mode Dispersion - is nonlinear. Polarization mode dispersion (PMD) is caused by ovality of the fiber shape as a result of the manufacturing process or from external stressors. CONT… Changes over time PMD is generally not a problem at speeds below OC-192. Smearing of the signal Fiber Non Linear ties Because nonlinear effects tend to manifest themselves when optical power is very high, they become important in DWDM. These nonlinearities fall into two broad groups: - scattering phenomena - refractive index phenomena Future of DWDM What the future holds Two-way video communication Digital video for our everyday use at home and at work. Change from voice telephony to digital data heavy with video to require multiplying backbone transmission capacity. The Ultimate Squeeze - reducing the “space” between wavelengths - expanding the range of transmission wavelengths - better EDFAs Develop better equipment for switching and manipulating the various wavelengths after the signal emerges from the optical “pipe.” WDM is creating huge new information pipelines that will bring better service at lower cost. But the real information revolution won’t come until cheap WDM pipelines reach individual residences. Applications of DWDM DWDM is ready made for long-distance telecommunications operators that use either point-topoint or ring topologies. Building or expanding networks Network wholesalers can lease capacity, rather than entire fibers. The transparency of DWDM systems to various bit rates and protocols. Utilize the existing thin fiber DWDM improves signal transmission Summary DWDM was introduced to increase bandwidth by better utilizing existing fiber optic cabling DWDM is able to place many network formats of different speeds on the same fiber optic cable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexers and Cross Connects are what places the digital signals on the fiber Less cable and therefore less optical repeating equipment is needed for DWDM DWDM SAVES $$$ THANKYOU FOR YOUR ATTENTION