* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hypertensive Urgency
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
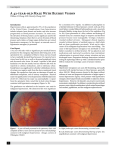
Hypertensive Urgency/Emergency Tanya Null Hypertensive Crisis • Broken down in to two groups: 1.Hypertensive Urgency 2.Hypertensive Emergency Hypertensive Urgency Is a situation when the blood pressure is acutely elevated. Defined per the American Heart Association as a Systolic BP of 180 or greater or a Diastolic BP of 110 or greater. With a hypertensive urgency, there are no symptoms of acute-end organ dysfunction Hypertensive Emergency Is an emergent situation when the blood pressure is elevated Defined by the American Heart Association as a Systolic BP of 180 or greater and or a diastolic BP of 120 or greater With a hypertensive emergency, the patient will have signs of acute, ongoing organ damage. Pathogenesis Noncompliance with medications Illicit drug use Renal disorders Pheochromocytoma Spinal cord injury causing increased intracranial pressure Clinical Manifestations of hypertensive urgency Headache Shortness of Breath Nosebleeds Anxiety Clinical Manifestations of hypertensive emergency Any signs and symptoms of acute organ damage such as 1. Chest pain 2. Asymmetry between pulses and or back pain 3. Shortness of breath, crackles, and or jugular venous distention 4. Numbness or weakness 5. Confusion, coma 6. Headache 7. Vision impairment 8. Hematuria Subjective/Social Assessment • Has the patient ever been diagnosed with hypertension? • If so is the patient compliant with medications? And what are the medications? • If the patient has no history of hypertension, is there a family history of hypertension? Does the patient smoke, drink alcohol, or do any illicit drugs? • Is the patient under a lot of stress? • What is the patients surgical and past medical history? Objective Assessment • Any patient with an elevated blood pressure consistent with hypertensive crisis needs to have a full through head to toe assessment with special focus on: Neurological Cardiovascular Pulmonary Renal Cotton wool spots Appear as fluffy white patches on the retina Caused by damage to nerve fibers Papilledema Is optic disc swelling Differential Diagnosis • Is this an acute or chronic problem • Do Not MISS or RED FLAGS • 1. Pheochromocytoma • 2. Ischemic Stoke or Intracerebral Hemorrhage • 3. Aortic Dissection • 4. Acute MI Diagnostic testing Blood Pressure Electrocardiogram Chest xray CT of the head Urinalysis Basic Metabolic Panel Funduscopic evaluation Treatment of Hypertensive emergency • If organ dysfunction or damage is confirmed the patient will need to be admitted to an intensive care unit for close monitoring and intravenous medications. • Nicardipine • Esmolol • Nitroglycerin • Clevidipine, • Labetalol • Nitroprusside • Loop diuretic • Benzodiazepines Goal of Therapy for Hypertensive Emergency • 25% drop in the mean arterial pressure in minutes to 1 to 2 hours. • Exception is those patients suffering from an aortic dissection or ischemic stroke. • Over a time period of 2 to 6 hours blood pressure goal should be around 160mmHG/100mmHG • After 48 hours and once the blood pressure is controlled oral agents can be started and the patient should be weaned off of the intravenous medications. Treatment for Hypertensive Urgency • If the patient has a history of chronic hypertension and is non compliant with medications, it is recommended that the patient be started back on their previously prescribed regimen. • If the patient with chronic hypertension is compliant with medications, it is recommended that the dose of current medications be increased if possible or a new agent be started. • If this is a new diagnosis of hypertension for the patient clonidine, captopril, and or nifedipine are good choices for treatment. Goal of Treatment for Hypertensive Urgency • Blood pressure should be lowered gradually over a period of days • This is something that can usually be done on an outpatient basis. • It is very important that these patients understand the importance of a 24-48 hour follow up. • They also need to be educated on medication compliance. References • In Papadakis, M. A., In McPhee, S. J., & In Rabow, M. W. (2016). Current medical diagnosis & treatment 2016. McGraw Hill Education. • Hypertensive Crisis. (2015, October 22). Retrieved from http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/Conditions/HighBloodPressure/AboutHighBloodPr essure/Hypertensive-Crisis_UCM_301782_Article.jsp#.Vsi3peaYLIU • Management of severe asymptomatic hypertension (hypertensive urgencies) in adults. (2014, May 6). Retrieved from http://www.uptodate.com/contents/management-of-severe-asymptomatichypertension-hypertensive-urgencies-in-adults • Evaluation and treatment of hypertensive emergencies in adults. (2014, July 7). Retrieved from http://www.uptodate.com/contents/evaluation-and-treatment-ofhypertensive-emergencies-in-adults • Goroll, A. H., & Mulley, A. G. (2014). Primary care medicine: Office evaluation and management of the adult patient. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.