* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Handout #2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Dr. J. Turner
Intro. to deities of Greek Mythology & Religion
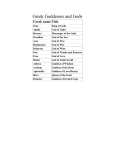
1. Physical Features:
1. Gaia (Gē) = Earth
4. Selēnē = Moon
2.Ouranos = Sky
5. Eos = Dawn
3. Helios (Phoebos)=Sun 6. Nyx= Night
7. Okeanos= Ocean
8. Oceanids (including Thetis,Achilles'mother)
=Nymphs of mountains, forest. lakes.
streams: River gods
I 1. Titans: Aside from Okeanos and Kronos (= Time [Latin = Saturn]), the Titans primarily are
important as ancestors of other gods. So Rea (with Chronos) is mother of Zeus@ Mnemosyne
(=Memory) is the mother of the Muses. Iapetus is the father of Prometheus and Atlas (who is
grandfather to Hermes). Themis (="What is divinely correct or usual according to nature") is,
however. a Titan of much importance in ethics. 'The Cyclopes and Hundred-Arms are different litters
of the Titans.
Ill. The original generation of Olympian gods:
most imp. of Olympian gods.)
1. Zeus: =chief god. Thunder, lightning, imposer of order, keeper of oaths, preserver of
hospitality, punishes wrong-doing, has an amorous bent.
'2. Hera: wife (& sister) of Zeus, to some extent, his female counterpart, often jealous of Zeus'
love affairs, is sometimes regarded as keeper of marriages, etc.
3.
Poseidon: god of the sea, causes earthquakes, especially associated w/horses, carries a
trident (pitchfork); w/his brothers-Zeus and Hades-he shares a third of the Universe:
(Poseidon-theSea, Hades-theUnderworld, Zeus-Sky&Earth).
4.
Hades (Pluto).- god of Underworld (=Hades' place); wife is Persephone
5.
Demeter: an Earth-mother type. Godess of Grain, then of all vegetation, of fertility, main
goddess of Eleusinian Mysteries which she taught to Triptolemos. Demeter is also
mother of Persephone.
6. Hestia: goddess of the Hearth, household.
I V. Others who made their way to Olympian status:
1.
Aphrodite (Venus): goddess of love, sex, attractiveness, accordng to Hesiod she rose
from the foam of Sky's castrated genitals. Others make her a daughter of Zeus and a
goddess Dione. Often called 'The Cyprian"; usually married to Hephaistos, god of Fire, but
has flings w/Ares and mortal men and boys.
2.
Eros (Cupid): the spirit of desire, usually sexual. Later Greek myth makes him a little boy
w/bow and arrows, attending his mother Aphrodite.
3. Hephaistos: god of Fire and divine blacksmith; son of Hera. He has a limp.
V.
1.
Children of Zeus:
Athena: mainly a goddess of war, perennial virgin, goddess of crafts (weaving, pottery-
making, etc.), later also symbol of intelligence and scholarship; sometimes called Pallas, often
associated w/olive tree, owl (wisdom), and aegis. No mother.
2.
Apollo (Phoebos): god mainly of prophecy (main oracle is Pythia at Delphi); also he is
in charge of archery and the lyre; associated w/poetry (He plays while the Muses sing.).
Associated w/medicine. His son was Asklepios, the first physician and later considered the god
of Medicine. Apollo's mother was Leto.
3.
Artemis: Apollo's sister; in some ways his female counterpart. Her special dominion is over
animals, known as the huntress-protectress of animals and goddess of hunters. A virgin, but
often presided over childbirth. Her mother was Leto.
4.
Persephone- daughter of Demeter, therefore a kind of vegetation goddess. She disappears to join her husband Hades and be Queen of the Underworld after harvest-time, only to
reappear in the Spring at seed/planting time.
5.
Ares (Mars): god of War, most hated of all the gods, cruel, not too smart, handsome warrior.
(Mars has a somewhat dff erent, more attractve personality.) His mother is Hera.
6.
Eileithuia: goddess of Childbirth and Hebe(eventually wife of Herakies), "Youth"; mother
is Hera.
7.
Hermes (Mercury): messenger of the gods, also leads the souls of the dead to the
Underworld. Carries a staff. Mother is Maia.
8.
Iris: "Rainbow", --girl messenger goddess.
9.
Dionysos (Bacchus, Liber): god of wine, drunkenness, orgies. Suppossed to have
come from the East, but was born in Thebes, Greece. Has a way w/ivy, grapes, and phallic-like
poles (thasoi). Often represents irrational element in life (often from a positive point of view, but
sometimes is a most destructive god.) Sometimes portrayed as pale, eff eminate, etc., but always
inciting passion of all kinds. Mother was Semelē, by way of Zeus' thigh. (*Semelē was one of
Kadmos' daughters.) Later, patron god of theater (at Athens).
I 0. Herakles (Hercules): The major instance of a human (although son of Zeus) who made it to
become a god. (Some other "heroes' did, too.) Primarily a man who clears the world
of monsters, etc.,to make it safe for men. Performs many marvelous exploits, andis a
kind of Superman. Carries a big club,wears a lionskin; travels alot. Takes after his
father with respect to women, but gets into more trouble through his affairs. Has a
bad temper (often kills people as well as moristers), but is fun-loving guy. Is the
"hero' par excellence. Later authors tend to portray him as dull, stupid, brutish,
similar to modem old-fashioned notion of a "dumb football player."
Note:
Lesser gods:
There are many other gods which appear in Greek myth: e.g, the Muses, the Fates (GreekThe Graces (Charites), the Seasons (Horai), the woodland god Pan; and his satyr
colleagues; such people as Leucothea ('White goddess"-a girl, Ino. who made it to become a seagoddess); and Circe; Gorgons; Sirens; Harpies, et al.
Hekate--a super-witch who is goddess of every matter (i.e., she has a timē in everything). She is
is not very important in mythology, but was important in everyday (folk) religion.