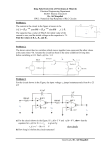
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SC.912.P.10.15 - Investigate and explain the relationships among
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Standard #: SC.912.P.10.15 This document was generated on CPALMS - www.cpalms.org Investigate and explain the relationships among current, voltage, resistance, and power. Subject Area: Science Grade: 912 Body of Knowledge: Physical Science Standard: Energy - Date Adopted or Revised: 02/08 A. Energy is involved in all physical and chemical processes. It is conserved, and can be transformed from one form to another and into work. At the atomic and nuclear levels energy is not continuous but exists in discrete amounts. Energy and mass are related through Einstein's equation E=mc2. B. The properties of atomic nuclei are responsible for energy-related phenomena such as radioactivity, fission and fusion. C. Changes in entropy and energy that accompany chemical reactions influence reaction paths. Chemical reactions result in the release or absorption of energy. D. The theory of electromagnetism explains that electricity and magnetism are closely related. Electric charges are the source of electric fields. Moving charges generate magnetic fields. E. Waves are the propagation of a disturbance. They transport energy and momentum but do not transport matter. Content Complexity Rating: Level 3: Strategic Thinking & Complex Reasoning - More Information Date of Last Rating: 05/08 Status: State Board Approved Remarks/Examples Use Ohm's and Kirchhoff's laws to explain the relationships among circuits. Related Courses Course Number 7920022: 0400410: 2002425: 2003500: 7920035: 2003385: 2002490: 2002420: 2002430: 0400408: 2003310: 2003320: 2003380: 2003390: 2003600: 2003610: 2002330: 2003836: Course Title (Specifically in versions: 2016 and beyond (current)) Technical Theatre Design & Production 1 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 and beyond (current)) Integrated Science 2 for Credit Recovery (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 and beyond (current)) Renewable Energy 1 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 and beyond (current)) Fundamental Integrated Science 2 (Specifically in versions: 2013 - 2015, 2015 - 2017 (course terminated)) Physics 1 for Credit Recovery (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 and beyond (current)) Forensic Sciences 2 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 and beyond (current)) Integrated Science 2 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 and beyond (current)) Integrated Science 2 Honors (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 and beyond (current)) Technical Theatre: Design and Production for Lighting and Sound (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 and beyond (current)) Physical Science (Specifically in versions: 2015 and beyond (current)) Physical Science Honors (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 and beyond (current)) Physics 1 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 and beyond (current)) Physics 1 Honors (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 and beyond (current)) Principles of Technology 1 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 and beyond (current)) Principles of Technology 2 (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018 (course terminated)) Space Technology and Engineering (Specifically in versions: 2014 - 2015, 2015 - 2018 (course terminated)) (Specifically in versions: 2015 and beyond (current)) Related Access Points Independent Access Points Number Access Points Title page 1 of 4 SC.912.P.10.In.8: Identify that some electrical devices use different types of power sources and explain what might happen if incorrect electrical components are used. Supported Access Points Number SC.912.P.10.Su.8: Access Points Title Recognize that some electrical devices use different types of power sources. Participatory Access Points Number SC.912.P.10.Pa.8: Access Points Title Demonstrate opening and closing an electrical circuit to turn an electrical device on and off. Related Resources Virtual Manipulative Name Battery Voltage: Description This simulation will allow you to look inside a battery to see how it works. You will be able to select the battery voltage and see the movement of the charges from one end of the battery to the other. A voltmeter will tell the resulting battery voltage. Some of the sample learning goals can be: Do the small blue spheres represent positive or negative charges? Which side of the battery is labeled positive, and which side is negative? How can you determine which side of the battery is positive and negative just by the location of the blue charges? Battery-Resistor Circuit: This simulation demonstrates how a resistor works and the relationship between voltage, current and resistance. A change in temperature is also recorded with varying the parameters. The students will be shown the flow of electrons to make a fan spin. The more resistance that they put the slower the elctrons will move and vice versa. The students will also see the power generated by the battery. Explore how a capacitor works in this simulation. Change the plates and add a dielectric to see how it affects capacitance. Change the voltage and see charges built up on the plates. You can observe the electric field in the capacitor, measure voltage and the electric field. Other investigations can include: Capacitor Lab: Determine the relationship between charge and voltage for a capacitor. Determine the energy stored in a capacitor or a set of capacitors in a circuit. Explore the effect of space and dielectric materials inserted between the conductors of the capacitor in a circuit. Determine the equivalent capacitance of a set of capacitors in series and in parallel in a circuit. An electronic kit in your computer! Build circuits with resistors, light bulbs, batteries, and switches. Take measurements with the realistic ammeter and voltmeter. View the circuit as a schematic diagram, or switch to a lifelike view. Other options for exploration: Circuit Construction kit: Circuit Construction Kit: Integrated Circuit: Discuss basic electricity relationships Build circuits from schematic drawings. Use an ammeter and voltmeter to take readings in circuits. Provide reasoning to explain the measurements and relationship in circuits. Discuss basic electricity relationships in series and parallel circuits. Provide reasoning to explain the measurements in circuits. Determine the resistance of common objects in the "Grab Bag". The students will have the opportunity to build their own circuit loop with the materials presented to them. This interactive game will help you learn about integrated circuits, which can be found in almost every modern electrical device such as computers, cars, television sets, CD players, cell phones, etc... The challenge in this game is to make it to the end. Ohm's Law: This virtual manipulative will allow the user to see how the equation form of ohm's law relates to a simple circuit. Learners can adjust the voltage and resistance, and see the current change according to Ohm's law. The size of the symbols in the equation change to match the circuit diagram. Resistance in a Wire: This manipulative will help the students to learn about the physics of resistance in a wire. The electrical resistance of a wire would be expected to be greater for a longer wire, less for a wire of larger cross sectional area, and would be expected to depend upon the material out of which the wire is made, to understand this, students can change the resistivity, length, and area to see how they affect the wire's resistance. The sizes of the symbols in the equation change along with the diagram of a wire. Some of the sample learning goals can be: What characteristics of a resistor are variable in this model? How does each affect the resistance (will increasing or decreasing each make the resistance correspondingly increase or decrease?) Explain your ideas about why they change the resistance. page 2 of 4 Learn how to build a circuit Virtual Construction Kit (DC only): Learn how to measure voltage in a circuit using a voltmeter Determine the resistance of certain objects that can be used as part of an electric circuit Explain the difference between parallel and series circuits Lesson Plan Name Description In this simple lab lesson, students will work in cooperative groups to construct simple series and parallel circuits. They Choose your path, series and will compare energy flow in circuits by observing lamp brightness as they change components in the various circuits. parallel circuits.: Note: This lesson does not cover the "power" element of the standard chosen. Video/Audio/Animation Name Description Learn how to build a circuit Show the difference between AC and DC Circuit Construction Kit (AC + Describe the effect of an inductor on a circuit DC): Describe the effect of a capacitor on a circuit Learn how to use an ammeter and a voltmeter in a circuit Perspectives Video: Professional/Enthusiast Name Description Current, Voltage, Resistance, Physics is cool, especially if you want to make super-cold, super-efficient, superconductive materials. and Superconductivity: See the light when this math teacher explains how he figured out energy system needs for a cross-Pacific kayak trip. KROS Pacific Ocean Kayak Related Resources: Journey: Solar Power and KROS Pacific Ocean Kayak Journey: GPS Data Set[.XLSX] Navigation: KROS Pacific Ocean Kayak Journey: Path Visualization for Google Earth[.KML] Student Resources Name Description Explore how a capacitor works in this simulation. Change the plates and add a dielectric to see how it affects capacitance. Change the voltage and see charges built up on the plates. You can observe the electric field in the capacitor, measure voltage and the electric field. Other investigations can include: Capacitor Lab: Determine the relationship between charge and voltage for a capacitor. Determine the energy stored in a capacitor or a set of capacitors in a circuit. Explore the effect of space and dielectric materials inserted between the conductors of the capacitor in a circuit. Determine the equivalent capacitance of a set of capacitors in series and in parallel in a circuit. An electronic kit in your computer! Build circuits with resistors, light bulbs, batteries, and switches. Take measurements with the realistic ammeter and voltmeter. View the circuit as a schematic diagram, or switch to a life-like view. Other options for exploration: Circuit Construction kit: Discuss basic electricity relationships Build circuits from schematic drawings. Use an ammeter and voltmeter to take readings in circuits. Provide reasoning to explain the measurements and relationship in circuits. Discuss basic electricity relationships in series and parallel circuits. Provide reasoning to explain the measurements in circuits. Determine the resistance of common objects in the "Grab Bag". Circuit Construction Kit: The students will have the opportunity to build their own circuit loop with the materials presented to them. Learn how to build a circuit Show the difference between AC and DC Circuit Construction Kit Describe the effect of an inductor on a circuit (AC + DC): Describe the effect of a capacitor on a circuit Learn how to use an ammeter and a voltmeter in a circuit Current, Voltage, Physics is cool, especially if you want to make super-cold, super-efficient, superconductive materials. Resistance, and Superconductivity: This interactive game will help you learn about integrated circuits, which can be found in almost every modern electrical device Integrated Circuit: such as computers, cars, television sets, CD players, cell phones, etc... The challenge in this game is to make it to the end. This virtual manipulative will allow the user to see how the equation form of ohm's law relates to a simple circuit. Learners page 3 of 4 Ohm's Law: can adjust the voltage and resistance, and see the current change according to Ohm's law. The size of the symbols in the equation change to match the circuit diagram. Resistance in a Wire: This manipulative will help the students to learn about the physics of resistance in a wire. The electrical resistance of a wire would be expected to be greater for a longer wire, less for a wire of larger cross sectional area, and would be expected to depend upon the material out of which the wire is made, to understand this, students can change the resistivity, length, and area to see how they affect the wire's resistance. The sizes of the symbols in the equation change along with the diagram of a wire. Some of the sample learning goals can be: What characteristics of a resistor are variable in this model? How does each affect the resistance (will increasing or decreasing each make the resistance correspondingly increase or decrease?) Explain your ideas about why they change the resistance. Learn how to build a circuit Learn how to measure voltage in a circuit using a voltmeter Virtual Construction Kit (DC only): Determine the resistance of certain objects that can be used as part of an electric circuit Explain the difference between parallel and series circuits Parent Resources Name Description Explore how a capacitor works in this simulation. Change the plates and add a dielectric to see how it affects capacitance. Change the voltage and see charges built up on the plates. You can observe the electric field in the capacitor, measure voltage and the electric field. Other investigations can include: Capacitor Lab: Determine the relationship between charge and voltage for a capacitor. Determine the energy stored in a capacitor or a set of capacitors in a circuit. Explore the effect of space and dielectric materials inserted between the conductors of the capacitor in a circuit. Determine the equivalent capacitance of a set of capacitors in series and in parallel in a circuit. An electronic kit in your computer! Build circuits with resistors, light bulbs, batteries, and switches. Take measurements with the realistic ammeter and voltmeter. View the circuit as a schematic diagram, or switch to a life-like view. Other options for exploration: Circuit Construction kit: Discuss basic electricity relationships Build circuits from schematic drawings. Use an ammeter and voltmeter to take readings in circuits. Provide reasoning to explain the measurements and relationship in circuits. Discuss basic electricity relationships in series and parallel circuits. Provide reasoning to explain the measurements in circuits. Determine the resistance of common objects in the "Grab Bag". Current, Voltage, Resistance, and Superconductivity: Physics is cool, especially if you want to make super-cold, super-efficient, superconductive materials. Integrated Circuit: This interactive game will help you learn about integrated circuits, which can be found in almost every modern electrical device such as computers, cars, television sets, CD players, cell phones, etc... The challenge in this game is to make it to the end. Ohm's Law: This virtual manipulative will allow the user to see how the equation form of ohm's law relates to a simple circuit. Learners can adjust the voltage and resistance, and see the current change according to Ohm's law. The size of the symbols in the equation change to match the circuit diagram. Resistance in a Wire: This manipulative will help the students to learn about the physics of resistance in a wire. The electrical resistance of a wire would be expected to be greater for a longer wire, less for a wire of larger cross sectional area, and would be expected to depend upon the material out of which the wire is made, to understand this, students can change the resistivity, length, and area to see how they affect the wire's resistance. The sizes of the symbols in the equation change along with the diagram of a wire. Some of the sample learning goals can be: What characteristics of a resistor are variable in this model? How does each affect the resistance (will increasing or decreasing each make the resistance correspondingly increase or decrease?) Explain your ideas about why they change the resistance. page 4 of 4