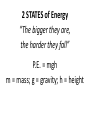* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Energy Mr. Skirbst What is energy? What is energy? - It is the ability to do work or cause change (remember: work = force x distance) Unit of energy = Joule 5 FORMS of Energy 5 FORMS of Energy 1. Mechanical - “matter in motion” - (ex. ball, bike, run, blood) 5 FORMS of Energy 2. Heat - “atomic motion” - (ex. melting, evaporation) 5 FORMS of Energy 3. Chemical - “atomic bonding” - (ex. burning, reactions) 5 FORMS of Energy 4. Electromagnetic - “moving electrons” - (ex. electricity, lights, motors) 5 FORMS of Energy 5. Nuclear - “fusion / fission” - (ex. stars, atomic bomb) 2 STATES of Energy 2 STATES of Energy 1. Kinetic (Greek – “kinetikos” motion) - energy of motion 2 STATES of Energy * depends upon mass & velocity K.E. = (mv2) / 2 m = mass; v = velocity 2 STATES of Energy 2. Potential - energy of position * stored energy (ex. food, fuel, suspended objects) 2 STATES of Energy “The bigger they are, the harder they fall” P.E. = mgh m = mass; g = gravity; h = height Energy Conversions Energy can be transferred from one object to another & from one form to another Energy Conversions Energy Conversions KE = ½ 2 mv medium slow 0 0 Velocity fast GRAPH light Mass medium heavy Example Problems m = 2 kg; v = 2 m/sec What is the KE? Example problem A 6 kg bowling ball is thrown with a velocity of 4m/sec. Calculate its kinetic energy. Example problem A 5,000 kg car hits a deer with a velocity of 10m/sec. Calculate its kinetic energy. What will happen to the deer? Activity 1 - Bowling Ball: Level 1: Bowling Ball – Find the Kinetic Energy Hint: You will need a ruler, stopwatch, and calculator to complete this. Also, remember that: velocity(m/sec) = distance(m) / time(sec) d = 10 m t= v= draw TOV m= v= KE = equation 2 KE = ½ mv PIV solution Level 2: Bowling Ball – Find the Potential Energy of the ball held at 1 meter above the floor. Don’t forget to use the spring balance to find the mass in kg. draw TOV equation PIV solution Level 3: Bowling Ball – How high would the bowling ball have to be to have a PE equal to the KE from level 1? (Hint: use algebra to solve for the height; PE=mgh) Level 3: Bowling Ball – How high would the bowling ball have to be to have a PE equal to the KE from level 1? (Hint: use algebra to solve for the height; PE=mgh)