* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproducton Development
Survey
Document related concepts
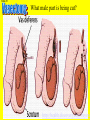
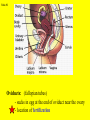
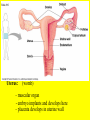
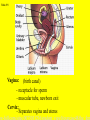
Transcript
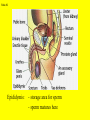
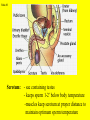
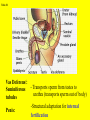
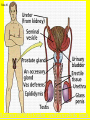
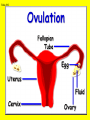
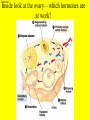
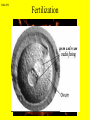
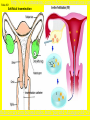
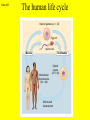
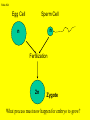
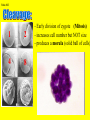
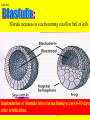
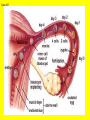
Slide #1 Testes: - Male gonads - Produce sperm - produce testosterone - sexual maturity - secondary sex characteristics (body hair, muscle mass, deeper voice) Puberty: maturity of male reproductive system (betweens ages of 12-18) Slide #2 Epididymis: - storage area for sperm - sperm matures here Slide #3 Scrotum: - sac containing testes - keeps sperm 1-2’ below body temperature -muscles keep scrotum at proper distance to maintain optimum sperm temperature Slide #4 Vas Deferens/: Seminiferous - Transports sperm from testes to urethra (transports sperm out of body) tubules -Structural adaptation for internal Penis: fertilization Slide #5 Sperm are made in the testes Stored in the epididymus Travels to the Vas Deferens Mix with semen(fluid) Seminal Vesicle Cowper’s Gland Secretes fluids into urethra Prostate - nourish sperm (sugar) Exit through the Urethra - protect sperm for acidity of female reproductive tract - transport medium Slide #6 ill.com/sites/0073031216/student_view0/exercise48/the_female_ Slide #7 What male part is being cut? http://health.discovery.com/beyond Slide #8 Ovaries: - produce eggs -at birth contains all eggs in immature form in follicles - releases approximately 1 egg per 28days - produces estrogen and progesterone Hormones that: - mature egg - prepare female body for pregnancy - secondary sex characteristics Slide #9 Oviducts: (fallopian tubes) - sucks in egg at the end of oviduct near the ovary - location of fertilization Slide #10 Uterus: (womb) - muscular organ - embryo implants and develops here - placenta develops in uterine wall Slide #11 Vagina: (birth canal) - receptacle for sperm - muscular tube, newborn exit Cervix: - Separates vagina and uterus Slide #12 Creatively describe the path a sperm takes to reach an egg Check to make sure you include the following: Gonad Ovaries Testes Egg Epididymis Oviduct Semen Vagina Sperm Uterus Vas deferens Cervix Urethra Prostate http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/miracle/media/2816_q_02.html http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/miracle/media/2816_q_03.html Slide #13 (28 day cycle) Puberty: beginning of menstrual Cycle (between ages of 9-14) Pregnancy: temporarily stops Menopause: permanently stops (ages 45-50) Stages: 1) Follicle Stage 2) Ovulation 3) Corpus Luteum Stage 4) Menstruation Slide #14 Concepts Hypothalamus • Involves three glands: – Hypothalamus – Pituitary – Ovaries Pituitary • Involves many hormones including: – FSH and LH – Estrogen and Progesterone Testis/Ovaries Body Tissue Slide #15 The phases • Follicular phase- FSH is secreted by the pituitary gland which stimulates an egg to mature in the follicle. This maturation causes the follicle to release estrogen which stimulates the uterus to thicken (10-14 days) • Ovulation- LH released from pituitary causes matured egg to be released from follicle into oviduct (0 days) • Luteal phase-LH causes the creation of the corpus luteum,which will maintain the pregnancy. The corpus luteum will produce progesterone which further thickens the uterine lining. (10-12 days) • Menstruation- If egg not fertilized, progesterone levels decrease and the uterine lining is shed. (3-5 days) Slide #16 Slide #17 Menstrual Cycle Slide #18 Inside look at the ovary—which hormones are at work? Slide #19 Fertilization Slide #20 - Fusion of male and female gametes - occurs in the *oviduct* -if fertilization does not occur in 24 hours after ovulation...egg disintegrates...menstruation occurs In Vitro Fertilization: -egg fertilized outside the body and embryo implanted in uterus http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/miracle/media/2816_q_04.html Slide #21 http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/con Artificial Insemination lth.discovery.com/beyond/index.html?playerId=&categoryId=219 Slide #22 - Fertilization of different eggs - Siblings developing at the same time - Fertilization of one egg and sperm - Embryo divides during morula stage - Twins have identical chromosomes Slide #23 The human life cycle Haploid gametes (n = 23) n Egg cell n Sperm cell Meiosis Fertilization Multicellular diploid adults (2n = 46) Diploid zygote (2n = 46) Mitosis and development 2n Slide #24 Egg Cell Sperm Cell n n Fertilization 2n Zygote What process must now happen for embryo to grow? Slide #25 - Early division of zygote (Mitosis) 1 2 4 8 - increases cell number but NOT size - produces a morula (solid ball of cells) Slide #26 Morula increases in size becoming a hollow ball of cells Implantation of blastula into uterine lining occurs 6-10 days after fertilization. Slide #27 Slide #28 Process of forming a Gastrula (indented blastula) Ectoderm Endoderm Mesoderm Slide #29 Can you recognize the stages of development? Slide #30 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. The Regents Diagram… Sperm and ovum Zygote (fertilized ovum) 2-cell stage 4-cell stage Morula Blastula Gastrula Slide #31 Layers become different tissues and organs made up of specialized cells Mesoderm: Ectoderm: - epidermis of skin - nervous system - muscles and skeleton - circulatory system - excretory system Endoderm: - reproductive system - respiratory tract - digestive tract - pancreas and liver http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/miracle/media/2816_q_05.ht ml Slide #32 Slide #33 Human fetal development http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/miracle/media/2816_q_06.html •http://www.visembryo.com/baby/1.html Slide #34 Slide #35 Embryo develops inside female body - characteristic of mammals -placenta: tissue containing mother and embryo blood vessels (capillaries) - No direct connection between blood vessels of mother and embryo - allows for exchange of nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, waste by diffusion - umbilical cord: attaches embryo to placenta at uterine wall (contains 2 arteries and 1 vein) - amniotic fluid: surrounds/protects embryo/fetus Slide #36 An average human pregnancy lasts 40 weeks, divided into trimesters. http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/miracle/media/2816_q_07.htm Slide #37 Women must be careful when pregnant as substances she ingests or breathes can impact the baby. Most of the fetus’ organs develop before a women is 10 weeks pregnant, and may be damaged if caution is not taken early in pregnancy. Pregnant women must eat very healthy and avoid the following risks: (Effects of FAS on children) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Tobacco (causes low birth weight) Drugs (causes many deformities) Alcohol (causes Fetal Alcohol Syndrome) Regular household chemicals/pesticides Radiation Infections Slide #38 http://health.discovery.com/beyond/ • At 40 weeks of pregnancy (38 weeks considered full term) •Babies born at 26 weeks live due to medical technology •During labor, the uterus contracts. Each contraction is stronger than the previous, pushing the baby further down the birth canal. The baby must pass through the cervix, then exit out of the vagina. http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/miracle/media/2816_q_08.html Slide #39 - External Fertilization - Yolk is source of food for developing embryo - Fish and Amphibians - Internal Fertilization - Eggs have special adaptations - Birds, many reptiles Slide #40 Slide #41 Slide #42 Egg parts • Amnion- Fluid filled and surrounds the embryo • Allantois- Stores the waste produced by the embryo • Yolk Sac- Stores nutrient-rich food • Chorion- Regulates O2 going to embryo and CO2 leaving embryo Slide #43 MOST LEAST LEAST MOST Slide #44 Time of development from fertilization until birth Human 40 weeks Gorilla Dog Mouse Cat Lion Tiger Rabbit 37 weeks 61 days 19 days 63 days 100 days 105 days 31 days