* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning Log Chapter 2
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
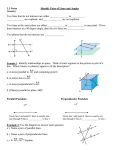
Chapter 2 Learning Log Definitions These are the terms and definitions you are responsible for from Chapter 2. They are listed in more or less the same order they appeared in the chapter. Be sure you are familiar with all of them before your tests. Angle can be formed by two rays meeting at the endpoint or two sides of a polygon. You can name an angle with three points. Vertex point where two rays or segments meet. “Corner” of a polygon. Complementary angles are two angles whose measures have a sum of 90. Supplementary angles are two angles whose measures have a sum of 180. Vertical angles are two non adjacent angles formed when two lines intersect. Vertical angles are always congruent. Transversal is a line that cuts across two other lines. Corresponding angles are congruent when the lines cut by a transversal are parallel. Angles are on the same side of the parallel lines and the same side of the transversal. Refer to your angles toolkit for a picture. Alternate interior angles are congruent when the lines cut by a transversal are parallel. Angles are on different sides of the transversal and inside the two parallel lines. Refer to your angles toolkit for a picture. Same-side interior angles are supplementary when the lines cut by a transversal are parallel. Angles are on the same side of the transversal and inside the two parallel lines. Refer to your angles toolkit for a picture. Triangle Angle Sum Theorem states that the measures of the angles of a triangle have a sum of 180. 1 Area of a triangle 𝐴 = 2 𝑏ℎ Area of a parallelogram 𝐴 = 𝑏ℎ 1 Area of a trapezoid 𝐴 = 2 (𝑏1 + 𝑏2 )ℎ Hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle in a right triangle. Legs in a right triangle are the two sides that form the right angle. Triangle Inequality states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle has to be greater than the length of the third side. 𝑎 + 𝑏 > 𝑐 Pythagorean Theorem states that the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs of a right triangle equals the square of the length of the hypotenuse. 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 = 𝑐 2