* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WELCOME TO PHYSICS 1103
Portable water purification wikipedia , lookup
Purified water wikipedia , lookup
Water testing wikipedia , lookup
Water conflict in the Middle East and North Africa wikipedia , lookup
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Flood control in the Netherlands wikipedia , lookup
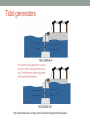
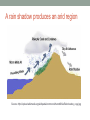
WELCOME TO PERIOD 24: WATER ENERGY Homework #23 is due today. PHYSICS 1104 – PERIOD 24 •What is the Earth’s water cycle? •How is water used to generate electricity? •What effects will climate change have on the fresh water supply? Source: http://pmm.nasa.gov/education/sites/default/files/article_images/Water-Cycle-Art2A.png&imgref The Earth’s water cycle Water from oceans, lakes, rivers, and the soil evaporates when radiation from Sun warms the Earth’s surface. Water vapor rises, is cooled, and condenses on dust particles, forming clouds. When clouds become saturated, precipitation falls as rain or snow. Precipitation eventually runs back into lakes and oceans and the cycle repeats. Latent heat of vaporization is removed from the atmosphere when water evaporates and is added when water vapor condenses. Solar energy drives the water cycle. Source: http://www.education.noaa.gov/Freshwater/Water_Cycle.html Example: you roll the cloud cube and are directed to a lake. Source: http://www.education.noaa.gov/Freshwater/Water_Cycle.html Water contamination points: for each move you made on the diagram, add or subtract contamination points. Move from: Clouds Animal Animal Soil Soil Soil Soil Plants Plants Ocean Lake Lake Lake Lake Glacier Glacier Glacier Groundwater River River River River To: all Soil Clouds Plants River Groundwater Clouds Animals Clouds Clouds Clouds Groundwater Animals River Groundwater River Clouds Lake or river Groundwater Lake or ocean Clouds Animals Points +1 +2 remove all -1 +2 -1 remove all +1 remove all remove all remove all -1 +1 +1 -1 +1 remove all -1 -1 +1 remove all +1 Explanation of points Airborne contaminants are absorbed Wastes Water is purified as it is respired Some plants absorb pollutants Runoff carries pollutants into river Soil filters some pollutants Water is purified as it evaporates Contaminants are ingested Water is purified as it is transpired Water is purified as it evaporates Water is purified as it evaporates Soil filters some pollutants Contaminants are ingested Water moves downstream Soil filters some pollutants Water moves downstream water is purified as it evaporates Soil filters some pollutants Soil filters some pollutants Water moves downstream Water is purified as it evaporates Contaminants are ingested Causes of ocean tides • The moon’s gravitational force causes the oceans to form two bulges, one on each side of the Earth. • As the Earth spins on its axis, land bordering the oceans passes through both bulges each day. • This produces two high tides and two low tides per day. • The gravitational attraction between the Earth and the moon causes the water on the side facing the moon to be pulled toward the moon. • On the opposite side of the Earth, water tries to continue moving away from the Earth, forming a bulge. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File: Tide_overview.svg Tidal generators http://www.alternative-energy-news.info/technology/hydro/tidal-power/ Ocean and river turbines Instead of damming a harbor, underwater turbines can use river and ocean currents or ocean waves to generate electricity. This reduces the environmental consequences of damming a harbor. The SeaGen tidal energy system in Northern Ireland's Strangford Lough is the world’s largest tidal current generator. http://www.alternative-energynews.info/technology/hydro/tidal-power/ Shallow geothermal wells provide water at 55 oF to heat and cool buildings Electricity from geothermal energy • Heat in the Earth’s core is the result of radioactive decay of unstable isotopes. • Thermal energy released from these fission reactions raises the temperature of the Earth’s core to 9,000 OF (5,000 OC). • Thermal energy is conducted from the core through the Earth’s mantle. • Hot water and steam can be vented in hot springs, such as the Old Faithful Geyser in Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming. • This thermal energy can produce the steam needed to turn generator turbines • This type of geothermal energy is available only in geologically unstable areas, such as volcanically active Iceland. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Old _Faithfull-pdPhoto.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Glacier_Mass_Balance_Map.png Retreat of Whitechuck Glacier Whitechuck Glacier in Glacier Peak Wilderness in 1973. Whitechuck glacier in 2006. Its edge has retreated 1.2 miles. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Whitechuck_glacier_2006.jpg A rain shadow produces an arid region Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/9a/Rainshadow_copy.jpg Retreat of mountain glaciers Mountain glaciers will disappear in this century, many before 2050. Billions of people depend on glacial melt water for drinking, irrigation, and hydroelectric power. Many glacial lakes are impounded by earthen dams. As melt water increases lake volume, these dams could fail, flooding valleys downstream. Consequences of decreased melt water Much irrigation water comes from lakes that are replenished by glacial melt water. This is particularly true in South America. Glacial melt water is the primary source of the river water used to generate hydropower, especially in the South America Andes Mountains, the European Alps, and the mountain ranges of the Pacific Northwest. Other energy sources will be needed to replace this hydropower. Consequences for fresh water supply After mountain glaciers disappear, one to two billion people will be affected by less fresh water. Possible solutions? Pipe water in from other locations Desalinize sea water Purify and recycle used “gray water” All of the options cost money and require energy! BEFORE THE NEXT CLASS… Read textbook chapter 25. Complete Homework Exercise 24. Print out Activity Sheet 25