* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Conducting System and EKG
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
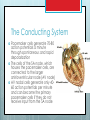
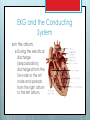
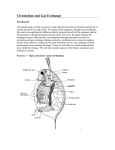
The Conducting System and EKG Danny Golinskiy, Joel Levy, Emily Brames The Conducting System Cardiac muscle contracts regardless of neural input (autorythmicity) All cardiac contractions are coordinated by the heart’s conducting system The conducting system is a network of specialized cells that initiate and distribute electrical impulses in the heart The network is comprised of two cells that do not contract: nodal and conducting cells The Conducting System Nodal cells establish the rate of cardiac contraction (located at the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes) Conducting cells distribute the contractile stimulus to the general myocardium Major cardiac sites for the conducting cells include the AV bundle, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers The Conducting System Nodal cells depolarize spontaneously and generate action potentials at regular intervals Nodal cells determine the heart rate by sweeping the cardiac tissue The normal rate of contraction is established by pacemaker cells, which reach the action potential threshold first, and are located in the sinoatrial node, referred to as the cardiac pacemaker The Conducting System Pacemaker cells generate 70-80 action potentials a minute through spontaneous and rapid depolarization The cells of the SA node, which houses the pacemaker cells, are connected to the larger antrioventricular node (AV node) AV nodal cells generate only 4060 action potentials per minute and can become the primary pacemaker cells if they do not receive input from the SA node The Conducting System From the AV node action potential travels to the AV bundle, which divides into left and right bundle branches that radiate across the inner surfaces of the ventricles It takes an action potential about 50 milliseconds to travel from the SA node to the AV node The action potential travels through cell to cell contact The Conducting System Bradycardia: the heart rate is slower than normal (60bpm or less) Tachycardia: the heart rate is faster than normal (100bpm or more) Ectopic pacemaker: the origin of abnormal signals Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) An EKG is a device that records the electrical events of the heart. Each time the heart beats a wave of depolarization passes through the heart muscle & this activity is recorded on the EKG. Leads are placed on the chest & limbs to obtain an EKG. Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) → → → EKG is “read” by medical personnel to monitor the electrical activity of a patient’s heart. Each heart beat has the following major components: P-Wave – represents the depolarization of the atria. QRS Complex - results when the ventricles depolarize. T-Wave – indicates repolarization of the ventricles , the ventricles are returning to a resting state. Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) When analyzing an EKG, the clinician measures voltage & size of the different components of the EKG. Electrocardiograms are also used to diagnose cardiac arrhythmias. Arrhythmias are abnormal patterns of cardiac activity. EKG and the Conducting System The image created by the EKG depicts the electrical cycle of the heart. The electrical signals are derived from a release of electrical potential from high to low across the heart. EKG and the Conducting System The 3 parts of the EKG: P-wave: electrical discharge across the atriums QRS-complex: this relates to the electrical discharge or depolarization of electrical potential across the ventricles. T-wave: Repolarization of heart, or restoring of the electrical potential in the membrane tissues of the heart. EKG and the Conducting System In the atrium: During the electrical discharge (depolarization), discharged from the SA node to the AV node and spreads from the right atrium to the left atrium. EKG and the Conducting System The Ventricles: QRS Complex: Electrical discharge of potential (depolarization) of the right and left ventricles. T-wave: Restores the electrical potential (repolarization) across the ventricles through the heart. Work Cited Bartholomew, Edwin F., and Frederic Martini. Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology. San Francisco, CA: Benjamin Cummings, 2007. Print. McDowell, Julie. Encyclopedia of Human Body Systems. Santa Barbara: Greenwood, 2010. Print. Whittemore, Susan, and Denton A. Cooley. The Circulatory System. Philadelphia [Pa.: Chelsea House, 2004. Print. Work Cited (Images) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:SinusRhythmLabels.svg http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&safe=off&sa=N&rlz=1C1SNNT_enUS397US397 &biw=948&bih=933&tbm=isch&tbnid=o4gA5m8ijQVASM:&imgrefurl=http:// http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&safe=off&sa=N&rlz=1C1SNNT_enUS397US397 &biw=948&bih=933&tbm=isch&tbnid=Cv3vBoTN_kqefM:& http://www.google.com/imgres?hl=en&safe=off&rlz=1C1SNNT_enUS397US397&biw=948&bih =933&tbm=isch&tbnid=jVJZTfuQsOCebM:&imgrefurl= http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&safe=off&sa=N&rlz=1C1SNNT_enUS397US397 &biw=948&bih=933&tbm=isch&tbnid=HJmuo7Xs7PTqIM:&imgrefurl=http://www.gadgetonia n.com/2010/04/portable-ekg-device-monitors-your-heart-rythm-everywhere-yougo/&docid=4cByiMFuy_uY3M&i http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&safe=off&sa=N&rlz=1C1SNNT_enUS397US397 &biw=948&bih=933&tbm=isch&tbnid=g_FrYA7qr_W2M:&imgrefurl=http://www.triathlontrainingisfun.com/tag/heart-rate-training/& http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&safe=off&sa=N&rlz=1C1SNNT_enUS397US397 &biw=948&bih=933&tbm=isch&tbnid=_K1GqwUl6hdUNM:&imgrefurl=http://en.wikipedia.org /wiki/Cardiac_muscle http://www.google.com/imgres?um=1&hl=en&safe=off&sa=N&rlz=1C1SNNT_enUS397US397 &biw=948&bih=933&tbm=isch&tbnid=xpv8QFAN9jyd6M:&imgrefurl=http://biology.about.co m/library/organs/heart/blsinoatrialnode.htm&docid=iIb7hq-