* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Outer Ear
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
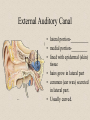
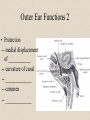
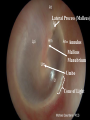
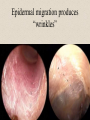
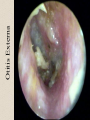
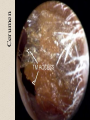
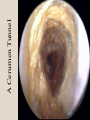
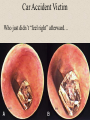
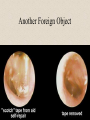
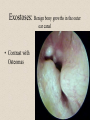
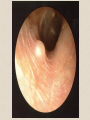
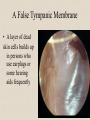
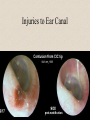
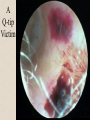
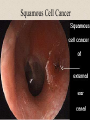
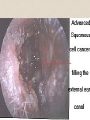
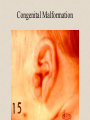
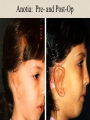
The Outer Ear SPA 4302 Summer 2007 Development of the Outer Ear • About __________ after conception the pharyngeal arches develop (bulges on the area of the embryo that will later develop into the head and neck) • As many as ____ all separated by grooves and clefts • First three: – __________ arch – __________ arch – ____________________ arch Development of the Outer Ear • Each of the arches has three layers – _______________ (outer layer) – _______________ (middle layer) – _______________ (inner layer) • Each arch contains four components: – An artery, muscle and cartilage (from mesoderm) – Nerve (from _______________) • Aurical develops from the first 2 pharyngeal arches • EAC develops from the first pharyngeal groove • TM develops from ______________: inner layer from endoderm, middle layer from mesoderm, and outer layer from ectoderm External Auditory Canal • lateral portion-__________ • medial portion-_________ • lined with epidermal (skin) tissue • hairs grow in lateral part • cerumen (ear wax) secreted in lateral part. • Usually curved. Outer Ear Functions 1 • Amplification / Filtering -- 1500 to 7000 Hz increased by ________________ -- produced by resonance of Concha (_______ kHz) & E.A.Canal (_____________ Hz) Outer Ear Functions 2 • Protection -- medial displacement of ___________ -- curvature of canal -- _____________ -- cerumen -- _____________ Outer Ear Functions 3 Localization -- The ability to _________________ ____ of a sound source Otoscopy • Viewing outer ear and TM Looking for: • _____________, • Evidence of infection • Other __________ Lateral Process (Malleus) = Annulus Malleus Manubrium Umbo Cone of Light Epidermal migration produces “wrinkles” Disorders of the Pinna: • Microtia- ___________________________ • Anotia- ____________________________ • Congenital malformation associated with syndromes and disorders • _____________- surgery performed to correct a pinna that either protrudes markedly from head or is pinned to closely Disorders: • Blockage: with earwax, foreign bodies, pus. • Otitis Externa: ________________. – Fungal or Bacterial in origin. – More frequent in ears with small canal • openings that cannot dry out as easily. – This is also sometimes a problem for people wearing _____________-. Otitis Externa Cerumen A Cerumen Tunnel Car Accident Victim Who just didn’t “feel right” afterward… Another Foreign Object Exostoses: Benign bony growths in the outer ear canal • Contrast with Osteomas A False Tympanic Membrane • A layer of dead skin cells builds up in persons who use earplugs or some hearing aids frequently Injuries to Ear Canal A Q-tip Victim Squamous Cell Cancer Malformations: congenital, traumatic or surgical. • ______________: external ear is small, malformed • ______________: ear canal is closed off. • Post-cancer surgery. Congenital Malformation Microtia Anotia: Pre- and Post-Op Mastoiditis Hearing Loss accompanying these disorders: • Blockage or atresia: – moderate ________________ hearing losses. – usually medically or surgically treatable. – additional HL if _______________--associated problems w/ cochlea • Surgical or traumatic: – ___________- frequency conductive. – prosthetics available, expensive.