* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Moody
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
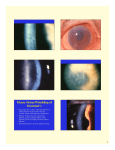
Keratoconus What is Keratoconus? Keratoconus is a thinning of the cornea resulting in significant visual impairments. The cornea is a shaped like a circle, but in Keratoconus the cornea begins to bulge and turn into a cone shape form. The cornea is a clear structure of the eye and is responsible for refracting most of the light taken in by the eye. Who Gets Keratoconus? Keratoconus is a rare disease, but not an unheard of disease. It is seen throughout the world and is believed about 1 out of 2,000 people get this disease. The onset of this disease is usually in late teen years to early twenties. This disease shows traits of progression for 10-20 years and then slows down and stabilizes. Eye glasses Contact lens Intacs- These are tiny plastic inserts are placed just under the eye's surface in the periphery of the cornea and help re-shape the cornea for clearer vision. As the Keratoconus Progresses: The cornea will continue to thin and become more of a cone shape. A type of contact lens will be prescribed called, rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lenses are to help correct vision. Corneal crosslinking This is a new type of treatment under research to slow down the progression of Keratoconus. This method works by increasing collagen crosslinking. These are natural anchors in the cornea. These anchors are responsible for preventing the cornea from bulging out and becoming steep and irregular. Cornea Transplant In the most severe cases a cornea transplant can be performed with a donor cornea. This usually happens if extreme thinning occurs or the eye does not accept contact lens. Risk Factors: References atopic history ocular allergies rigid contact lens vigorous eye rubbing Over exposure to ultraviolet rays from the sun Bailey, G., & Contributions, J. L. (2000). Keratoconus - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment. Is There a Cure? Consumer Guide to Eyes, Eye Care and Vision Correction - LASIK, Contact Lenses and Eyeglasses. Retrieved June 26, 2010, from http://www.allaboutvision.com/conditions/keratoconus.htm Keratoconus. (2006). American Optometric Association - Serving Doctors of Optometry & their Patients. Retrieved June 26, 2010, from http://www.aoa.org/x4721.xml Signs and Symptoms: Bulging eye Blurred vision Sensitivity to light CxL Corneal Collagen Crosslinking with Riboflavin. (2010, April 12). Corneal Crosslinking. Retrieved June 26, 2010, from http://www.usaeyes.org/lasik/faq/cxl-crosslinking.htm What is Keratoconus? (1997). National Keratoconus Foundation. Retrieved June 26, 2010, from http://www.nkcf.org/en/aboutkeratoconus.html Treatment: Early stages of Keratoconus: These are efforts to help with the beginning of nearsightedness and astigmatism. Keratoconus: eMedicine Ophthalmology. (2010, February 12). EMedicine - Medical Reference. Retrieved June 26, 2010, from http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1194693-overview