* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 12-1 - Ithaca Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Name_____________________________________ Class____________________________ Date________________
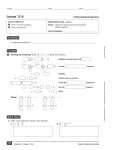
Lesson 12-1
Probability Distributions
Lesson Objectives
1 Making a probability distribution
2 Using a probability distribution in
conducting a simulation
NAEP 2005 Strand: Data Analysis and Probability
Topic: Probability
Local Standards: ____________________________________
Vocabulary.
All rights reserved.
A frequency table is
Cumulative probability is
A probability distribution is
Example.
1 Finding Probability Use the frequency table. Find the probability
that a student is involved in at least one extra-curricular activity.
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
P (more than one activity) P (one activity) 720
720
720
720
720
Find the experimental
probability for each event
in the table that represents
at least one extra-curricular
activity.
More than
one activity
144
One activity
360
No activities
216
Total
Students
720
Add to find the
cumulative probability.
Quick Check.
1. Use the information in Example 1. Find the probability that a student is involved
in one activity or no activities.
Daily Notetaking Guide
Algebra 2 Lesson 12-1
231
Name_____________________________________ Class____________________________ Date ________________
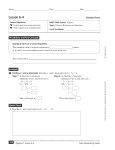
Example.
2 Probability Distributions Suppose you spin two spinners. Each spinner has
4 possible outcomes: 1, 2, 3, and 4. Show the probability distribution for the
sum of the numbers.
Method 1 Make a frequency table. Extend the table to include probabilities.
Spinning Two Spinners
3
2
Sum
4
5
6
7
8
Frequency
There are 16 possible outcomes.
Divide to find the probability.
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
All rights reserved.
Probability
Method 2 Graph.
Spinning Two Spinners
3
16
1
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2. Use a table or a graph to show the probability distribution for the roll of one
number cube labeled with numbers 1–6.
232
Algebra 2 Lesson 12-1
Daily Notetaking Guide
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
Quick Check.
Name_____________________________________ Class____________________________ Date ________________
Example.
3 Genetics Use the information in the chart. Graph the probability distribution
for each sample space.
Inherited Gene Pairs From
One Recessive and One Hybrid Pea Plant
Parent Plant
All rights reserved.
Parent
Plant
r
r
R
Rr
Rr
r
rr
rr
RR dominant gene pair (red flower)
Rr hybrid gene pair (pink flower)
rr recessive gene pair (white flower)
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
3
4
2
4
1
4
Plant Color Distribution
{red, pink, white}
1
Probability
Probability
Genotype Distribution
{RR, Rr, rr}
1
RR
Rr
rr
Event
3
4
2
4
1
4
Red Pink White
Event
Quick Check.
3. Make a probability distribution table for each sample space in Example 3.
Daily Notetaking Guide
Algebra 2 Lesson 12-1
233
Name_____________________________________ Class____________________________ Date ________________
Example.
4 Market Research The probability of an information desk at a library
receiving C calls each hour varies according to the following distribution.
C
0
1
2
3
4
5
P(C)
0.05
0.15
0.25
0.3
0.2
0.05
Outcome
Probability
Cumulative
Probability
0
0.05
0.05
1
0.15
0.20
2
0.25
3
0.30
0.20
5
0.05
01
–
05
Since P(0) 0.05, assign
numbers to this outcome.
75
There are
–
–
0.75
46 –
–
1.00
numbers
from 46 to 75.
96 – 100
Step 2 Conduct the simulation. Model an eight-hour period by generating
eight random numbers from 1 to 100.
Hour
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th
Random
95 91 15 52 41 74
5
34
numbers
Number
of calls
4
4
Step 3 Interpret the simulation. A total of
3
0
calls came in over an eight-hour period.
Quick Check.
4. Use the information in Example 4. Conduct a simulation to predict the number
of calls received during a 16-hour period.
234
Algebra 2 Lesson 12-1
Daily Notetaking Guide
© Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
4
Assigned
Numbers
All rights reserved.
Use random numbers to predict the number of calls received during an
eight-hour shift.
Step 1 Set up a random-number simulation. Assign numbers from 1 to 100
based on the probability of each event. Use cumulative probabilities.