* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stagflation is unique situation where there is high
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Great Recession in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
2000s commodities boom wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
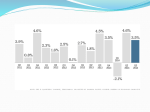
Stagflation Sunday, 19 June 2011 15:35 Stagflation is unique situation where there is high inflation coupled with stagnant economy with low income and employment rates. Inflation is a result of high growth which increases the income and correspondingly increases the demand, thereby leading to hiking of prices. Stagnation on the other hand results from low demand, leading low output resulting into collapse. Stagflation is contraction of stagnant and inflation. Inflation or stagnant economy in itself is a difficult situation for any country. This is why stagflation is so dangerous. Imagine a scenario in which you have both a sinking economy and runaway inflation. With high unemployment, consumers have less money to spend. Add inflation, and the money they do have is worth less and less every day. What are the causes of stagflation? Stagflation can be result of supply side shock. Imagine a situation where a country is already suffering from stagnation and high unemployment. This country is also very big importer of oil. Suddenly there is rise in the oil prices. Increase in oil prices govern corresponding rise in the other commodity prices. Oil being the major commodity in most of the production activities, any price rise in the oil increase the overall production cost. In order to cover for the rise in the production cost, the manufacturing units need to increase the price of the commodities. Thus the combined effect of stagnant economy and increase in the price of essential commodity lead to stagflation. Stagflation can also be caused by mismanaged macroeconomic policies. Central banks can increase money supply in order to increase the money supply and provide spurt to the economy. These actions are bound to increase the prices of commodities. These policies need to be complemented by appropriate labor and goods policies. If there is mismatch between monetary policies and labor & good policies, it may lead to decrease in production. If such a 1/2 Stagflation Sunday, 19 June 2011 15:35 situation continues for long time, then it may lead to stagflation. During the recession countries suffers from reduced output in terms of GDP and increase in unemployment. The threat of stagflation is greatly increases during recession. According to standard monetary policy, the central bank across the world lowers interest rates during a recession to encourage borrowing and spending. The key to preventing stagflation is to avoid allowing too much money to enter the economy too quickly. We just saw above terms inflation and stagflation. There are two other key terms, deflation and hyperinflation. Deflation is decline in general price level caused by reduction in supply of money or credit. It is often caused by contractions in spending either in the form of reduction in government spending, personal spending or investment spending. Deflation has side effect of increasing unemployment in the economy, since it leads to lower level of demand in the economy. Hyperinflation is a condition in which prices rises very rapidly and currency loses value. Hyperinflation is mainly caused by an extremely rapid growth in the supply of paper money. It occurs generally when government recklessly prints currency to fund its expenditures. The growth in the output of goods and services is exceedingly inferior to the money printed out. The rate at which the government is printing the money is lesser than the rate at which it is getting devalued; hence the value of currency keeps on going in the downward direction. 2/2