* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gut Microbiota
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Crohn's disease wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Ulcerative colitis wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
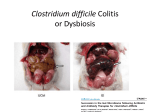
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
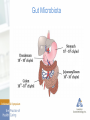
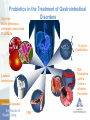
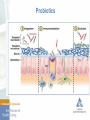
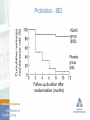
The Microbiome and Probiotics: Fact and Fiction Ameet Parikh, MD Microbiome Human Gut microbiome - What is it - What role does it play in health and in disease - Modification of the microbiome to maintain health or treat disease Microbiome Microbiota • The microorganisms that live in an established environment Microbiome • The full complement of microbes, their genes, and genomes in a particular environment The Gut Microbiota - Complex community of microbes – estimated to contain 200 trillion cells - > 1000 diverse microbial species - 10 x the number of human cells in our body - Gut microbiome is 150 x larger than the human genome Gut Microbiota Gut Microbiota Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes make up around 90% of the gut microbiota Each individual harbors his/her own distinctive pattern of gut microbial communities For a given individual, the fecal microbiota remains remarkably stable over a person’s lifetime Gut Microbiota - Functions Prevents colonization by pathogens “Educates the immune system” Metabolic role - Caloric salvage - Produces • SCFA • Vit K and folate Participates in drug metabolism • Activates 5-ASA Deconjugates bile acids Gut Microbiota Colonization of the gastrointestinal tract begins immediately after birth Initial bacterial colonization (normal) starts from a “Germ free” intrauterine environment and is populated through maternal vaginal/fecal flora and oral feeding (breast milk vs formula) Complete adult colonization : by 3 yrs of life Factors affecting Gut Microbiome Microbiome Alterations in gut microbiota have been linked with FBD IBD CDI Celiac disease Allergies Autism Metabolic diseases Obesity Malignancy Type I DM NASH Depression Gut Microbiota Does the intestinal microbiota differ in patients with specific disorders (IBS/IBD) from healthy subjects? If the microbiota does differ, is it an important factor in the pathogenesis of the disorder? Gut Microbiota - IBD Pathogenesis – linked to inappropriate activation of GI immune system toward the gut microbiota in genetically susceptible hosts &under the influence of environmental factors Gut Microbiota - IBD Gut Microbiota - FBD IBS, functional bloating/constipation/diarrhea Change in gut microbiota – cause abn fermentation of dietary substrates elicit excess stimulation of the mucosal immune system through a ‘leaky gut’ – leads to low grade inflammation, affects gut motor responses & elicits visceral hypersensitivity Decreased Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus in IBS Gut Microbiota - CDI Gut Microbiota - Diet - Antibiotics - Prebiotics - Probiotics - Symbiotics - FMT Probiotics Global sales of Probiotics – 21.6 billion dollars in 2010, expected to reach 31.1 billion in 2015 Fastest growing segment of the global dietary supplement & functional food industries People are looking for ‘natural’ or non-drug ways to maintain health or treat disease Probiotics First described by Metchnikoff in 1907 Probiotics Probiotics Live microorganisms which, when administered in adequate amounts, confer a health benefit on the host Prebiotics Nondigestible substances that provide a beneficial physiological effect for the host by selectively stimulating the favorable growth or activity of a limited number of indigenous bacteria Probiotics Synbiotics Products that contain both probiotics and prebiotics Probiotics in the Treatment of Gastrointestinal Disorders Diarrhea Acute infectious Antibiotic-associated C. difficile H. pylori Eradication IBD Ulcerative colitis Crohn’s disease Pouchitis Lactose Intolerance FBD Probiotics Characteristics of Effective Probiotics • Able to survive the passage through the digestive system. • Able to attach to the intestinal epithelia and colonize. • Able to maintain good viability. • Able to utilize the nutrients and substrates in a normal diet. • Non pathogenic and non toxic. • Capable of exerting a beneficial effect on the host. • Stability of desired characteristics during processing, storage and transportation. Probiotics – Diarrheal Diseases Probiotics - AAD Antibiotic Associated Diarrhea Antibiotic Associated Diarrhea Antibiotic Associated Diarrhea Probiotics - FBD 10 – 15% of population has IBS pathogenesis – dysmotility, visc hypersensitivity, disturbances in GI flora, and chronic immune activation leading to low grade mucosal inflammation have all been implicated Probiotics - CDAD FMT – LGI experience • First Transplant was in November 2013 • Performed 62 transplants to date for recurrent CDI • Of the elective cases we have had sustained cures in 57/62 first time FMT- 5 relapses occurred • 3/5 relapses needed antibiotics after FMT • 3 competed 2nd FMT, no continued issues to date • 2 treated with Vanco or Dificid and did not require 2nd FMT Probiotics - IBD FMT - IBD FMT - IBD FMT - IBD Much work remains: • Is FMT effective and safe in IBD? - Adequately powered trials • Ideal recipient? - Genotype - Phenotype: Pouchitis, Proctitis, Post-op prophylaxis, ileal Crohn’s, maintenance of remission, Microbiome - Concomitant meds - Can FMT make some patients worse? FMT Great success story for recurrent CDI Being studied for multiple other conditions – IBD, IBS, Obesity Autism, NASH/Met synd, reversal of multidrug resistance to abx IBD is associated with dysbiosis –More complicated than C. difficile Patients are eager for alternative therapies FMT appears generally “pretty safe” – Infections and disease flares have been reported Therapeutic Manipulation of gut microbiota holds promise & may eventually prove beneficial for other conditions – We must not be overly enthusiastic and remember that this is experimental and unproven therapy. Microbiome - Future Lachnospiraceae family Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Akkermansia muciniphila Probiotic ecosystems Gut Microbiome “All disease begins in the gut” Hippocrates 460 BC – 370BC “Health is determined by the microbiota in our gut” Hippocrates Gut Microbiome Thank You