* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Blood cell
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
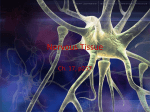
Human Body Systems I. Nervous System – Ch 35 A. Functions 1. Controls & coordinates body’s response to internal & external environment B. Structures 1. Brain 2. Spinal cord 3. Peripheral nerves C. Fundamental unit = neuron (nerve cell) A. H. F. B. G. C. D. E. A = Dendrites – receives message/impulse from neuron before it B = Cell body – contains nucleus & cytoplasm C = Nucleus – genetic information D = Axon – transmits the message/impulse away from cell body E = Myelin sheath – protective covering that insulates the axon F = Node – gaps in the myelin sheath where the axon is exposed G = Schwann cells – makes the myelin sheath H = Axon terminal – transmits message/impulse to dendrites of the next neuron; contains neurotransmitters D. Action potential – transmission of an impulse down a neuron E. Communication between neurons – occurs at the synapse II. Skeletal System – Ch 36 A. Functions 1. Support body & protect internal organs 2. Movement 3. Stores minerals 4. Blood cell formation - bone marrow B. Structures 1. Bones 2. Cartilage 3. Ligaments – attaches bone to bone; Ex. bones of hand 4. Tendons – attaches muscle to bone; Ex. Achilles tendon III. Integumentary System – Ch 36 A. Function 1. Barrier against infection & injury 2. Regulates body temperature 3. Protection against UV radiation B. Structures 1. Skin 2. Hair 3. Nails 4. Sweat & oil glands IV. Muscular System – Ch 36 A. Functions 1. Works with skeletal system to produce voluntary movement 2. Works with circulatory system to help circulate blood 3. Works with digestive system to help move food through the digestive tract B. Structures 1. Skeletal muscle - for voluntary movements - Ex. walking, running, chewing 2. Smooth muscle - for involuntary movements - Ex. movement of foods through digestive tract, pupil size 3. Cardiac muscle - only to pump the heart V. Circulatory System – Ch 37 A. Function 1. Carries O2, nutrients & hormones to cells 2. Fights infection 3. Removes cell waste 4. Regulates body temp B. Structures 1. Heart - pumps blood 2. Blood a. Red blood cells – contain hemoglobin b. White blood cells – immune response c. Plasma d. Platelets – clotting factors 3. Blood vessels C. Works closely with the respiratory system! VI. Respiratory System – Ch 37 A. Functions 1. Provide O2 needed for cellular respiration 2. Remove excess CO2 from body B. Structures 1. Nose 2. Pharynx 3. Larynx 4. Trachea 5. 6. 7. 8. Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Lungs C. The diaphragm is a muscle that allows the volume of the chest cavity to expand. 1. Nose 2. Mouth 3. Larynx 4. Lungs 5. R. Bronchus 6. Diaphragm 7. Pharynx 8. Trachea 9. L. Bronchus 10. Bronchioles 11. Alveoli VII. Digestive System – Ch 38 A. Function 1. Converts food into smaller molecules that can be used by the cells of the body 2. Eliminates waste B. Structures 1. Mouth 2. Pharynx 3. Esophagus 4. Stomach 5. Small intestine 6. Large intestine 7. Rectum C. Components 1. Mouth - mechanical & chemical digestion - teeth & saliva 2. Pharynx - throat 3. Esophagus – connects mouth to stomach - Peristalsis 4. Stomach - muscular pouch food empties in to - mechanical & chemical digestion (churning & acids) 5. Small Intestines – absorbs nutrients diffuses into circulatory system - Villi increase surface area for absorption 6. Large Intestine - removes water from solid waste 7. Rectum - stores waste until it is eliminated D. Accessory Organs 1. Liver - produces bile, which breaks down fats 2. Gall bladder - stores bile 3. Pancreas – produces hormones to control blood sugar, produces enzymes VIII. Excretory System – Ch 38 A. Function 1. Removes wastes products, such as urea, from the body to maintain homeostasis B. Structures 1. Skin – excretory & integumentary work together 2. Lungs – excretory & respiratory work together 3. Kidneys 4. Bladder 5. Ureters 6. Urethra – has dual purpose in men excretory & reproductive IX. Endocrine System – Ch 39 A. Functions 1. Controls growth, development, metabolism 2. Maintains homeostasis B. Structures 1. Hypothalamus 5. Adrenals 2. Pituitary 6. Pancreas 3. Thyroid 7. Ovaries 4. Parathyroid 8. Testes C. Release hormones into the bloodstream 1. Hormones - chemicals that are produced in one part of the body that affect the functioning of another part of the body - target cells D. Remember the goal is to maintain homeostasis! 1. Feedback inhibition (RECALL from Nervous System notes) E. Glands of the Endocrine System 1. Hypothalamus – controls pituitary gland 2. Pituitary gland – controls other glands 3. Parathyroid glands – controls level of calcium in blood 4. Thymus – stimulates T cell development (immune response) 5. Adrenal glands – control stress reaction 6. Pineal gland – controls sleep/wake cycles 7. Thyroid – controls metabolism 8. Pancreas – controls sugar level in blood (video 39-2) 9. Ovaries – control female characteristics 10. Testes – control male characteristics X. Reproductive System – Ch 40 A. Function 1. Produces gametes 2. In females, nurtures & protects the developing embryo B. Structures 1. Testes 6. Ovaries 2. Epididymis 7. Fallopian Tubes 3. Vas deferens 8. Uterus 4. Urethra 9. Vagina 5. Penis C. Fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube! D. Fertilized egg then travels to the uterus & implants in the wall.














![Neuron [or Nerve Cell]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000229750_1-5b124d2a0cf6014a7e82bd7195acd798-150x150.png)


