* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exponential Functions Objectives Exponential Function
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Functional decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard calculus wikipedia , lookup
Dirac delta function wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of the function concept wikipedia , lookup
Function (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
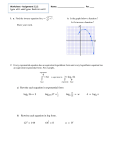
Objectives Exponential Functions Exponential Function – Evaluate exponential functions. – Graph exponential functions. – Evaluate functions with base e. – Use compound interest formulas. Definition of Exponential Function • The exponential function is very important in math because it is used to model many real life situations. • For example: population growth and decay, compound interest, economics, and much more. Graphing Exponential Functions • To graph an exponential function, follow the • How is this different from functions that we worked with previously? • Some DID have exponents, but NOW, the variable is found in the exponent. – (Example: exponential function) is NOT an Graph of an Exponential Function • Graph steps listed: 1. Compute some function values and list the results in a table. 2. Plot the points and connect them with a smooth curve. Be sure to plot enough points to determine how steeply the curve rises. 1 Graph of Graph ____________ • Subtract 3 from x-values (move 3 units left) • Subtract 4 from y-values (move 4 units down) Note: Point (0,1) has now been moved to (-3,-3) Example Graph the exponential function y = f(x) = 3x. x y = f(x) = 3x (x, y) 0 1 (0, 1) 1 3 (1, 3) 2 9 (2, 9) 3 27 (3, 27) −1 1/3 (−1, 1/3) (−2, 1/9) (−3, 1/27) −2 1/9 −3 1/27 Example Graph the exponential function x 0 −1 −2 −3 1 2 3 1 3 9 27 1/3 1/9 1/27 (x, y) (0, 1) (−1, 3) (−2, 9) (−3, 27) (1, 1/3) (2, 1/9) (3, 1/27) Graph y = 3x + 2. Example The graph is the graph of y = 3x shifted _____ 2 units. x y −3 1/3 −2 1 −1 3 0 9 1 27 2 81 3 243 Characteristics of _________ • The domain consists of all real numbers: (- ∞, ∞) • The range consists of all positive real numbers: (0, ∞) • The y-intercept is the point (0,1) (a non-zero base raised to a zero exponent = 1). • If the base b is greater than 1, the graph extends up as you go right of zero, and gets very close to zero as you go left. (Is an increasing function) • If the base b lies between 0 & 1, the graph extends up as you go left of zero, and gets very close to zero as you go right. (Is a decreasing function) 2 The Number e Other Characteristics of _________ • This function is one-to-one and has an inverse that is a function. • The graph approaches, but does not touch, the xaxis. The x-axis (y=0) is a horizontal asymptote. • Transformations of the exponential function are treated as transformation of polynomials. (Follow order of operations, x’s do the opposite of what you think.) • e is known as the natural base (Most important base for exponential functions.) • e is an irrational number (can’t write its exact value) • We approximate e Natural Exponential Function Graphs of Exponential Functions, Base Graph f(x) = ex x f(x) −2 0.135 Remember −1 0.368 • e is a number 0 1 • e lies between 2 and 3 1 2.718 2 7.389 Graph f(x) = e x + 2. x f(x) −4 0.135 −3 0.368 −2 1 −1 Example Graph e Example f (x) = 2 − e −3x. x f(x) −2 −401.43 −1 −18.09 2.718 0 1 0 7.389 1 1.95 1 20.086 2 1.99 3 Applications of Exponential Functions • Exponential growth (compound interest!) Example • A father sets up a savings account for his daughter. He puts $1000 in an account that is compounded quarterly at an annual interest rate of 8%. How much money will be in the account at the end of 10 years? (Assume no other deposits were made after the original one.) • Exponential decay (decomposition of radioactive substances) 4