* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solving Linear Equations
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
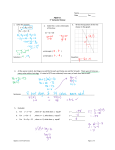
Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 Intersections and the graphing calculator. Find all intersections of the graphs of the following equations: x – y = –3 2y = – x – 2 y = 4x – 2 Find all intersections of the graphs of the following equations: y = 1/2x2 – 2 y=–x+2 y = – .25x – 1 1 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 Sysytems of Equations How many solutions do each have, and what do those solutions look like graphically? 3x + 1 =4 3x + 1 > 4 3x + 2y = 4 3x + 2y > 4 2x - y = 4 x + 4y = -7 A system of equations : Is (0, 2) a solution to the above system? Is ( 0, -4) ? Is ( 1, -2) ? How many solutions does this system have? 2 Chapter 4 Consistent systems: Analytical Algebra 2 Independent Dependent Inconsistent systems: Homework Page 228 1 – 4 4 methods for solving a system of equations: Solving by Graphing x+y=1 3x – y = -5 y= 4 3x – 2y = 4 3 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 Use your calculator to slolve each. Sketch, on the axes below, the graphs as you see them on the calculator. Use the clauclator to find the intersection, the solution, if it exists to the system. y = 2x - 1 y = -3x + 2 y=3 3x – 2y = 6 ans ________________ ans. ___________________ y=x-5 2x + y = 4 y=x+1 2x – 5y = 3 ans. ___________________ ans. _________________ 4 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 Be on the lookout for inconsistent and dependent solutions. When solving by graphing: Inconsistnet systems : Dependent systems: Homework Page 228 5 – 8 , 10 2x + 3y = 6 y = -2/3x + 1 Homework Page 229 11, 13, 15, 21, 23 5 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 Solving by Substitution 2x – y = 5 Steps: y= -x + 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 3x – 2y = -11 4x + y = 9 x = 2y – 9 3x – 4y = 2 Be on the lookout for inconsistent and dependent solutions. When solving by substitution: Inconsistnet systems : Dependent systems: 6 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 3x – 12y = -24 -x + 4y = 8 Homework Page 230 29, 30, 37 39, 47, 53, 61 Solving by the Addition (Elimination) Method x+y=1 Steps 2x – y = 5 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 7 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 x – 2y = 7 x + 2y = 4 3x – 2y = 9 2x + y = -1 2x – 3y = 6 3x + 9y = -9 Homework Page 239 3, 5, 7, 11 8 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 Be on the lookout for inconsistent and dependent solutions. When solving by addition (elimination): Inconsistnet systems : Dependent systems :: 3x + 6y = 7 3x – 4y = 0 2x + 4y = 5 4x – 7y = 0 Homework Page 239 9, 13, 19, 23, 36, 37 9 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 Solve the following system three ways: 3x + y = 4 x+y=2 Solve x + 2y – z = 1 x – 2y + z = 6 2x – y + z = 6 3x + y – 2z = 2 x + 3y – z = 2 2x – 3y + 2z = -7 Homework Page 241 43, 47 10 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 Matrices Matrix: Used to solve many different types of math problems. Sometimes thought of as the coefficient of terms in equations. Noted by Captial letters. Size is given in rows X columns 3 1 2 A= 0 7 2 Square matrix Determinant of a matrix: 3 4 Find the determinant of B = 1 2 3 1 6 2 11 Chapter 4 2 1 5 0 Analytical Algebra 2 2 1 5 0 3 5 Homework Page 256 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 11 2 1 4 2 5 0 1 0 1 2 3 5 3 4 1 0 Homework Page 256 13, 14, 15 3 2 12 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 Solving Systems using Matrices Cramer’s Rule 2x – 3y = 8 5x + 6y = 11 1. Create and find determinant of coeff matrix 2. Create and find determinant of “x” matrix 3. Create and find determinant of “y” matrix 4. Find x by dividing: 5. Find y by dividing: 13 Chapter 4 Solve using Cramer’s Rule Analytical Algebra 2 6x – 6y = 5 2x – 5y = 26 2x – 10y = -1 5x + 3y = 3 Homework Page 257 24, 25, 26 Solve using Cramer’s Rule 3x – 2y = 6 4x – 8y = 36 6x – 4y = 4 3x - 6y = 27 14 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 When solving a system using Cramer’s Rule we find inconsistent systems, no solutions, when… When solving a system using Cramer’s Rule we find dependent systems, ∞ solutions, when… Solve using Cramer’s Rule: 3x – 2y + z = 2 2x + 3y + 2z = -6 3x – y + z = 0 15 Chapter 4 x – 2y + z = 6 Analytical Algebra 2 3x + y – 2z = 2 2x – 3y + 2z = -7 Remember to be on the lookout for inconsistent and dependent systems. Homework Page 257 35, 37, 39 16 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 Solving Systems of Linear Inequalities 2x – y ≤ 3 3x + 2y > 8 Steps 1. 2. 3. y ≥ 1/2x – 3 y ≤ 1/2x + 2 17 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 y≥x–1 y < -2 Be on the lookout for inconsistent systems. 2x + 3y > 9 y < -2/3x + 1 Homework Page 274 5, 7, 12, 17, 28 18 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 Word Problems All problems must be solved by solving equations. All variables used must be defined. All problems must be answered in sentence form. 1. The larger of two numbers is 1 less than three times the smaller. The difference between the two numbers is 9. Find the numbers. 2. If 14 is added to a number and that sum is multiplied by 2, the result is equal to 8 times the number decreased by 14. Find the number. 3. Twice the smaller of two numbers is one-half the larger number. The larger is 10 more than 3 times the smaller. 4. The sum of 1/3 of the smaller of two numbers and 2/3 of the larger is 34. Also, ½ of the smaller number is equal to ¼ of the larger number. Find the numbers. 5. Walter is 3 times as old as Martin. Ten years from now, Walter will be twice as old as Martin will be then. How old is each now? 6. The sum of Carl’s age and Ellen’s age is 40 years. Carl’s age 10 years from now will be 1 year less than 4 times Ellen’s age 6 years ago. What are their present ages? 7. Ray is 20 years older than Bill. Five years ago, Ray was 5 times as old as Bill was then. How old is Ray right now? 8. Sidney is 30 years old and Edward is 15 years old. In how many years will Sidney be 1.5 times as old as Edward will be then? 9. The ratio of Paul’s age to Joy’s age is 3 : 5. The sum of their ages is 48 years. How old are Paul and Joy? 10. A 180 degree angle is divided into three angles. Two angles are in the ratio of 2 : 3. The third angle is equal to the sum of the degrees of the other two angles. Find the degree measure of each of the three angles. 11. There are 54 marbles. The marbles are red, white and blue. The ratio of the number of each color, red, white and blue respectively is 3 : 7 : 8. How many red marbles are there? 12. A will states that Gail, you and Pepe are to split the inheritance in the respective ratios of 1 : 3 : 7. If there is $3,300 to split, how much will you receive? 19 Chapter 4 Analytical Algebra 2 13. Mr. Carter invested a sum of money in a 4% interest rate account. He invested a second sum, $250 more than the first sum in a 6% account. He earned a total of $90. How much did he invest in each account? 14. Miss Green invested $1000 at 2% and $6000 at 4%. How much must she invest at 8% to make her total income 5% of her total investment? 15. Billy invests $42,000, some in 3.5% account and the rest in a 4.5% account. IF the interest earned was the same for both accounts, how much did Billy invest in the 4.5% account? 16. Mr. Rose invested a sum of money at 4%. He invested a second sum, $1000 more than the first sum at 3%. If the income earned was equal for both how much did he invest in each account? 17. The width of a rectangle is 2 inches less than its length. If the width is increased by 4 inches and the length is decreased by 2 inches the area will be increased by 8 square inches. Find the dimensions of the original rectangle. 18. The base of a rectangle is 5 feet less than 2/3 of its width. The perimeter of the rectangle is 80 feet. Find the dimensions of the rectangle. 19. The base of a triangle is 2 inches more than its altitude. If the base is increased by 2 inches and the altitude is decreased by 5 inches, the area of the new triangle will be 25 less than the area of the old triangle. Find the base and altitude of the original triangle. 20. If one pair of opposite sides of a square are increased by 2 inches and the other opposite sides in deceased by 3 inches a rectangle is formed whose area is 14 square inches less than the squares area. Find the length of a side of the square. 20