* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2-2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
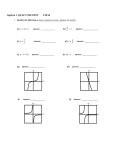
NAME DATE 2-2 PERIOD Study Guide and Intervention Linear Relations and Functions Linear Relations and Functions A linear equation has no operations other than addition, subtraction, and multiplication of a variable by a constant. The variables may not be multiplied together or appear in a denominator. A linear equation does not contain variables with exponents other than 1. The graph of a linear equation is always a line. A linear function is a function with ordered pairs that satisfy a linear equation. Any linear function can be written in the form f(x) = mx + b, where m and b are real numbers. If an equation is linear, you need only two points that satisfy the equation in order to graph the equation. One way is to find the x-intercept and the y-intercept and connect these two points with a line. Example 1 x a linear function? Explain. Is f(x) = 0.2 - − 5 Yes; it is a linear function because it can be written in the form 1 f(x) = -− x + 0.2. 5 Is 2x + xy - 3y = 0 a linear function? Explain. No; it is not a linear function because the variables x and y are multiplied together in the middle term. Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Exercises State whether each function is a linear function. Write yes or no. Explain. 18 2. 9x = − y 1. 6y - x = 7 Yes; it can be written x 7 +− . as y = − 6 6 x 4. 2y- − -4=0 6 Yes; it can be written x + 2. as y = − 12 7. f(x) = 4 - x3 No; the variable x is being multiplied by itself. Chapter 2 x 3. f (x) = 2 - − 11 No; the variable y appears in the denominator. 11 0.4 6. 0.2x = 100 - − y 5. 1.6x - 2.4y = 4 Yes; it can be written 5 2 as y = − x-− . 3 Yes; it can be written x + 2. as f(x) = - − 3 4 8. f(x) = − x No; the variable y appears in the denominator. 9. 2yx - 3y + 2x = 0 No; the variable x appears in the denominator. 11 No; the variables x and y are being multiplied together. Glencoe Algebra 2 Lesson 2-2 Example 2 NAME DATE 2-2 PERIOD Study Guide and Intervention (continued) Linear Relations and Functions Standard Form The standard form of a linear equation is Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are integers whose greatest common factor is 1. Example 1 Write each equation in standard form. Identify A, B, and C. a. y = 8x - 5 y = 8x - 5 -8x + y = -5 8x - y = 5 b. 14x = -7y + 21 14x = -7y + 21 14x + 7y = 21 2x + y = 3 Original equation Subtract 8x from each side. Multiply each side by -1. So A = 8, B = -1, and C = 5. Original equation Add 7y to each side. Divide each side by 7. So A = 2, B = 1, and C = 3. Example 2 Find the x-intercept and the y-intercept of the graph of 4x - 5y = 20. Then graph the equation. The x-intercept is the value of x when y = 0. 4x - 5y = 20 Original equation 4x - 5(0) = 20 Substitute 0 for y. x=5 y 2 O x 6 4 −2 Simplify. −4 So the x-intercept is 5. Similarly, the y-intercept is -4. Exercises Write each equation in standard form. Identify A, B, and C. 2. 5y = 2x + 3 2x - 4y = -1; A = 2, B = -4, C = -1 3. 3x = -5y + 2 2x - 5y = -3; A = 2, B = -5, C = -3 3 2 5. − y=− x+5 4. 18y = 24x - 9 4 8x - 6y = 3; A = 8, B = -6, C = 3 7. 0.4x + 3y = 10 6. 6y - 8x + 10 = 0 3 8x - 9y = -60; A = 8, B = -9, C = -60 8. x = 4y - 7 2x + 15y = 50; A = 2, B = 15, C = 50 3x + 5y = 2; A = 3, B = 5, C = 2 4x - 3y = 5; A = 4, B = -3, C = 5 9. 2y = 3x + 6 x - 4y = -7; A = 1, B = -4, C = -7 3x - 2y = -6; A = 3, B = -2, C = -6 Find the x-intercept and the y-intercept of the graph of each equation. Then graph the equation using the intercepts. 10. 2x + 7y = 14 11. 5y - x = 10 y 12. 2.5x - 5y + 7.5 = 0 y 2 4 2 y 2 O 2 4 6 8x −2 −4 −2 2 O 4x −4 −2 −2 O 2 x −2 x-int: 7; y-int: 2 Chapter 2 x-int: -10; y-int: 2 12 x-int: -3; y-int: 1.5 Glencoe Algebra 2 Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 1. 2x = 4y -1