* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A Linear Regulator with Fast Digital Control for Biasing of Integrated
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
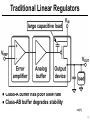
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
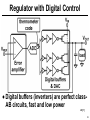
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
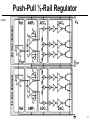
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
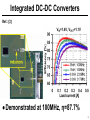
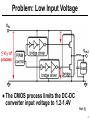
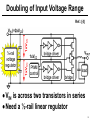
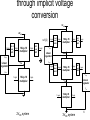
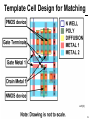
A Linear Regulator with Fast Digital Control for Biasing of Integrated DC-DC Converters A-VLSI class presentation Adopted from isscc Presented by: Siamak Mehrnami Outline ● Integrated DC-DC converters ● Linear regulator with digital control ● Implementation details ● measurements ● Conclusions 2 Integrated DC-DC Converters Ref.: [3] ● Demonstrated at 100MHz, η=87.7% 3 Problem: Low Input Voltage ● The CMOS process limits the DC-DC converter input voltage to 1.2-1.4V Ref: [1] 4 Doubling of Input Voltage Range Ref.: [4] ● VIN is across two transistors in series ● Need a ½-rail linear regulator 5 through implicit voltage conversion 3VDD 2VDD ref:[2] 1-logic 1 to 2 2-logic level shift 16-by-16 multiplier 2-logic Vhigh Linear regulator 2 to 1 1-logic level shift VDD 1-logic 1 to 3 3-logic level shift 1-logic 16-by-16 multiplier 3-logic 3 to 1 1-logic level shift Vhigh 2VDD Linear regulator Vlow 1-logic 1 to 2 2-logic level shift Vlow 16-by-16 multiplier 16-by-16 multiplier 2-logic 2 to 1 1-logic level shift Vhigh 1-logic Linear regulator VDD Vlow 1-logic 2VDD system 16-by-16 multiplier 1-logic 3VDD system 6 Auxiliary Regulator Requirements ● Calculate Figure of Merit – single value to measure performance Ref:[1] 7 Auxiliary Regulator Figure of Merit ● Best known regulator had FOM=22ps – Rajapandian, et al., 2005 ISSCC, p. 298 ● Need same speed at 3X lower power ref:[1] 8 Traditional Linear Regulators ● Class-A buffer has poor slew rate ● Class-AB buffer degrades stability ref:[1] 9 Regulator with Digital Control ● Digital buffers (inverters) are perfect classAB circuits, fast and low power ref:[1] 10 Push-Pull ½-Rail Regulator ref:[1] 11 Template Cell Design for Matching ref:[1] 12 Customized Inverter Cells ref:[1] 13 Floorplan of Matched Inverters ref:[1] 14 Regulator Test Chip in 90nm CMOS ref:[1] 15 Input-Output DC Characteristic ref:[1] 16 Output DC Characteristic ref:[1] 17 Load Step Response (5ns/div) ref:[1] 18 Performance Comparison ref:[1] 19 Conclusions ● Digital buffers (inverters) are more power-efficient than analog buffers ● Achieved 3.64X lower quiescent current at 28% slower response – FOM is 2.84X better than the prior art ● The power bottleneck moved from the analog buffer to the error amplifier – matching requirements influence transistor sizes and the quiescent current ref:[1] 20 References: ● 1-P.Hazucha, “A Linear Regulator With Fast Digital Control For Biasing Integrated DCDC Converters” ISSCC dig. tech. papers 29.2 feb.2006 ● 2-S. Rajapandian, et al., “High-Tension Power Delivery- Operating 0.18µm CMOS Digital Logic at 5.4v,” ISSCC dig. Tech. papers,pp.298299,Feb., 2005 [page 6] ● 3- Hazucha, et al., 2004 VLSI Symposium, p. 256. ● 4-Xiao, et al., 2004 ISSCC, p. 280. 21