* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Mittelbau-Dora wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
United States home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
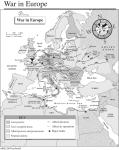
WORLD WAR II Unit Overview ORGANIZING PRINCIPLE The 1930s began with a Great Depression that kept all American eyes fixed on domestic affairs. However, the isolationism of the 1920s waned as a new international menace threatened the future of democracy. At the close of the decade, the United States was on the brink of war. Japan’s decision to bomb Pearl Harbor pushed us over the brink and dragged the U.S. into the conflict. During World War II, America experienced changes that reached into virtually every corner of the country. The conflict revamped the economy and pulled us out of the Depression. While the war effort started off as cumbersome, America shaped up and prevailed on both fronts and redefined America’s position in the world. TRADING SPACE FOR TIME Pressing issues Retooling for all-out war production Government and big business German advancements Rocket bombs Atomic bombs? Einstein’s letter Allied survival—US readiness Selective Service 5 million volunteer 10 million drafted Distances to ship goods and troops Winning the minds: Hollywood Propaganda THE MIRACLE OF PRODUCTION Economic Recovery Industry awakens Farmers Unemployment—decreases drastically $100 billion in military orders R.I.P. Great Depression European demand Labor Opportunities in manufacturing Discrimination in hiring Unions Membership up 3 million (13 million total) Smith-Connally Anti-Strike Act (1943) ECONOMIC PLANNING Office of Price Administration (OPA) Battled inflation Taxes Rationing War bonds National War Labor Board (NWLB) Ceilings on wage increases Restrictions on unions War Production Board Halted the manufacture of nonessential items Tanks, planes, boats, bomb parts, jeeps, liberty ships etc… Dictated transportation and access to raw materials Rationing Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) Manhattan Project WOMEN AND WWII Rosie the Riveter 6 million women working Wage prejudice “Men’s work” WAACs, WAVEs, SPARs, WAFs “Auxiliary”—non combat Army, Navy, Coast Guard, Air Force Clerical work Ambulance drivers Radio operators Electricians Pilots AFRICAN AMERICANS A. Philip Randolph March for integration of workforce Fair Employment Practices Commission (FEPC) Military Black servicemen: 700,000 plus Served in segregated units Noncombat roles until 1943 Double “V” Tuskegee Airmen Congress of Racial Equality (CORE) Sit-ins and demonstrations Chicago, St. Louis JAPANESE AMERICANS Discrimination 135,000 Japanese Issei Nissei “Conspirators” Relocation Centers Executive Order 9066 Prison camps in mountains and deserts Korematsu v. U.S. Supports internment MINORITY WARTIME EXPERIENCE Mexican-Americas 300,000 served Bracero program High casualties Contract laborers Zoot-Suit Riots Asian-Americans 13,000 Chinese serve 30,000 Japanese serve Native Americans 25,000 served “Windtalkers” African-Americans Second Great Migration Detroit HOLDING THE HOME FRONT Economic gains Inflation, wage ceilings, expansive income tax Disposable personal income doubled (GD!) Check please! $ 330 billion Note WWI cost 32 billion! 2/5 of war costs paid by revenues National debt rose from 49 billion to 259 billion GDP $100 billion to $200 billion in 4 years HALTING HITLER The Battle of the Atlantic U-Boat hunting Kept Britain alive—allied springboard Cologne 1,000 plane bombing raid North Africa The “Desert Fox” Erwin Rommel Convoys, depth charges, air patrol, radar and code breaking Nazi sought the Suez Canal Allies drove them back to Tunisia Stalingrad The tide turns on the eastern front ITALIAN CAMPAIGN The “soft underbelly” Sicily falls in August 1943 Mussolini deposed Italy joins the allies German occupied Italy Rome was taken 04 June 1944 Campaign diverts Nazi troop strengths REOPENING THE WESTERN FRONT Teheran Conference (11/28-12/1/1943) Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin Coordinating attacks D-Day 06 June 1944 Allied invasion of Nazi occupied Europe Led by Eisenhower Began the decline of German dominance on the Western front “Lafayette, we are here again.” REOPENING THE WESTERN FRONT Teheran Conference (11/28-12/1/1943) Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin Coordinating attacks D-Day 06 June 1944 Allied invasion of Nazi occupied Europe Led by Eisenhower Began the decline of German dominance on the Western front “Lafayette, we are here again.” V-E DAY Germany collapsing Soviets were closing on East British and Americans closing in on West Battle of the Bulge Last German offensive Unveiling the genocide Winter of 1944—allies push them back Nazi death camps exposed Russians capture Berlin April 1945 FDR passes Hitler takes his own life V-E Day (07 May 1945) THE RISING SUN IN THE PACIFIC Japanese imperialists Guam, Wake, Philippines, Hong Kong, British Malaya, and Burma Strategic locations and natural resources Struggle in the Philippines Bataan defensive MacArthur evacuated—“I shall return” Bataan Death March POWs THE SUN ALSO SETS…LEAPFROGGING TO CHECKMATE Japan sets its eyes on Australia Battle of the Coral Sea Carrier based aircraft—Allied victory Midway The tide turns—1,000 miles NW of Hawaii Admiral Nimitz out maneuvers Japanese Japan loses three carriers “Island-Hopping” U.S. strategy—capturing nearby islands to weaken fortified ones V-J DAY American Submarines Sank 50% of Japanese merchant marine Firebombing in Tokyo March 9-10, 1945 Killed 83,000 Leyte Gulf, Iwo Jima, and Okinawa Crippled Japanese fleet “kamikazes” Little Boy and Fat Man Hiroshima—06 August 1945 Nagasaki—09 August 1945 V-J Day 10 August 1945— “unconditional” surrender