* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Development? Key Issue
Survey
Document related concepts
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Rostow's stages of growth wikipedia , lookup
Gross domestic product wikipedia , lookup
Genuine progress indicator wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
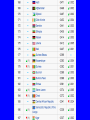
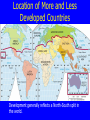
International Development LQ’s for Development – chapter 9 1) Why does development vary among countries? 2) Where are more and less developed countries distributed? 3) How does development affect gender? 4) Why do LDC’s face obstacles to development? The single most important geographic fact of development is its striking UNEVENNESS. What is development? What does it mean to be developed? Developing? Development: evolution, growth, expansion, enlargement, progress More Developed Country (MDC): have a highly developed economy and advanced technological infrastructure. The criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are gross domestic product (GDP), the per capita income, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living. Development: evolution, growth, expansion, enlargement, progress Less Developed Country (LDC): Meets three criteria: Poverty Human resource weakness (poor nutrition, health, education and adult literacy) Economic vulnerability: unstable agricultural production, lacking exports of goods and services, and the percentage of population displaced by natural disasters Human Development Index (HDI) Developed by the United Nations, the HDI combines several measures of development: life expectancy at birth, adjusted GDP per capita, and knowledge (schooling and literacy). Indicators of Development 1. GDP 293-294 2. Types of jobs & productivity 294-295 3. Raw Materials 295 4. Consumer Goods 295-296 5. Education/Literacy 297 6. Health and Welfare 298 Life Expectancy, Infant Mortality Rate 300 8. Natural Increase Rate, Crude Birth Rate 300-301 7. Thoroughly explain the concept(s), include any vocab associated, draw a picture. What Do We Mean By Development? Key Issue 1… The three objectives of development increases in availability and improvements in the distribution of food, shelter, health, protection, etc. improvements in ‘levels of living,’ including higher incomes, more jobs, better education, etc. expansions in the range of economic and social choices available to individuals and nations What is the Human Development Index? (HDI) Measuring Development - HDI United Nations Development Program Overview 2005 Click for Animated Graphs Economic Indicators Gross Domestic Product (GDP, also GNI, PPP) Types of Work (Economic Sectors) Social Indicators Education and Literacy Health and Welfare Demographic Indicators Life Expectancy (37 - 80 years) Infant Mortality (<10 - >100 per thousand) Natural Increase (0 - 4.7 %) http://hdr.undp.org/en/countries ECONOMIC INDICATORS Gross domestic product: value of total output of goods and services produced in a country. Gini coefficient: income distribution of a nation’s residents, who has what out of the total income? Upper, middle, or lower class? WATCH THIS! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v =QPKKQnijnsM GNI: Gross national income, the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP) plus factor incomes earned by foreign residents. PPP: purchasing power parity, compares currencies, what your currency can buy in another country that uses another currency ECONOMIC INDICATORS Primary sector: directly extract materials from Earth through agriculture, mining, fishing, and forestry Secondary sector: includes manufacturers that process, transform, and assemble raw materials into useful products Tertiary sector: involves the provision of goods and services to people in exchange for payment. Types of Jobs: Comparing MDC vs. LDC ECONOMIC INDICATORS • **Quinary sector: jobs in health, education, research, government, retailing, tourism, and recreation. **Quaternary sector: jobs in business services such as trade, insurance, banking, advertising, and wholesaling. ECONOMIC INDICATORS Productivity: value of a particular product compared to the amount of labor needed to make it. Value added: gross value of the product minus the cost of raw materials and energy. Gross=total Why have primary and secondary jobs declined in MDC’s in recent years??? What are businesses doing? ***New International OUTSOURCING! Division of Labor!!!*** What does AP call this? Social Indicators Access to healthcare 8% is spent on healthcare in MDC, 6% in LDC MDC = more calories per day Public healthcare: Obamacare (ACA), Europe’s healthcare system Social Security, public assistance Sanitation and utility (gas, power)services Education and Literacy Average schooling years: 10 years in MDC’s, a couple years in LDC’s Student/teacher ratio is twice as high in MDC’s Measuring Development Social Indicators Education and Literacy Measuring Development Social Indicators Health and Welfare Demographic Indicators Life Expectancy: 60’s in LDC, 70’s MDC Young people is 6 times higher than old people in LDC Literacy Infant Mortality NIR CBR GII: Gender Inequality index GDI: Gender related Development Index GEM: Gender empowerment index Key Issues 2 & 3 2: Where are more and less developed countries distributed? 3: Where does level of development vary by gender? Let’s read intro to Key Issue 2 on page 301 Location of More and Less Developed Countries Development generally reflects a North-South split in the world. Why the HDI? Read about your assignmed region and tell us something about it! Pages 301-309 MDC LDC 1. Anglo-America: 0.94 2. Western Europe: 0.93 3. Eastern Europe: 0.80* 4. Japan 0.94* 5. South Pacific: 0.87 6. Latin America: 0.80 7. East Asia: 0.76 8. Middle East: 0.68 9. Southeast Asia 0.58 10.South Asia: 0.58 11.Sub-Saharan Africa: 0.51