* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The big ideas
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
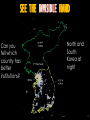
The Big Ideas Chapter 1 1 PRINCIPLES: MACROECONOMICS COWEN AND TABARROK © 2010 WORTH PUBLISHERS MODERN Incentives in the Prisoner Transport Business Only when the ship captains began to be paid per living convict on arrival did the death rate fall from over 1/3 to less than 1%. British prison transport vessel 2 “Success”. Source: public domain Chapter Outline • Big Ideas in Economics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Incentives Matter Good Institutions align Self-interest with the Social interest Trade-offs are Everywhere Thinking on the Margin Tampering with the Laws of Supply and Demand has Consequences The importance of wealth and economic growth Institutions matter Economic booms and busts cannot be avoided but can be moderated 9. Prices rise when the government prints too much money 10.Central banking is a hard job • The Biggest Idea of All: Economics is Fun • See the Invisible Hand Blog (click) for more examples. 3 Big idea #1: Incentives Matter • Incentives: rewards and penalties that motivate behavior. • People respond to incentives in predictable ways. • Self-interest is an important incentive in economics. 4 Big idea #2: Good institutions align selfinterest with the social interest • Markets magically align your selfinterest with social interest (usually). Because the cheesemonger wants profit, you get your cheese! 5 SEE THE INVISIBLE HAND “It is not from the benevolence of the butcher, the brewer, or the baker that we expect our dinner, but from their regard to their own interest.” The Wealth of Nations Adam Smith Adam Smith saw the invisible hand. 6 Big idea #3: Trade-offs Are Everywhere • For every choice something is gained, something lost. • The Opportunity Cost of a choice is the value of the opportunities lost. (key concept) – AND people respond to changes in opportunity costs. – Unemployment rates and college enrollment: related. 7 Big idea #4: Thinking on the Margin Actual trade-offs are usually “on the margin.” • Marginal means additional. • Most economic choices are marginal choices. • E.g. Newt Gingrich wanted mandatory executions for drug dealers… • … but the effect was to reduce the EXTRA penalty for murdering police offers during arrest. higher punishments for lesser crimes reduces the marginal cost of harsher crimes 8 Big idea #5: Tampering with the Laws of Supply and Demand Has Consequences • Roman Emperor Diocletian set a maximum price on beef, eggs, grain and clothing on pain of death. – Result? No one sold much… The shortages were severe and the policy was abandoned. – U.S. President Nixon repeated the price controls in 1971 as oil prices rose- and then abandoned them. 9 Big idea #6: The Importance of Wealth and Economic Growth • Wealth brings higher standards of living. • Understanding economic growth is crucial. 10 World Distribution of Income, 2000. Source: Penn World Tables 11 Big idea #7: Institutions Matter • Why are some countries rich and others poor? • Incentives are sometimes lacking. • Strong institutions that support these incentives foster economic growth. 12 SEE THE INVISIBLE HAND Can you tell which country has better institutions? North and South Korea at night 13 Big idea #8: Economic Booms and Busts Cannot Be Avoided but Can Be Moderated • Policymakers use Fiscal Policy and Monetary Policy to attempt to smooth out this economic volatility. Can we make the economy smoother? 14 Big idea #9: Prices Rise When the Government Prints Too Much Money • Inflation is an increase in the general level of prices. • Heavily indebted nations often print money to pay down debt… Brother can you spare 10 million Zim dollars? – Zimbabwe: highest inflation ever 15 Big idea #10: Central Banking Is a Hard Job • The Federal Reserve is the U.S.’s central bank. • “The Fed” is in charge of money supply. – Helping the economy be stable – Balancing inflation and unemployment – Preventing banking crises? Ben Bernanke, Chairman of the Fed, wondering where the nearest aspirin supply is. 16 Try it! As land prices near the U.S. coast increase, what changes do you expect to see in burial practices (other things equal)? Think opportunity cost. a) b) Traditional burials will increase and cremation will decrease. Cremation will increase and traditional burials will decrease. 17 Try it! As land prices near the U.S. coast increase, what changes do you expect to see in burial practices (other things equal)? Think opportunity cost. a) b) Traditional burials will increase and cremation will decrease. Cremation will increase and traditional burials will decrease. 18 Try it! True or false: As women’s wages have risen over the past 50 years, the opportunity cost of being a stayat-home mother has risen. a) True b) False 19 Try it! True or false: As women’s wages have risen over the past 50 years, the opportunity cost of being a stayat-home mother has risen. a) True b) False 20 Try it! Would you expect to find companies developing cures for rare diseases or common ones? Think about incentives. a) Rare diseases b) Common diseases 21 Try it! Would you expect to find companies developing cures for rare diseases or common ones? Think about incentives. a) Rare diseases b) Common diseases 22 Try it! In which country would a person face a lower opportunity cost for holding cash? a) Zimbabwe b) The U.S. 23 Try it! In which country would a person face a lower opportunity cost for holding cash? a) Zimbabwe b) The U.S. 24