* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - KSUMSC
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
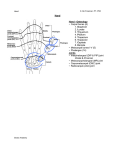
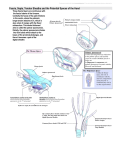
Dr. Ahmed Fathalla Ibrahim THE SKIN 1. Flexure creases (lines of palm) 2. Papillary ridges (fingerprints): improve grip & increase surface area 3. Abundant sweat gland SUPERFICIAL FASCIA 1. Contains: cutaneous nerves & vessels 2. Contains: Palmaris brevis DEEP FASCIA • PALM: thickened at 3 sites: Palmar aponeurosis: • Definition • Description • Function • Clinical anatomy: Dupuytren’s contracture PALMAR APONEUROSIS • • 1. 2. 3. • • DEFINITION: It is a thickening of deep fascia in the middle of the palm DESCRIPTION: It is triangular in shape: Apex: directed proximally, continuous with tendon of palmaris longus Base: directed distally, divided into 4 slips for the medial 4 fingers Margins: send septa to metacarpal bones separating the structures under the aponeurosis from thenar & hypothenar muscles FUNCTION: It protects the underlying tendons, vessels & nerves CLINICAL ANATOMY: DUPUYTREN’S CONTRACTURE: shortening of the medial part of aponeurosis resulting in flexion of the little & ring fingers DEEP FASCIA Flexor retinaculum: • Definition • Attachments • Relations • Functions • Clinical anatomy: Carpal tunnel syndrome FLEXOR RETINACULUM • DEFINITION: It is a thickening of deep fascia that lies over the front of the carpal bones converting the carpal groove (formed by carpal bones) into a tunnel • ATTACHMENTS: 1. Lateral: by 2 laminae: superficial (to tubercles of scaphoid & trapezium) & deep (to the medial lip of the groove on the trapezium) 2. Medial: to pisiform & hook of hamate FLEXOR RETINACULUM • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. • 1. 2. RELATIONS: Superficial: from lateral to medial: Superficial palmar branch of radial artery Palmar cutaneous branch of median nerve Tendon of palmaris longus Palmar cutaneous branch of ulnar nerve Ulnar vessels Ulnar nerve Deep: Structures passing through carpal tunnel Tendon of FPL & its synovial sheath (radial bursa) Tendons of FDS & FDP & their common synovial sheath (Ulnar bursa) 3. Tendon of FCR & its synovial sheath ( in a special compartment) 4. Median nerve FLEXOR RETINACULUM • FUNCTION: It keeps the flexor tendons in position during movement of wrist joint • CLINICAL ANATOMY (CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME): Compression of median nerve under the flexor retinaculum DEEP FASCIA Fibrous flexor sheaths • Definition • Attachments • Function FIBROUS FLEXOR SHEATH • DEFINITION: It is a thickening of deep fascia in front of the fingers • ATTACHMENTS: 1. Proximal: to the slips of palmar aponeurosis 2. Distal: to the base of distal phalanx 3. On either side: to the side of phalanx • FUNCTION: It holds the long flexor tendons during flexion of the fingers INTRINSIC MUSCLES • LATERAL GROUP: FOUR THENAR MUSCLES • MEDIAL GROUP: THREE HYPOTHENAR MUSCLES PALMARIS BREVIS • CENTRAL GROUP: FOUR LUMBRICALS FOUR PALMAR INTEROSSEI FOUR DORSAL INTEROSSEI • ALL MUSCLES ARE SUPPLIED BY C8 & T1 SPINAL SEGMENTS THROUGH MEDIAN & ULNAR NERVES INTRINSIC MUSCLES THENAR MUSCLES THENAR MUSCLES 1. Abductor pollicis brevis 2. Flexor pollicis brevis 3. Opponens pollicis 4. Adductor pollicis N.B.: • Muscles # 1, 2, 4 are inserted into the proximal phalanx of thumb: act on MP & CM joints of thumb • Muscle # 3 is inserted into 1st metacarpal bone: opposition of CM joint of thumb (abduction + flexion + medial rotation) HYPOTHENAR MUSCLES HYPOTHENAR MUSCLES • Abductor digiti minimi • Flexor digiti minimi • Opponens digiti minimi N.B.: • Muscles # 1, 2 are inserted into the proximal phalanx of little finger: act on MP joint of little finger • Muscle # 3 is inserted into 5th metacarpal bone: rotates 5th metacarpal bone LUMBRICALS 1. Origin: tendons of FDP 2. Insertion: tendons of ED 3. Action: Writing position (flexion of MP & extension of IP joints of medial 4 fingers INTEROSSEI • PALMAR INTEROSSEI 1.Origin: metacarpal bone 2.Insertion: proximal phalanx 3.Action: Adduction of fingers (PAD) • DORSAL INTEROSSEI 1.Origin: adjoining sides of 2 metacarpal bone 2.Insertion: proximal phalanx 3.Action: Abduction of fingers (DAB) PALMARIS BREVIS 1. Origin: Palmar aponeurosis 2. Insertion: skin of medial border of hand 3. Action: deepening the hollow of palm to get a firmer grip ARTERIAL ARCHES IN HAND • • 1. 2. 3. 4. SUPERFICIAL PALMAR ARCH DEEP PALMAR ARCH Formation Site Surface anatomy Branches SUPERFICIAL PALMAR ARCH • 1. 2. • • • • 1. 2. FORMATION: Direct continuation of ulnar artery (mainly) Superficial branch of radial artery SITE: between palmar aponeurosis & long flexor tendons SURFACE ANATOMY: level with the distal border of the fully extended thumb BRANCHES: digital branches to the medial three & half fingers N.B.: Radial artery gives 2 branches that supplies the lateral one & half fingers: Radialis indicis: supplies lateral side of index Princeps pollicis: supplies both sides of thumb DEEP PALMAR ARCH • 1. 2. • FORMATION: Direct continuation of radial artery (mainly) Deep branch of ulnar artery SITE: between long flexor tendons & metacarpal bones • SURFACE ANATOMY: lies one inch proximal to superficial palmar arch • BRANCHES: 1. Branches sharing in anastomosis around wrist joint 2. Articular & muscular branches ULNAR NERVE IN THE HAND • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. • MUSCULAR BRANCHES: Palmaris brevis Adductor pollicis Hypothenar muscles Interossei Medial two lumbricals CUTANEOUS BRANCHES: Palmar digital to medial 1 ½ fingers MEDIAN NERVE IN THE HAND • 1. 2. 3. 4. • MUSCULAR BRANCHES: Abductor pollicis brevis Flexor pollicis brevis Opponens pollicis Lateral two lumbricals CUTANEOUS BRANCHES: Palmar digital to lateral 3 ½ fingers



























![Forearm and Hand [PPT]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000953850_1-fbf4b9850ae3ed83f7b082693c84a32e-150x150.png)