* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Right Triangle Geometry
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Metric tensor wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
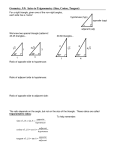
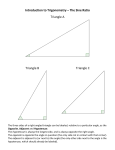
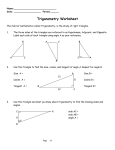
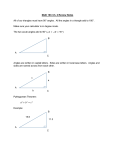
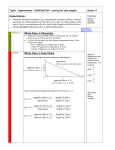
Right Triangle Geometry “for physics students” Right Triangles • Right triangles are triangles in which one of the interior angles is 90o – A 90o angle is called a right angle. – The other two interior angles are complementary, i.e. their sum equals 90o. Anatomy of a Right Triangle • The side opposite of the right angle is called the hypotenuse. • The sides adjacent to the right angle are the legs. – c – hypotenuse – a & b – the other two legs The Pythagorean theorem • The Pythagorean Theorem states that: – In a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. – Using the Pythagorean Theorem, if the lengths of any two of the sides of a right triangle are known and it is known which side is the hypotenuse, then the length of the third side can be determined from the formula. Sine, Cosine & Tangent Functions • Sine, Cosine, and Tangent are all functions of an angle, which are useful in right triangle calculations. • For an angle designated as θ, the sine function is abbreviated as sin θ, the cosine function is abbreviated as cos θ, and the tangent function is abbreviated as tan θ. • In a right triangle, – the sine of a non-right angle equals the length of the leg opposite that angle divided by the length of the hypotenuse. – the cosine of a non-right angle equals the length of the leg adjacent to it divided by the length of the hypotenuse. – the tangent of a non-right angle equals the length of the leg opposite that angle divided by the length of the leg adjacent to it. SOH CAH TOA S – sine O – opposite H – hypotenuse C – cosine A – adjacent H – hypotenuse T – tangent O – opposite A – adjacent •Neat website Now you try. 1. What would a be if b were 34 N and c were 60 N? 2. What would b be if ϴ2 were 30° and a was 50 N? 3. If ϴ1 was 55° and c was 100 N what would a and b be?