* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download transparent 18.3 Behavior of Light
Bicycle lighting wikipedia , lookup
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Doctor Light (Kimiyo Hoshi) wikipedia , lookup
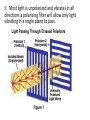
18.3 Behavior of Light • Light and Materials – How light behaves when it hits a surface depends on the material it is made of • Materials can be Transparent - A material that transmits (allows through) light unaffected Translucent - A material that transmits light but scatters it into different directions Opaque – A material that does not transmit any light. Light is either absorbed, reflected, or both. The jelly fish is Transulcent These bananas are opaque This cell phone is transparent 18.3 Behavior of Light Interactions of Light – When light strikes a new medium there are three possible outcomes I Reflection II Absorption III Transmission Reflection - Light bouncing off an object to form an image. We depend on reflection to see. Regular reflection – light bounces off an object in the same direction to from a reflected image Diffuse reflection – light bounces off an object in different directions no reflected image formed Regular and Diffuse Reflection Images are formed by Regular reflection NOTE: Absorption of light produces the colors we see. Only the color reflected reaches our eyes When light is transmitted there are three possible outcomes I Refraction – Bending of light as it enters a new medium (Chapter 17) II Polarization – Occurs when light waves vibrate in only one plane. III Scattering – Light waves are bent as it diffracts around tiny particles in the atmosphere I. Refraction of light causes this affect Remember the light changes speed as it enters the new medium causing it to change direction A mirage is caused by diffraction of light through different layers of heated air http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_M0FcpQ Wh5E II. Most light is unpolarized and vibrates in all directions a polarizing filter will allow only light vibrating in a single plane to pass. Reflected light (glare) is often polarized and is blocked by polarized glasses The sky looks blue because of scattering and sunsets Look red. This sunset is caused by scattering. Only the longer wave lengths get through.