* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth`s Revolution and seasons File
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
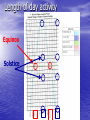
Warm up: Monday Week of March 28-April 1 4 friends were talking about why we have longer periods of daylight in the summer than in the winter. This is what they said: Will: “It’s because one side of Earth faces the Sun and the other side faces away.” Ava: “It’s because the Sun gives off more heat in the summer than in winter.” Rick: “It’s because the Northern hemisphere is closer to the sun in summer than in the winter.” Susan: “It’s because Earth’s tilt causes the angle of sunlight hitting Earth to change.” Which friend do you most agree with? Describe and explain your thinking about why we have longer periods of daylight in the summer than in the winter. Earth’s Revolution/Seasons Earth orbiting/going all the way around the sun Drawing 1 revolution = 1 year or 365 days, or 12 months revolves/turns counterclockwise/to the left Tilt stays towards North star the whole revolution Earth’s Revolution Earth’s tilt causes the sun’s rays to hit Earth at different angles causing seasons Questions 1. Why does the Earth experience seasons? 2. What does “revolve” mean? 3. How long does it take for the Earth to revolve around the sun one time? 4. What direction does the Earth revolve? 5. What is a limitation of the model? Less daytime Direct vs Indirect Rays of the sun More daytime Northern winter v Indirect Northern summer Most Direct Most Direct Indirect Southern summer Southern Winter Length of day activity Equinox Solstice The Four Seasons: The Effect of the Tilt Solstices and Equinoxes Equinox: The two days that the Earth is not tilted towards or away from the sun (autumnal/fall and vernal/spring). It is the days where daylight and nighttime are about equal (12hr day, 12 hr night). Sun is directly on the Equator. Solstice: The days when Earth is most tilted towards or away from the Sun (summer and winter). It is the longest and shortest days of the year. Spring Equinox ~ March 21 Summer Solstice ~ June 21 Fall Equinox ~ September 22 Winter Solstice ~ December 21 The dates on which these occur mark the change from one season to the next. Solstices and Equinoxes North star (Polaris) Seasons Diagram Create a diagram in your journal of how the sun revolves around the Sun, labeling the seasons for both Northern and Southern Hemispheres. See the Season’s Diagram Activity handout for all of the instructions