* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download simple machines.
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
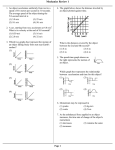
Simple Machines & Mechanical Advantage Simple Machines • A machine is any device that transmits or modifies force, usually by changing the force applied to an object. • All machines are combinations or modifications of six fundamental types of machines, called simple machines. • These six simple machines are the lever, pulley, inclined plane, wheel and axle, wedge, and screw. Mechanical Advantage • Because the purpose of a simple machine is to change the direction or magnitude of an input force, a useful way of characterizing a simple machine is to compare the output and input force. • This ratio is called mechanical advantage. • If friction is disregarded, mechanical advantage can also be expressed in terms of input and output distance. Fout din MA Fin dout The diagrams show two examples of a trunk being loaded onto a truck. • In the first example, a force (F1) of 360 N moves the trunk through a distance (d1) of 1.0 m. This requires 360 N•m of work. (Work = Fxd) • In the second example, a lesser force (F2) of only 120 N would be needed (ignoring friction), but the trunk must be pushed a greater distance (d2) of 3.0 m. This also requires 360 N•m of work. A machine uses an input force of 200 newtons to produce an output force of 800 newtons. What is the mechanical advantage of this machine? Fout = 800 N Fin = 200 N MA = 800N/200N = 4 Another machine uses an input force of 200 newtons to produce an output force of 80 newtons. What is the mechanical advantage of this machine? Fout = 80 N Fin = 200 N MA = 80N/200N = 0.4 A machine is required to produce an output force of 600 newtons. If the machine has a mechanical advantage of 6, what input force must be applied to the machine? Fout = 600 N MA = 6 Fin = Fout/MA = 600N/6 = 100N An input force of 35 newtons is applied to a machine with a mechanical advantage of 0.75. What is the size of the load this machine could lift (how large is the output force)? Fin = 35 N MA = 0.75 Fout = MA x Fin = (0.75)(35N) = 26.25N A person lifts a 950 N box by pushing it up an incline. If the person exerts a force of 350 N along the incline, what is the mechanical advantage of the incline? What is the mechanical advantage of a lever that allows Jorge to lift a 24-newton box with a force of 4 newtons? A machine with a mechanical advantage of 2.5 requires an input force of 120 newtons. What output force is produced by this machine? Levers Example of a lever A lever can be made by balancing a board on a log. Pushing down on one end of the board lifts a load on the other end of the board. The downward force you apply is the input force. The upward force the board exerts on the load is the output force. Parts of the lever All levers include a stiff structure that rotates around a fixed point called the fulcrum. The side of the lever where the input force is applied is called the input arm. The output arm is the end of the lever that applies the output force. Levers are useful because you can arrange the fulcrum and the input and output arms to make almost any mechanical advantage you need. A construction worker uses a board and log as a lever to lift a heavy rock. If the input arm is 3 meters long and the output arm is 0.75 meters long, what is the mechanical advantage of the lever? Lin = 3 m Lout = 0.75 m MA = 3m/0.75m = 4 A child’s toy rake is held so that its output arm is 0.75 meters. If the mechanical advantage is 0.33, what is the input arm length? A lever has a mechanical advantage of 4. Its input arm is 60 centimeters long. How long is its output arm? Lin = 60 cm MA = 4 Lout = Lin / MA = 60cm/4 = 15 cm A lever used to lift a heavy box has an input arm of 4 meters and an output arm of 0.8 meters. What is the mechanical advantage of the lever? What is the mechanical advantage of a lever that has an input arm of 3 meters and an output arm of 2 meters? Sometimes levers are used to multiply distance. For a broom, your upper hand is the fulcrum and your lower hand provides the input force: Notice the input arm is shorter than the output arm. The mechanical advantage of this broom is: Ramps A ramp is another type of simple machine. Using a ramp allows you to push a heavy car to a higher location with less force than is needed to lift the car straight up. Ramps reduce the input force needed by increasing the distance over which the input force acts. For example, suppose a 10-meter ramp is used to lift a car one meter. The output work is work done against gravity. If the weight of the car is 500 newtons, then the output work is 500 joules Mechanical advantage of a ramp The input work is the input force multiplied by the length of the ramp (10 meters). If you set the input work equal to the output work, you quickly find that the input force is 50 newtons (Fd = F × 10 m = 500 J). The input force is one-tenth of the output force. For a frictionless ramp, the mechanical advantage is the length of the ramp divided by the height. A 5-meter ramp lifts objects to a height of 0.75 meters. What is the mechanical advantage of the ramp? A ramp with a mechanical advantage of 6 is used to move a 36-newton load. What input force is needed to push the load up the ramp? MA Solutions 1. 5 2. 1.5 3. 0.5 meters 4. 4.8 meters 5. 0.4 6. 0.8 meters 7. 0.25 meters 8. 6.7 9. 2 meters 10.12 meters 11. 2.4 12. 6 newtons 13. 560 newtons Honors Mixed MA Worksheet 1. 26 N 2. 3 3. 150 N 4. 1.5 5. 4.8 meters 6. 0.4 7. 0.8 meters 8. 0.25 meters 9. 2.4 10. 6 N 11. 560 N 12. 4 meters Mixed MA Worksheet 1. 26 N 2. 3 3. 4.8 meters 4. 0.4 5. 0.8 meters 6. 0.25 meters 7. 2.4 8. 6 N 9. 560 N 10. 4 meters