* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Road to Revolution
Roanoke Colony wikipedia , lookup
Jamestown supply missions wikipedia , lookup
Colonial South and the Chesapeake wikipedia , lookup
English overseas possessions in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms wikipedia , lookup
Province of New York wikipedia , lookup
Peace of Paris (1783) wikipedia , lookup
Queen Anne's War wikipedia , lookup
Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
Stamp Act 1765 wikipedia , lookup
Cuisine of the Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
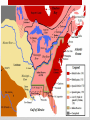
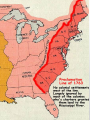
The Road to Revolution A • http://www.wordle.net/show/wrdl/4279615/Road_to_Rev olution Toward Independence Navigation Acts of 1660: Empire is both a political and economic construct. The first British empire was built upon the concept of mercantilism—that the economic interests of the nation have priority over those of all other groups and areas and thus the periphery, or provinces, must profit the mother country. Acting upon such a doctrine, the British government enacted a series of Navigation Acts over the course of the second half of the seventeenth century. The first was passed by the Parliament of Oliver Cromwell's Commonwealth in 1651. When the monarchy was restored in 1660, the new Parliament, to ensure the legality as well as continuation of the mercantile system that had been established, renewed the earlier legislation and added to it. The Navigation Act of 1660 further defined how trade among the mother country, colonies, and foreign lands was to be conducted. Virginia House of Burgesses: The first law making body in America. http://www.socialstudiesforkids.com/articles/ushistory/houseofburgesses.htm What events strained the colonists’ relationship with England? • By 1750, the America colonies were bursting with growth. Population of the colonies had grown from 50,000 to more than a million people. • During this time, Americans had learned to govern themselves. • Each colony elected its own assembly. • Like the British Parliament, the assemblies had the power to pass laws and create taxes. • Each assembly also decided how the colony’s tax money should be spent. • Americans had more freedom to run their own affairs than ordinary people in any country in Europe. Prior to 1763……………. Escalating Tension Between England and the Colonies • As the colonies grew, settlers began to dream of moving across the Appalachian Mountains and into the Ohio Valley (the region between the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers). Both Britain and France claimed this land. • In 1754, the French made good on their claim by building a fort where the city of Pittsburgh stands today. They called it Fort Duquesne. • News of the fort alarmed the governor of Virginia. He ordered a small force of Virginia militia to drive the French out of the Ohio Valley. • To head the militia, the governor chose a 22 year old volunteer named George Washington. Conflicts in the Ohio Valley • Today, Americans remember George Washington as a great Patriot, a military hero, and the first president of the United States. • In 1754, however, he was just an ambitious young man with no land or money. • Washington believed that his best chance of getting ahead was to become an officer in the British army. • There was one problem with his plan. Most British officers believed that colonists made lousy soldiers. • The expedition into the Ohio Valley gave Washington a chance to prove them wrong. George Washington • Near Fort Duquesne, Washington came across a French scouting party. He ordered his men to open fire. It was an easy victory. “I heard the bullets whistle,” he wrote afterward. “And, believe me, there is something charming in the sound.” • Washington’s whistling bullets were the first shots in a conflict known as the French and Indian War. • This war was part of a long struggle between France and Britain for territory and power. • Since many Native Americans fought with France in this latest conflict, the colonists called it the French and Indian War. • In 1755, Britain sent 1,400 British soldiers to Virginia to finish the job that Washington had begun. They were led by a bumbling general named Edward Braddock. The soldiers job was to clear the French out of the Ohio Valley. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=keewRkg46MA The French & Indian War • The British army’s march into the Ohio Valley was a disaster. • The troops bright red made them perfect targets for French sharp shooters and their Indian allies. • Two Thirds of the soldiers were killed. • Washington himself narrowly escaped death. “I had four bullets through my coat and two horses shot under me,” he wrote in his journal. • Showing great courage, Washington led the survivor’s back to Virginia. There, he was greeted as a hero. • The French and Indian War raged for seven long years. Seven long years • The turning point came in 1759, when British troops captured Canada. • In 1763, Britain and France signed a peace treaty ending the war. • In this treaty, France ceded, or gave, Canada to Great Britain. • Americans were thrilled with this victory. Great Britain now controlled a vastly expanded American empire. • Never before had the colonists felt so proud of being British, and never before had the future of the colonies looked so bright. The turning point in the war •North America 1755 - 1763 •What makes wars important, besides the human suffering, is how they change things. •The French and Indian War changed quite a bit for the colonists. It expanded the 13 Colonies, and therefore England's, grip on North America. It also was expensive and meant that the colonists had to pay more to the Crown (England) to cover the costs of that war. •Who was involved? It was the British, its loyal Colonists and some native tribes, versus the French and some native tribes. The French and Indian War Summary • Changes that were taking place in Britain soon clouded the colonists’ bright future. • A new king, George III, had been crowned in 1760. He was not a bright man. One historian wrote that “he was very stupid, really stupid.” He was also proud and stubborn. Worse yet, he was determined to be a “take-charge” kind of ruler, especially in the colonies. • Unfortunately, the people George III chose to help him were not much brighter than he was, and they knew very little about conditions in America. • Before long, they were taking actions that enraged the colonists. Early British Actions Let’s ponder & think…….. • The British government faced a number of problems after the French and Indian War. One was how to keep colonists and Native Americans from killing each other as settlers pushed westward. • George III solution: Draw a line down the crest of the Appalachian Mountains. Then tell settlers to stay east of that line and Indians to stay west of it. • This solution ordered by the King became known as the Proclamation of 1763. The Proclamation of 1763 • To Americans, the King’s order suggested tyranny, or the unjust use of government power. • They argued that the lands east of the Appalachians were already mostly settled. The only place that farmers could find new land was west of the mountains. • In addition, the proclamation seemed to come much too late. Settlers were already crossing the mountains. Tyranny or not Tyranny? On April 5, 1764, Parliament passed a modified version of the Sugar and Molasses Act (1733), which was about to expire. Under the Molasses Act colonial merchants had been required to pay a tax of six pence per gallon on the importation of foreign molasses. But because of corruption, they mostly evaded the taxes and undercut the intention of the tax — that the English product would be cheaper than that from the French West Indies. This hurt the British West Indies market in molasses and sugar and the market for rum, which the colonies had been producing in quantity with the cheaper French molasses. The First Lord of the Treasury, and Chancellor of the Exchequer Lord Grenville was trying to bring the colonies in line with regard to payment of taxes. He had beefed up the Navy presence and instructed them to become more active in customs enforcement. Parliament decided it would be wise to make a few adjustments to the trade regulations. The Sugar Act reduced the rate of tax on molasses from six pence to three pence per gallon, while Grenville took measures that the duty be strictly enforced. The act also listed more foreign goods to be taxed including sugar, certain wines, coffee, pimiento, cambric and printed calico, and further, regulated the export of lumber and iron. The enforced tax on molasses caused the almost immediate decline in the rum industry in the colonies. The combined effect of the new duties was to sharply reduce the trade with Madeira, the Azores, the Canary Islands, and the French West Indies (Guadelupe, Martinique and Santo Domingo (now Haiti)), all important destination ports for lumber, flour, cheese, and assorted farm products. The situation disrupted the colonial economy by reducing the markets to which the colonies could sell, and the amount of currency available to them for the purchase of British manufactured goods. This act, and the Currency Act, set the stage for the revolt at the imposition of the Stamp Act. The Sugar Act • The British government had other problems besides keeping colonists and Native Americans from killing each other. One was how to pay off the large debt left over from the French and Indian War. • The solution seemed obvious to Prime Minister George Grenville, the leader of the British government. • People in Britain were already paying taxes on everything from windows to salt. • In contrast, Americans were probably the most lightly taxed people in the British Empire. • It was time, said Grenville, for the colonists to pay their fair share of the cost of protecting them. It’s Time to Pay Your Fair Share • In 1765, Grenville proposed a new act, or law, called The Stamp Act. • This law required colonists to buy a stamp for every piece of paper they used. • Newspapers had to be printed on stamped paper. • Wills, licenses, and even playing cards had to have stamps. • Once again, the colonists sensed tyranny. Part I http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TYYwW7_zuYI&feature=related Part II http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=R3JurSo01EQ Part III http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kNQOiqx8jjg&feature=related The Stamp Act • It wasn’t just the idea of higher taxes that upset the colonists. • They were willing to pay taxes passed by their own assemblies, where their representatives could vote on them. But the colonists had no representatives in Parliament. • For this reason, they argued, Parliament had no right to tax them. • They saw the Stamp Act as a violation of their rights as British subjects. “No taxation without representation!” they cried. What’s the big deal? http://historymatters.gmu.edu/d/6764/ Colonies Reduced • Some colonists protested the Stamp Act by sending messages to parliament. • Loyalists simply refused to buy stamps. • Patriots, however, took more violent action. • Mobs calling themselves “Sons of Liberty” attacked tax collectors’ homes. • Protestors in Connecticut even started to bury one tax collector alive. Only when he heard dirt being shoveled onto his coffin did the terrified tax collector agree to resign from his post. • After months of protest, Parliament repealed, or canceled, the Stamp Act. • Americans greeted the news with great celebration. Church bells rang, bands played, and everyone hoped the troubles with Britain were over. Drastic times call for drastic measures! • As anger over the Stamp Act began to fade, Americans noticed another law passed by Parliament in 1765. This was called the Quartering Act which ordered colonial assemblies to provide British troops with quarters, or housing. • The colonists were also told to furnish the soldiers with “candles, firing, bedding, cooking utensils, salt, vinegar, and……beer or cider.” The Quartering Act • Of course, providing for the soldiers cost money $$$$$. • New Jersey protested that the new law was “as much an Act for laying taxes” on the colonists as the Stamp Act. • New Yorkers asked why they should pay to keep troops in their colony. After all, they said, the soldiers just took up space and did nothing. • In 1767, the New York assembly decided not to vote any funds for “vinegar and liquor.” • The British government reacted by refusing to let the assembly meet until it agreed to obey the Quartering Act. • Once again, tempers began to rise on both sides of the Atlantic. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jKnN8Jg36kA The Colonists Response • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zNArfnsy_fM&NR=1 The Townshend Acts Events leading to War Signing Party