* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 Pillars of Islam
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Morality in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
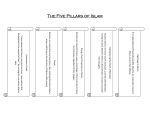
Islamic Religious Practices 5 Pillars of Islam • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The order for living righteously is apparent in the 5 Pillars Support one’s faith Are mentioned in the Qur’an Creed Prayer Charity to the poor Fasting Pilgrimage • Confession of faith – “There is no god but the God and Muhammad is his prophet” – The confession refers to two basic teachings of Islam: monotheism and the uniqueness of Muhammad as a prophet • This sentence makes a person a Muslim • It is the first sentence whispered into the ears of a newborn infant • It is recited daily in prayer 1. Creed • 5 times a day • Before dawn and at midday, mid-afternoon, sunset, and nighttime • Times for prayer are announced by a muezzin- from the minaret • Before prayer, Muslims perform a ritual purification with water – Washing the hands, arms, face, neck and feet – If water is unavailable, purification may be done with sand • Pray facing Mecca-mihrab • Passages from the Qur’an and other prayer formulas are recited from memory in Arabic – Accompanied by several bodily postures: standing, bowing, prostrating, and sitting 2. Prayer Prayer cont. • Friday is the day of public prayer – Friday prayers are directed by an Imam –leader of worship • The imam delivers a sermon as well – it used to be on Saturdays following the Jewish tradition but Muhammad received a revelation that public prayer on Friday was God’s will – Public prayer is performed at midday on Friday – Usually only men perform public prayer at a mosque • When women are allowed to pray with men at a mosque, they are assigned their own area, separated by a curtain or screen or located in an upstairs gallery – Women pray at home • The public day of rest is Sunday 3. Charity to the poor • Believers donate certain percentages of their total income, herds, and produce from fields each year to the poor – Muhammad was troubled by injustice, inequality, and poverty • The percentages vary depending on what is taxed – But are commonly about 2.5 percent • A good Muslim is expected to perform isolated acts of generosity and charity for the poor 4. Fasting • To fast means to abstain from food for a specified period of time • The purpose of fasting is to discipline oneself – To develop sympathy for the poor and hungry • Fasting is thought to be good for individual spiritual growth • Required during Ramadan – The 9th month of the Muslim calendar – Ramadan is the time during which Muhammad first received his revelations – From dawn until sundown – Avoid eating, drinking, smoking, sex • Exceptions are made with regard to food and drink for travelers, pregnant women and the sick- but they are expected to make up the days of fasting at a later time • During Ramadan, Muslims open extra soup kitchens • Ramadan = Lent= Yom Kippur 5. Pilgrimage • Pilgrimage is a religious journey by a believer to a sacred city or site • Pilgrimage to Mecca – At least once in a lifetime – Anyone who dies on the journey is considered a martyr and enters paradise – All sins are forgiven of those who make the journey – Pilgrimage to Mecca, or Hajj, was already a practice before Muhammad was born Pilgrimage: Kabah shrine • The pilgrimage to Mecca lasts for 15 days • Includes circling the Kabah – Kabah means cube – The Kabah is a black meteorite known as the Black Stone located in the Great Mosque of Mecca – It is covered with a black cloth, remade every year- edges are embroidered in gold with words from the Qur’an – The interior of the Kabah is empty and is entered only by caretakers – who clean the interior with rosewater – Pilgrims walk counterclockwise around the Kabah seven times – Pilgrims kiss or salute the Kabah Pilgrimage cont.: origins of the Black Stone • The meteorite was thought of as a special gift from God • It is believed that Abraham and even Adam venerated it • The angel Gabriel carried it to earth Pilgrimage: reenacting important events: recalling Hagar 1. After walking around the Kabah, pilgrims ritually recall Hagar • A long covered corridor connects two sacred hills • Between these hills Hagar is believed to have searched for water for her son Ishmael • Pilgrims walk speedily seven times along the corridor, reenacting Hagar’s thirsty search • They drink from the well of Zamzam in the mosque area, which is believed to be the well shown to Hagar by an angel Pilgrimage: reenacting important events: sacrifice of Ishmael • Pilgrims reenact important events in the life of Abraham 2. Muslims believe that Abraham was asked by God to sacrifice his son Ishmael – The near-sacrifice took place in Mecca – Abraham was divinely directed to substitute a ram for his son – Pilgrims sacrifice an animal – The slaughtered animals is cooked and eaten – After the sacrifice, the men’s heads are shaven, the women’s hair is cut, and all fingernails and toenails are trimmed to signify a new purified life Pilgrimage: reenacting important events: Day of Sacrifice 3. On the Day of Sacrifice, pilgrims go to Mina- a few miles outside Mecca • Here they throw seven small stones at three square pillars, a ritual that recalls how Abraham responded to a temptation: • when a demon tempted him to disobey God’s command to sacrifice his son, Abraham threw stones at the demon and drove it away • Many pilgrims visit Medina to honor the memory of Muhammad who is buried there Types of pilgrimage • Muslims distinguish between the “greater pilgrimage” and – Made only during the special month of pilgrimage • The “lesser pilgrimage” – Can be made at other times of year as well – A visit to Mecca and nearby holy sites • In the past, about 30,000 people visited Mecca each year • Now 2,000,000 make the journey Pilgrimage: clothing • Men have to wear a special clothing called the robe of Abraham – Consisting of two pieces of white, seamless cloth. – One piece is worn around the waist and lower body – The other covers the upper body and the left arm – The uniformity of clothing for males emphasizes their basic equality before God • women have no special clothing, but many dress in white – They do not veil their faces when they are participating in the pilgrimage