* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5.5 Inequalities Involving TWO Triangles
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Systolic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
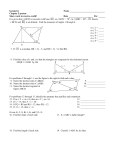
5.5 Inequalities Involving TWO Triangles What you’ll learn: 1. To apply the SAS Inequality 2. To apply the SSS Inequality Theorem 5.13 SAS Inequality/Hinge Theorem If 2 sides of a triangle are congruent to 2 sides of another triangle and the included angle in one triangle has a greater measure than the included angle in the other, then the 3rd side of the 1st triangle is longer than the 3rd side of the 2nd E triangle. B If AB=DE and AC=DF F and A>D, then A C D BC>EF Theorem 5.14 SSS Inequality if 2 sides of a triangle are congruent to 2 sides of another triangle and the 3rd side in one triangle is longer than the 3rd side in the other, then the angle between the pair of congruent sides in the 1st triangle is greater than the corresponding angle in the 2nd triangle. E A If AB=DE, AC=EF, and D B BC<EF, then A<B C F Write an inequality relating the given pair of angles or segment measures. 1. 15 20 D A 50 B 15 C P 2. 8 Q S 6 AB _______ CD 4 4 R mPQS ______ mRQS Write an inequality describe the possible values of x. 1. 3x-3<33 60 cm 36 cm 33 (3x-3) 60 cm 30 cm and 3x-3>0 3x<36 3x>3 x<12 x>1 1<x<12 (½x -6) 2. 30 52 30 12 28 ½x-6<52 and ½x-6>0 ½x<58 ½x>6 x<115 x>12 12<x<115 Given: CDAB, mACB+mBCD<mABC+mCBD AC=BD Prove: AB<CD 1. CDAB, mACB+mBCD<m ABC+mCBD AC=BD 2. BC=BC 3. ABC=BCD 4. mACB+mABC<m ABC+mCBD 5. mACB<mCBD 6. AB<CD A B 1. Given 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. C Reflexive Alt. int. angles substitution Subtraction SAS Inequality D Homework p. 271 10-20 all, 34-40 even, skip 38