* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download COLD WAR Battles and protests (1950s
Cuban Missile Crisis wikipedia , lookup
War in Vietnam (1954–59) wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
History of Egypt under Gamal Abdel Nasser wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1947–1953) wikipedia , lookup
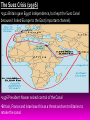
COLD WAR BATTLES AND PROTESTS (1950S-70S) The Korean War (1950-1953) •End of WWII Soviets took North Korea (Communist) and the USA took south Korea (capitalist/democratic)- both withdrew by 1947. •1950 Communist North Korea attacked the South (USA immediately came to the south’s aid). •U.N called for nations to help (only 16 provided aid, Canada being one of the biggest supporters) - 25,000 soldiers sent: 1000 wounded and 406 killed. •1953 a truce was made (Canadian peace-keepers stayed until 1955) The Suez Crisis (1956) •1922 Britain gave Egypt independence, but kept the Suez Canal because it linked Europe to the East (important channel). •1956 President Nasser seized control of the Canal •Britain, France and Israel saw this as a threat and sent militaries to retake the canal. •Soviets threatened to use atomic weapons if they did not withdraw (USA asked U.N to condemn Suez invasion) •Pearson won the Nobel Peace Prize for his successful proposal: - End all shooting - Create special UN special peace-keeping force to monitor withdrawal of invaders (800 Canadian soldiers were sent) Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) •American spy planes photographed Soviet missile construction in communist Cuba (made North America an easier target for Russians). •US President Kennedy quickly made a naval blockade around Cuba to stop Soviets from delivering rockets and nuclear weapons. ---Canada recommended further investigating before blockading, however they were ignored. •The blockade caused Soviet ships to turn back, preventing a ‘spark’ for WWIII Vietnam War (1961-1973) •1957 Vietnam won its freedom from being a French colony in a battle against France. •North Vietnam (Vietcong) became communist and tried to overthrow the South Vietnamese government. •1961 USA increased military and economic aid to the South, 1965 USA began large-scale combat against the Vietcong. •1968, realizing Vietcong would not be defeated, President Nixon began negotiating peace and in 1973 a peace was made. •Canada was vocal in its opposition to this war (Pearson and Public) ---But Canada sold billions of dollars of weapons to US, despite opposition from public. •USA ‘Draft dodgers’ poured into Canada to avoid conscription Protesting War (Most popular in 1960s) Why protesting war was popular after WWII: -Following WW2 people were tired of generations of war. -There was a new generation following the war (the babyboomers), who, especially in their teenage years, were rebelling against their parent’s - With more young people staying in school longer (and going to college/university), more people were educated on issues and were free to protest government policies they did not agree with. - Televisions in every home also made the ‘horrors of war’ more visible to people. People saw firsthand from news reporters what was happening, and many did not like it. - The idea of peace was promoted, as freedom of speech was allowed.