* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPTX - Florida Institute of Technology
Minimum control speeds wikipedia , lookup
Reusable launch system wikipedia , lookup
Flight dynamics (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle wikipedia , lookup
Saturn (rocket family) wikipedia , lookup
Single-stage-to-orbit wikipedia , lookup
Woodward effect wikipedia , lookup
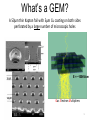
SpaceGEM A Novel Electric Ion Thruster for Space Vehicles Section 1: In-space systems Dr. S. Colafranceschi & Dr. M. Hohlmann Dept. of Physics & Space Sciences Florida Institute of Technology Introduction SPACE Exploration – the inspiration After Apollo-era we finally witness a renewed interest in a human space exploration program to the Moon and Mars. SPACE Exploration – where are we? Launch system technology still relies on powerful chemical rockets while interplanetary missions use fly-by, electrical engines in addition to chemical propulsion systems but no real scalable or modular engine for inter-planetary missions... This is our objective! “To confine our attention to terrestrial matters would be to limit the human spirit.” S. Hawking 2 Introduction http://dawn.jpl.nasa.gov/mission/ion_prop.asp Specific Impulse (s) Propulsion system: technologies and applications Thrust (N) 3 Introduction Propulsion system: technologies and applications Specific Impulse (s) High impulse – Low Thrust Orbital corrections Long-term space missions High Thrust – Low impulse Launch rockets + satellite in-orbit operation Thrust (N) 4 Introduction Propulsion system: technologies and applications (s)(s) Specific Total engine Impulse burn time High impulse – Low Thrust Orbital corrections Long-term space missions THIS WOULD BE GREAT BUT… Not possible, Limitation is given by chemistry/thermodynamics NO High Thrust – Low impulse Launch rockets + satellite in-orbit operation Thrust (N) 5 Introduction Propulsion system: technologies and applications (s)(s) Specific Total engineImpulse burn time High impulse – Low Thrust Orbital corrections Long-term space missions THIS WOULD BE ALSO GREAT AND… possible! Although most of these engines are not easily scalable YES High Thrust – Low impulse Launch rockets + satellite in-orbit operation Thrust (N) 6 Introduction Propulsion system: technologies and applications (s)(s) Specific Total engineImpulse burn time High impulse – Low Thrust Orbital corrections Long-term space missions THIS WOULD BE ALSO GREAT AND… possible! Although most of these engines are not easily scalable YES High Thrust – Low impulse Launch rockets + satellite in-orbit operation Thrust (N) 7 SpaceGEM in a nutshell • What is a GEM? What is a SpaceGEM? • How does it work? • What is the origin of GEM technology? • SpaceGEM for Mars missions 8 What’s a GEM? A 50µm thin Kapton foil with 5µm Cu coating on both sides perforated by a large number of microscopic holes E = ~100kV/cm get better quality, e.g. GE1/1 TDR Gas Electron Multipliers 9 Electrical field What’s a SpaceGEM? Ions Discharge plasma volume Accelerated Ions ION BEA OBJECTIVE Development of a general-purpose electric thruster for station-keeping, orbit raising, or possibly primary propulsion Basic concept is the miniaturization of propellant-accelerating stage using millions of “nozzles” where a very intense electrical field can impart momentum on ions: • • • • • Much higher efficiency Less engine wear Cost-effective Modular Scalable Gas Propellant Injection Discharge plasma volume Thrust THRUST ION BEAM ION BEAM Exaust ION BEAM Stack of SpaceGEM SPACEGE Electrons injector !! GEM stack for charge M films neutralizer STACK 10 E x h a u s t Electrical field What’s a SpaceGEM? Ions Discharge plasma volume Accelerated Ions ION BEA OBJECTIVE Development of a general-purpose electric thruster for station-keeping, orbit raising, or possibly primary propulsion Electrical field lines Gas Propellant Injection Discharge plasma volume Thrust THRUST ION BEAM ION BEAM Exaust ION BEAM Stack of SpaceGEM SPACEGE Electrons injector !! GEM stack for charge M films neutralizer STACK 11 E x h a u s t The GEM case study What is the origin of GEM technology? GEM Detectors – Applications • Particle Detector (High Energy Physics) • Tomography • Cosmic ray stations GEM working principle Collection of the electrons released by radiation ionizing a gas, guiding them to a region with a large electric field and thereby initiating an electron avalanche. Operation in gas at atmosperic pressure and standard temperature. 1 12 The GEM case study SpaceGEM for Mars missions OBJECTIVE Development of a general purpose electric thruster for stationkeeping, orbit raising, or primary propulsion. Can a GEM be used as an active panel/wing to actively exploit the ion space concentration and/or the upper atmosphere of Mars? SpaceGEM wings It will perform similarly to an air-breathing engine without any onboard propellant. • Small wings: • Orbital correction • Artificial gravity • Large/flexible deployable wings • Primary propulsion • Orbit changing • Rendezvous Could a solar sail made from GEM foils act simultaneously as sail and ion engine? 13 The GEM case study Proposed Project OBJECTIVE – FIRST STEP Measure thrust produced by a small SpaceGEM prototype Basic setup: • Vacuum room P/SS (Mars Simulation Chamber?) • Plasma chamber • Trial small-sized HEP GEMs • Diagnostics (beam monitor devices/ micro-balance) Needed manpower (2 years: 1 post-doc & grad student) • Physics simulation • Setup installation • Data-taking • Data-analysis/interpretation • Data-extrapolation and further developments on full-scale prototypes if R&D on small-sized HEP GEMs is positive 14 The GEM case study BACKUP 15 The GEM case study What is the origin of GEM technology? GEM in High Energy Physics – working principle Collection of the electrons released by radiation ionizing a gas, guiding them to a region with a large electric field and thereby initiating an electron avalanche GEM in High Energy Physics – how they are made • 50 μm kapton foil sheet with 5 μm copper-coated sides perforated with (bi)conical holes is a hexagonal pattern (hole diameter 70 μm, pitch 140 μm) • Developed using PCB manufacturing techniques Industrial production of large areas (〜1m x 2m) GEM in High Energy Physics – performance • Electrical Field across holes ~100kV/cm • Excellent spatial and time resolution (~100 μm, 〜5 ns) • Efficiency 〜98% • High rate capability 〜105 Hz/cm2 • Typical Gas Gain > 104 • Radiation hardened Particle detector / tomography timing measur….1 High rate expeirment