* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download One of the best things you can do to study is to go
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Contour line wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
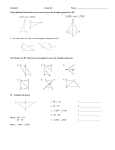
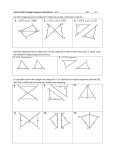
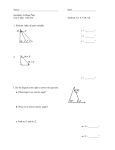
Geometry Topics for Final Exam ***You are expected to know all vocabulary, postulates, theorems, formulas and definitions gone over in class for all lessons*** One of the best things you can do to study is to go through all of your old homework assignments and reviewing problems you don’t understand, using your textbook for help! Chapter 1: Essentials of Geometry 1.1: Identify Points, Lines, and Planes -Undefined terms -Name points, lines, planes, segments, rays, opposite rays 1.2: Use Segments and Congruence -Postulate 2 1.3: Use Midpoint and Distance Formulas -Use midpoint and distance formulas -Use algebra with segment lengths 1.4: Classify Angles -Naming and classifying angles -Postulate 4 -Find angle measures using algebra and identify congruent angles 1.5: Angle Pair Relationships -Identify and find special angle pairs (complementary, vertical, etc…) 1.6: Classify Polygons -Identify and classify polygons Chapter 2: Reasoning and Proof 2.2: Analyze Conditional Statements -Write statements in if-then form -Converse 2.4: Use Postulate and Diagrams -Postulates 5-11 -Identify postulates from a diagram 2.5: Reason Using Properties from Algebra -Using properties of algebra 2.6: Prove Statements about Segments and Angles -Two-column proofs (fill in blank only) -Theorem 2.1 and 2.2 2.7: Prove Angle Pair Relationships -Theorems 2.3 – 2.6 -Postulate 12 Chapter 3: Parallel and Perpendicular Lines 3.1: Identify Pairs of Lines and Angles -Postulate 13 and 14 -Angles formed by transversals 3.2: Use Parallel Lines and Transversals -Postulate 15 -Theorems 3.1 – 3.3 3.3: Prove Lines are Parallel -Postulate 16 -Theorems 3.4 – 3.6 3.4: Find and Use Slopes of Lines -Slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines (postulate 17 and 18) 3.5: Write and Graph Equations of Lines -Write equations of parallel and perpendicular lines -Slope-intercept form -Standard form (finding intercepts) 3.6: Prove Theorems about Perpendicular Lines -Theorem 3.8 – 3.12 Chapter 4: Congruent Triangles 4.1: Apply Triangle Sum Properties -Classify triangles by sides and angles -Theorem 4.1 and 4.2 4.2: Apply Congruence and Triangles -Congruent figures -Congruence statements and congruent parts -Theorem 4.3 and 4.4 4.3: Prove Triangles Congruent by SSS -Postulate 19 4.4: Prove Triangles Congruent by SAS and HL -Postulate 20 -Theorem 4.5 4.5: Prove Triangles Congruent by ASA and AAS -Postulate 21 -Theorem 4.6 4.7: Use Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles -Theorem 4.7 and 4.8 4.8: Perform Congruence Transformations -Translations, Reflections, Rotations -Notation for a Translation