* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Knight_ch29
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
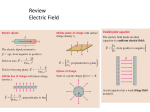
Chapter 29 The positive charge is the end view of a positively charged glass rod. A negatively charged particle moves in a circular arc around the glass rod. Is the work done on the charged particle by the rod’s electric field positive, negative or zero? 1. Positive 2. Negative 3. Zero The positive charge is the end view of a positively charged glass rod. A negatively charged particle moves in a circular arc around the glass rod. Is the work done on the charged particle by the rod’s electric field positive, negative or zero? 1. Positive 2. Negative 3. Zero Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the potential energies Ua to Ud of these four pairs of charges. Each + symbol represents the same amount of charge. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ua = Ub > Uc = Ud Ua = Uc > Ub = Ud Ub = Ud > Ua = Uc Ud > Ub = Uc > Ua Ud > Uc > Ub > Ua Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the potential energies Ua to Ud of these four pairs of charges. Each + symbol represents the same amount of charge. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ua = Ub > Uc = Ud Ua = Uc > Ub = Ud Ub = Ud > Ua = Uc Ud > Ub = Uc > Ua Ud > Uc > Ub > Ua A proton is released from rest at point B, where the potential is 0 V. Afterward, the proton 1. moves toward A with an increasing speed. 2. moves toward A with a steady speed. 3. remains at rest at B. 4. moves toward C with a steady speed. 5. moves toward C with an increasing speed. A proton is released from rest at point B, where the potential is 0 V. Afterward, the proton 1. moves toward A with an increasing speed. 2. moves toward A with a steady speed. 3. remains at rest at B. 4. moves toward C with a steady speed. 5. moves toward C with an increasing speed. Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the potentials Va to Ve at the points a to e. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Va = Vb = Vc = Vd = Ve Va = Vb > Vc > Vd = Ve Vd = Ve > Vc > Va = Vb Vb = Vc = Ve > Va = Vd Va = Vb = Vd = Ve > Vc Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the potentials Va to Ve at the points a to e. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Va = Vb = Vc = Vd = Ve Va = Vb > Vc > Vd = Ve Vd = Ve > Vc > Va = Vb Vb = Vc = Ve > Va = Vd Va = Vb = Vd = Ve > Vc Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the potential differences ∆V12, ∆V13, and ∆V23 between points 1 and 2, points 1 and 3, and points 2 and 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. ∆V12 > ∆V13 = ∆V23 ∆V13 > ∆V12 > ∆V23 ∆V13 > ∆V23 > ∆V12 ∆V13 = ∆V23 > ∆V12 ∆V23 > ∆V12 > ∆V13 Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the potential differences ∆V12, ∆V13, and ∆V23 between points 1 and 2, points 1 and 3, and points 2 and 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. ∆V12 > ∆V13 = ∆V23 ∆V13 > ∆V12 > ∆V23 ∆V13 > ∆V23 > ∆V12 ∆V13 = ∆V23 > ∆V12 ∆V23 > ∆V12 > ∆V13 Chapter 29 Reading Quiz What are the units of potential difference? 1. Amperes 2. Potentiometers 3. Farads 4. Volts 5. Henrys What are the units of potential difference? 1. Amperes 2. Potentiometers 3. Farads 4. Volts 5. Henrys New units of the electric field were introduced in this chapter. They are: 1. V/C. 2. N/C. 3. V/m. 4. J/m2. 5. W/m. New units of the electric field were introduced in this chapter. They are: 1. V/C. 2. N/C. 3. V/m. 4. J/m2. 5. W/m. The electric potential inside a capacitor 1. is constant. 2. increases linearly from the negative to the positive plate. 3. decreases linearly from the negative to the positive plate. 4. decreases inversely with distance from the negative plate. 5. decreases inversely with the square of the distance from the negative plate. The electric potential inside a capacitor 1. is constant. 2. increases linearly from the negative to the positive plate. 3. decreases linearly from the negative to the positive plate. 4. decreases inversely with distance from the negative plate. 5. decreases inversely with the square of the distance from the negative plate.