* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 state of matter particle motion and heat transfer
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
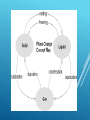
WARM UP 8/31 Identify each as a solid liquid or gas. State which one has the highest average energy and temperature level. WARM UP 8/31 Identify each as a solid liquid or gas. State which one has the highest average energy and temperature level. STATES OF MATTER Solid Liquid Gas And there is a fourth one. STATES OF MATTER Write down all observations during the dry ice demo. Sublimation Use the hand out to complete the simulation you see taking place. STATES OF MATTER SIMULATOR WARM UP 9/1 1.)Which state of matter has no definite shape but has a definite volume? The Four States of Matter Solid Liquid Gas Plasma STATES OF MATTER Based upon particle arrangement Based upon energy of particles Based upon distance between particles STATES OF MATTER Matter is made up of particles which are in continual random motion. KINETIC THEORY OF MATTER •Particles of solids are tightly packed, vibrating about a fixed position. •Solids have a definite shape and a definite volume. STATES OF MATTER SOLIDS Heat STATES OF MATTER LIQUID Particles of liquids are tightly packed, but are far enough apart to slide over one another. Liquids have an indefinite shape and a definite volume. Heat STATES OF MATTER GAS Particles of gases are very far apart and move freely. Gases have an indefinite shape and an indefinite volume. Heat Description of Phase Change Solid to liquid Term for Phase Change Melting Liquid to Freezing solid PHASE CHANGES Heat Movement During Phase Change Heat goes into the solid as it melts. Heat leaves the liquid as it freezes. Description of Phase Change Liquid to gas Term for Phase Change Vaporization, which includes Heat goes into the boiling and liquid as it vaporizes. evaporation Gas to liquid Condensation Solid to gas Heat Movement During Phase Change Sublimation PHASE CHANGES Heat leaves the gas as it condenses. Heat goes into the solid as it sublimates. BUT WHAT HAPPENS IF YOU RAISE THE TEMPERATURE TO SUPER-HIGH LEVELS… BETWEEN 1000°C AND 1,000,000,000°C ? Will everything just be a gas? STATES OF MATTER PLASMA A plasma is an ionized gas. A plasma is a very good conductor of electricity and is affected by magnetic fields. Plasmas, like gases have an indefinite shape and an indefinite volume. • Plasma is a common state of matter STATES OF MATTER SOLID Tightly packed, in a regular pattern Vibrate, but do not move from place to place LIQUID Close together with no regular arrangement. Vibrate, move about, and slide past each other GAS Well separated with no regular arrangement. Vibrate and move freely at high speeds PLASMA Has no definite volume or shape and is composed of electrical charged particles SOME PLACES WHERE PLASMAS ARE FOUND… 1. Flames 2. Lightning 3. Aurora (Northern Lights) The Sun is an example of a star in its plasma state COLD PLASMA PEN 2 minutes: Study notes 2 minutes: Record any information you can remember without notes 2 minutes: Share with one other student. Add his/her knowledge to your list. 2 minutes: Leave your buddy. Compare with another student. Receive a point for each fact that you have that the other student doesn’t have. BOGGLE WARM UP 9/2 1.) Which state of matter has a definite shape and has a definite volume? 2.) Draw a picture of what gas molecules look like in a beaker. LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MATTER The law of conservation of mass indicates that mass cannot be created nor destroyed only transformed into different matter. This means the total mass of reactants in a chemical reaction will equal the total mass of the products. If a gas is produced during a reaction, which mass is often forgotten when calculating the final mass because we are unable to see the gas. LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MATTER LAB Material Managers please come up and grab a lab hand out for everyone at your group. Everyone needs to quietly read the directions of the lab if you fail to follow the lab procedure you will be dismissed from lab and will be doing book work. Alternative assignment: Read pgs. 64-78 complete all sections reviews LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MATTER LAB WARM UP 9/6 1.) Which state of matter has an indefinite shape and has a indefinite volume? 2.)What is sublimation. WARM UP Why is it very dangerous to leave a child or animal in a locked car with the window closed in bright sunlight? WORK SESSION Go to pages 74-79 to complete the guided notes on phase changes. You can also use your notes to help you. WORK SESSION Be the teacher: present three key ideas you think everyone should have learned. We learned what? Students write open ended questions on a half sheet of paper. CLOSING Two students are selected to come forward, The first students draws a questions card and posed the question to the class. After the class discusses the question and answers with their partner - the second student draws a student name card to respond to the questions. WARM UP Draw and label the different parts of the atom. WARM UP Draw and label the different parts of the atom. THERMAL ENERGY AND HEAT TRANSFER Take out your science notebooks and start to record your notes on the next available odd page. THERMAL ENERGY The sum of ALL of the energy possessed by ALL of the particles in a substance Volume affects thermal energy (the bigger the object the more thermal energy it has) Temperature affects thermal energy: the higher the temp, the more thermal energy ENERGY AND CHANGING STATES OF MATTER Adding energy causes particles to increase in speed, increase their spacing resulting in higher temp Removing energy causes particles to decrease in speed, decreasing their spacing resulting in lower temp Boiling and condensation points are the same temp…(100°C/ 212°F for H2O) ENERGY AND CHANGING STATES OF MATTER Melting & freezing points are the same temp…0°C/ 32°F (H2O) Sublimation occurs when the surface of a solid gains enough thermal energy to become a gas, skipping the liquid phase TEMPERATURE AND HEAT Temperature is the AVERAGE kinetic energy ( energy of motion) of the particle sin a substances Temp is not affected by volume (a giant piece of ice will have the same temp as a small piece of ice) Change in thermal energy does not affect temperature TEMPERATURE AND HEAT Heat is the transfer or flow of thermal energy From higher temp to lower temp Heat is transferred 3 ways Conduction is by direct particle contact. Particle collisions TEMPERATURE AND HEAT Convection results from unequal heating in a liquid or a gas, where the warmer substance is less dense b/c its particles are further apart. They rise as the cooler substance is denser b/c its particles are closer together, which causes them to sink. TEMPERATURE AND HEAT Radiation requires no medium (that’s why the Sun’s heat energy can travel through the empty space/vacuum of outer space). There are no collisions between particles. The energy excites the particles of the substance it strikes TWO MINUTE TALK Procedure: 1. Group students into pairs. 2. Inform students that they will each be talking about topic X for two minutes. They will need to select which student will begin first. An easy way to do this is to say something like: "Find out whose birthday comes first in a calendar year." Then tell students that, "That person gets to go second!" 3. Using a stop watch or other timing device, tell students to begin talking. 4. At two minutes, instruct students to switch. At this point, the other partner begins talking. It is okay for the second person to repeat some of the things the first person said. However, they are encouraged to try and think of new information to share. 5. Have a few groups share some of their responses with the entire class when the activity is done. WARM UP Webquest http://www.questgarden.com/109/2 1/4/100919191126/task.htm