* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Celiac Disease
Race and health wikipedia , lookup
Seven Countries Study wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Huntington's disease wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
2001 United Kingdom foot-and-mouth outbreak wikipedia , lookup
Coeliac disease wikipedia , lookup
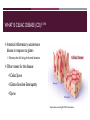
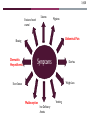
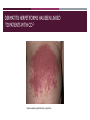
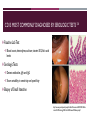
CELIAC DISEASE PRESENTED BY: DALLAS MONTAG DATE: 12/6/16 WHAT IS CELIAC DISEASE (CD)? 3,4,6 Intestinal inflammatory autoimmune disease in response to gluten Destroys the villi, lining of the small intestine Other names for the disease: Celiac Sprue Gluten-Sensitive Enteropathy Sprue https://medivizor.com/blog/2016/10/19/celiac-disease/ COMMON SOURCES OF GLUTEN 5,8 Beer Cookies Bread Pasta/Noodles Bagels Pastries/Pies Cakes Rolls Cereal Salad Dressings CELIAC DISEASE OCCURS PRINCIPALLY IN INDIVIDUALS OF EUROPEAN DESCENT 3,4,5 Other epidemiology's include: Occurrence: 1 in 250 individuals 20% of first degree relatives are affected Females > Males Age of diagnosis http://www.whattoexpect.com/first-year/celiac-disease-in-children.aspx CELIAC DISEASE HAS A STRONG GENETIC COMPONENT 3,5,6 Genetic Factors Environmental Factors HLA-DQ locus Foods containing GLUTEN Majority: DQ2 (DQA1*05/DQB1*02) Infant Feeding Minority: DQ8 (DQA1*03/DQB1*0302) Drug exposures Females create a larger risk factor than Microbial Infections (trigger) males WHAT IS GLUTEN? 4,8 Name for proteins found in wheat and other grains such as barley, rye, and to some extent oats Gluten helps food maintain their shape Gliadin and glutenin: comprise ~80% of protein contained in wheat seed Binds to the serotypes formed from the DQ2 and DQ8 genes Gluten is the “glue” http://www.elisilvernd.com/health-news/what-exactly-is-gluten IMMUNOLOGICAL MECHANISM 1,5,6 http://www.nature.com/scientificamerican/journal/v301/n2/box/scientificamerican0809-54_BX3.html THE ROLE OF TISSUE TRANSGLUTAMINASE (TTG) 1,4 Calcium dependent enzyme Extracellular and Intracellular Irreversible crosslinking of glutamine and lysine residues Gliadin is the preferred substrate https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tissue_transglutaminase STEP 1: Entrance of gluten STEP 2: Accumulation of gluten STEP 3: Release of IL-15 STEP 4: TTG Release STEP 5: APCs present antigens to TH cells STEP 6: Attraction of immune cells STEP 7: Tc cells attack STEP 8: Secretion of ABs STEP 9: Damaged epithelial cells 3,4,5,8 Seizures Erosion of tooth enamel Migraines Abdominal Pain Bloating Dermatitis Herpetiformis Symptoms Diarrhea Weight Loss Short Stature Malabsorption Vomiting Iron Deficiency Anemia DERMATITIS HERPETIFORMIS HAS BEEN LINKED TO PATIENTS WITH CD 2 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dermatitis_herpetiformis CD IS MOST COMMONLY DIAGNOSED BY SEROLOGIC TESTS 5,6 Routine Lab Test Blood count, electrolytes, calcium, vitamin B12, folic acid levels Serologic Tests Detect antibodies, IgA and IgG Show variability in sensitivity and specificity Biopsy of Small Intestine http://www.napavalley.edu/people/briddell/Documents/BIO%20218/Ana tomical%20Pathology%20Celiac%20Disease%20Example.pdf THERE ARE FEW TREATMENTS FOR PATIENTS WITH CD 4,5,6 Gluten-Free Diet Includes all food, bath products, cosmetics, medications etc. Small amount of gluten in food will effect a person with CD Ex. Eating gluten- free food served on a plate with food containing gluten Anti-inflammatory medications Vaccine Trial Experimental Possibility: blocking binding sites of the DQ2 and DQ8 HLA molecules??? TREATMENT CONT’D 8 Consultation Education Lifelong diet Identification of deficiencies Advocacy group Continuous follow-up https://gfjules.com/celiac-awareness-month/ REFERENCES & ACKNOWLEDGMENTS 1. Sabatino AD,Vanoli A, Giuffrida P, Luinetti O, Solcia E, Corazza GR. 2012. The function of tissue transglutaminase in celiac disease. Autoimmunity Reviews. 11(10): 746-753. 2. Fergunson A, Arranz E, O’Mahony S. 1993. Clinical and pathological spectrum of coeliac disease-active, silent, latent, potential. Journal of The American Dietetic Association. 34(7): 150-151. 3. King AL, Ciclitira PJ. 2000. Celiac disease: strongly heritable, oligogenic, but genetically complex. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. 71(1-2): 70-75. 4. Kuper SS, Jabri B. 2012. Celiac Disease Pathophysiology. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Clinics of North America. 22(4): 1-28. REFERENCES & ACKNOWLEDGMENTS 5.Murray A. 1999. The widening spectrum of celiac disease1,2. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 69(3): 354-365. 6. Sollid LM, Benedicte AL. 2005. Celiac Disease Genetics: Current Concepts and Practical Applications. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 3(9): 843-851. 7. Sollid LM, Markussen G, Ek J, Gjerde H, Vartdal F, Thorsby E. 1989. Evidence for a primary association of celiac disease to a particular HLA-DQ alpha/beta heterodimer. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 169(1): 345-350. 8. Thalheimer J. 2016. Getting to the bottom of food sensitivities. Environmental Nutrition. p.7. THANK YOU DR. SPILATRO!! Questions???? STUDY QUESTIONS: MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Celiac disease is the result of the intolerance to the proteins most commonly found in which three grains? A. rice, wheat, rye B. oats, wheat, rice C. wheat, barley, rye D. oats, wheat, rye 2. Which of the following statements concerning celiac disease is TRUE? (select all correct answers) A. Symptoms of celiac disease often mimic those of other intestinal disturbances. B. It occurs more frequently amongst the elderly C. Celiac disease occurs in 5 percent of Americans. D. There is no cure for celiac disease. STUDY QUESTIONS: MULTIPLE CHOICE 3. Why does the immune system respond to gluten in patients with celiac disease? A. It is a foreign protein B. It is modified by the transglutaminase enzyme C. It is very large and disrupts the villi D. It is modified by the alanine transaminase enzyme 4. Which of the following statements concerning celiac disease is NOT true? A. Celiac disease is more often in females than in males. B. Celiac sprue is another name for the disease C. Celiac disease patients have excessive growth of villi D. Individuals with celiac disease often have malabsorption issues