* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sound and Ear Power Point
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sound barrier wikipedia , lookup
Sensorineural hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Speed of sound wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles wikipedia , lookup
Sound from ultrasound wikipedia , lookup
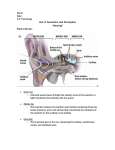
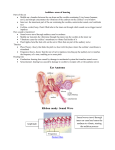
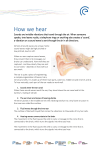
Sound and Ear Day one Sound & Ear Learning objectives: • What is sound? • What part(s) of the body receive sound? • How does the brain perceive sound? Key Points on Sound 1. Waves transmit energy – not matter 2. Sound can only travel through matter, through a “medium.” 3. The easier it is to move the molecules, the faster the wave will travel. – If the material is dense, the molecules are closer to each other. – If material is hot, the molecules are already moving faster. 4. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) – the number of waves that go by in one second. 5. Wavelength is the length of one wave. 6. The larger (bigger) the wavelength, the ___er the frequency (higher or lower) The lower the frequency – fewer waves per second. Page 423 – Find definition of a Wave What does a wave transfer / move? • ENERGY Read definition of sound What produces sound? • A vibrating object Finger to vocal cords. What does sound have to travel through? • Matter / molecules – a “medium” • Globe. Explain vacuum, not a vacuum cleaner! Pg 428 All waves have a wavelength and a frequency Transverse wave Longitudinal wave Pg 424 Sound “wave” LAHN-jih-TOOD-n-uhl Pg 425 Slinky demo Page 423 – Read directions for spoon and string Pg 427 – caption under scuba diver Speed of sound in miles per hour mph in Air? Water? Steel? What makes sound have a higher or lower “pitch”? Talk to your neighbor and use what you know about sound waves – vibrations, wavelength and/or frequency – to explain. Write on left. Demos: • Sound changes as the marble drops down the “tree”? • Different guitar strings Page 432 Faster vibrations produce higher frequencies / pitch. • The smaller pieces of wood or smaller/ tighter guitar strings vibrate faster. • Ruler demo? • Lets move to the organ that lets us receive and perceive sound. • What is the difference between “receive” and “perceive”? Perceiving is the brain becoming aware of anything through any of the senses. Is thinking the same as perceiving? Sound and Ear Day two Major Parts of the Ear • Video using ear model. Has answers to WS! • video-ear model.asf Student demos drum Sound waves hit the ear drum and were turned into vibrations Outer ear acts like a funnel, directing and focusing the sound to ear drum Cup hand behind ears. What do the 3 bones do? Amplify and magnify the vibrations Pg 437 Hammer, anvil & stirrup bones (smallest bones in the body) Stirrups on a saddle How mammals got ear bones and how they work Do We Listen With Our Jaw Bones? (4 min) http://ca.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/b07a81ee-2640-474e-a08f8c30043705da/do-we-hear-with-jaw-bones-your-inner-fish/ Path of the sound wavy waves Path of the sound wavy waves Path of the sound wavy waves The cochlea is a ___-____ ___ tube Fluid-filled hairy tube! “Oval “Window” Draw this Touch the hair, not the skin, on your arm, leg, or head (from best to worst) When the nerve at the ends of each hair sends an electrical nerve impulse to the brain, the brain perceives _______ Touch at that spot. When the hairs/cilia inside the cochlea are moved, the brain perceives _______ Sound! The vibrations have been turned into electrical nerve impulses. Questions about the ear and hearing? • Different frequencies/pitches move different cilia. High pitches at beginning, low at end. • Cilia are nerve cells, not hair cells. They do not grow back if broken. : Ear drum turns ____ into ____. • Ear drum turns sound waves into vibrations. Cochlea turns ____ into ____. • Cochlea turns vibrations into electrical nerve impulses that go to the brain. Semicircular canals are also fluid-filled tubes that have nothing to do with hearing. Fluid- and stone-filled hairy tubes! Pg 404 “Otoliths” Greek for stones. They “fall” as we move our head, and trigger the cilia to send that sensation to the brain. 3 canals are perceived as 3 different types of motion Learning objectives from last class: What is sound? What part(s) of the body receive sound? How does the brain perceive sound? • Put your finger on the definition of perceiving in your notes. • Perceiving is the brain becoming aware of anything through any of the senses. Learning objectives from last class: What part(s) of the body receive sound? • How the ear works How does the brain perceive sound? • The five steps Key Points on Sound 1. Waves transmit energy – not matter 2. Sound can only travel through matter, through a “medium.” 3. The easier it is to move the molecules, the faster the wave will travel. 4. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) – the number of waves that go by in one second. 5. Wavelength is the length of one wave. 6. The larger the wavelength, the lower the frequency Faster vibrations produce higher frequencies/ pitch (guitar, marble tree). What is the function of the outer ear? Direct, or “funnel,” sound into the ear canal to the ear drum. What is the function of the ear drum? Turns the sound “pressure waves” back into vibrations.. What is next? The ear drum hits the … What is the function of the bones? “Levers” to magnify and transmit/move the vibrations from the ear drum to the …. What is next? The cochlea is a fluid-filled hairy tube What are the hairs actually called? Cilia Show high & low freq. cilia. Cochlea turns ____ into ____. Cochlea turns vibrations into electrical nerve impulses that go to the brain. When do we actually “perceive” sound? When the nerve/electrical signal reaches the brain. ABC news on hearing loss in YOUNG people https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ErUWnEOoKls How Old are Your Ears? ASAP video – set to 1080 bandwidth https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VxcbppCX6Rk&index=5&list=PLvFsG9gYF xY_lAm8jnex08LeiGMTiZQOW You CAN avoid losing your hearing! Page 443 Read “Response of the Ear” • Repeat/long exposure to 100 dB will damage in the long-term (music, hand dryers!) • LOUD sounds of 130 dB or more will damage cilia Ringing in your ear? • Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the head or the ears. The term comes from Latin word tinnire, meaning “to ring.” • Most tinnitus comes from damage to the microscopic endings of the hearing nerve in the inner ear. • Injury to these nerve endings brings on hearing loss and often tinnitus. • Source: http://www.entnet.org/healthinfo/hearing/tinnitus.cfm Ear Plugs are your friend! • They are cheap, soft and comfortable. Roll to compress and put into ear. • You can still hear, but they lower the overall volume and save your hearing.. Audio illusions (instead of optical illusions) Can you trust your ears? ASAP, 3 min https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kzo45hWXR WU&feature=em-subs_digest Ear Wax Its purpose is to trap dust and other small particles and prevent them from reaching, and potentially damaging or infecting the eardrum. Normally, the wax dries up and falls out of the ear, along with any trapped dust or debris. Motion sickness, What is it? ASAP 1:30 • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0CP0VX9XFXU Is your Chp 12 WS right? • Q 10 & 11: Did you draw a longitudinal wave? Is the frequency different? Did you label one wavelength in both 11 and 12? • Q13: Answer IS on on page 435! • Q15: Info from page 436 and page 440. • Q16: Info from page 437 and 441. • Q17: What happens inside cochlea and what does that have to do with how we hear? • ParrMr song: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0C54NqkwB2c