* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download fdm-dfgsm2-grammar-activity2-parts-of-speech
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Arabic nouns and adjectives wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Sotho parts of speech wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian declension wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
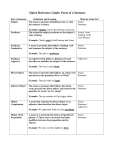
Grammar Activity #2: Parts of Speech Introduction “Parts of speech” are the basic types of words that English has. Most grammar books say that there are eight parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions, prepositions and interjections. We will add one more type: articles. It is important to be able to recognize and identify the different types of words in English, so that you can understand grammar explanations and use the right word form in the right place. Here is a brief explanation of what the parts of speech are: Noun Verb Adjective A noun is a naming word. It names a person, place, thing, idea, living creature, quality, or action. Examples: cowboy, theatre, box, thought, tree, kindness, arrival A verb is a word which describes an action (doing something) or a state (being something). Examples: walk, talk, think, believe, live, like, want An adjective is a word that describes a noun. It tells you something about the noun. Examples: big, yellow, thin, amazing, beautiful, quick, important An adverb is a word which usually describes a verb. It tells you how something is done. It may also Adverb tell you when or where something happened. Examples: slowly, intelligently, well, yesterday, tomorrow, here, everywhere Pronoun Conjunction A pronoun is used instead of a noun, to avoid repeating the noun. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, we, they A conjunction joins two words, phrases or sentences together. Examples: but, so, and, because, or A preposition usually comes before a noun, pronoun or noun phrase. It joins the noun to some other Preposition part of the sentence. Examples: on, in, by, with, under, through, at An interjection is an unusual kind of word, because it often stands alone. Interjections are words Interjection which express emotion or surprise, and they are usually followed by exclamation marks. Examples: Ouch!, Hello!, Hurray!, Oh no!, Ha! Article An article is used to introduce a noun. Examples: the, a, an Practice Exercise 1: Identify the correct part of speech for each word. 1. oh 4. speak 2. cat 5. and 3. quickly 6. by 7. the 8. they 9. beautiful Practice Exercise 2: Identify the correct part of speech for each word. 1. difficult 4. on 2. an 5. she 3. slowly 6. learn 7. hi 8. class 9. but For more help: The University of Calgary: The Basic Elements of English Grammar Guide An overview of nouns: NOUN: any word which names a person, place, thing, idea, animal, quality, or action 1. Count Nouns: anything which can be counted; singular & plural Example: car - cars 2. Mass Nouns: entities which cannot be counted; no plural form Example: money 3. Collective Nouns: groups of people or things; sing. & pl. Example: herd - herds 4. Possessive Nouns: express ownership by adding an apostrophe Examples: (sing.) Kelly's anger (pl.) birds' feathers An overview of pronouns: PRONOUN: a word which takes the place of a noun (called "the antecedent") 1. Personal: refer to person/people speaking, spoken to or spoken about Examples: I, me, you, he, him, she, her, it, we, us, they 2. Possessive: function independently; show possession Examples: my, mine, your, yours, our, ours, his, her, hers 3. Indefinite: have no specific antecedents Examples: another, both, everything, nothing 4. Reflexive: shows the subject performs actions to/for itself Examples: myself, yourself, itself, ourselves, themselves 5. Intensive: refer back to a noun/pronoun to add emphasis to it Examples: (same forms as reflexive pronouns) 6. Reciprocal: show a mutual action or relationship Examples: each other, one another 7. Interrogative: used to ask a question Examples: who, which, what 8. Relative: used to introduce a relative clause Examples: who, which, that 9. Demonstrative: substitutes for specific nouns Examples: this, that, these, those An overview of verbs: VERB: expresses action or state of being 1. Transitive: action verb; passes action on to a direct object Example: We bought a car. 2. Intransitive: do not indicate a transfer of action; no D.O. Example: The eagle soared. 3. Linking: joins subject with a word that renames/describes it Example: The sky is blue. 4. Main: indicates the primary activity 5. Auxiliary: "helps" the main verb 6. Modal: indicates ability, obligation, permission, possibility Examples: can, may, must, should, could, might, ought, would 7. Finite: describes a definite and limited action or condition 8. Non-finite/Verbal: shows an unfinished action or condition o Infinitives: to + verb; act as nouns, adjectives, adverbs o Participles: past or present; always act as adjectives o Gerunds: present participle form; act as nouns An overview of adjectives: ADJECTIVE: modifies nouns and pronouns 1. Descriptive: name a quality of the noun o Attributive: Ex. The brown cow. o Predicate: Ex. It was a brown cow. 2. Limiting: limit a noun o Definite/Indefinite Articles: Ex. the, a, an o Possessive: Ex. his, her, its, their o Demonstrative: Ex. this, that, these, those o Indefinite: Ex. several, few, less, many, more o Interrogative: Ex. what, which, whose o Cardinal: Ex. one, two, four o Ordinal: Ex. third, fourth, fiftieth o Nouns: Ex. the milk cow o Proper: Ex. the German cow An overview of adverbs: ADVERB: modifies verbs, adjectives, adverbs, sentences Examples: sang loudly, ran swiftly An overview of prepositions: PREPOSITION: links a noun or a pronoun (the object of the preposition) with some other word or expression Examples: about, below, in, over, until An overview of conjunctions: CONJUNCTION: links sentence elements, ie. words, phrases, clauses 1. Coordinating: join sentence parts of equal grammatical status Examples: and, but, for, nor, or, so, yet 2. Correlative: coordinating conjunctions that work in pairs; join words, phrases, clauses, sentences Examples: both...and, either...or, neither...nor 3. Subordinating: connect clauses of unequal status Examples: after, because, that, though An overview of interjections: INTERJECTION: used in speech to indicate emotion, or transition Examples: yuk, ouch, eh A Quick Review: PARTS OF SPEECH Definition: All words are divided into grammar groups. The grammar groups are called parts of speech. The groups are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Nouns (people, places, or things) Verbs (the state or action word in a sentence) Adjectives (give more information about nouns) Adverbs (give more information about verbs) Determiners (words that come before most nouns) Prepositions (give information about place and time) Pronouns (replace nouns) Conjunctions (join sentences) Example (The numbers in the example below refer to the numbers in the list above.) Explanation: Each part of speech - has its own rules. is necessary to write grammatically correct sentences. Practice Exercise #3: Find the modified word form according to the part of speech asked for. For example: Medicine (noun): __________ (adjective) Medicine (noun): Medical (adjective) 1. dentist (noun): ___________ (adjective) 2. responsible (adjective): ______________ (adverb) 3. young (adjective): __________________ (noun) 4. stress (noun): _______________ (adjective) 5. anxious (adjective): ______________ (noun) 6. spine (noun): ________________ (adjective) Practice Exercise #4: Plural Nouns: Give the plural form of the following nouns 1. roof 5. medicine 2. mouse 6. leaf 3. remedy 7. illness 4. patient 8. injury 9. goose 10. hoof 11. person 12. life