* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT - SEAS | The George Washington University
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power supply wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
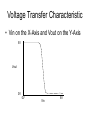
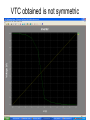
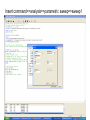
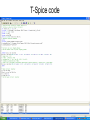
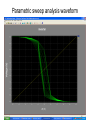
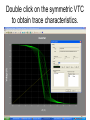
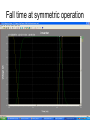
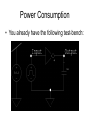
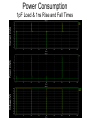
The George Washington University School of Engineering and Applied Science Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE122 Lab 4: VTC & Power Consumption Jason Woytowich Ritu Bajpai September 28, 2006 Voltage Transfer Characteristic • Vin on the X-Axis and Vout on the Y-Axis 5V Vout 0V 0V Vin 5V Voltage Transfer Characteristic • A symmetric VTC is one where the Vin vs Vout curve crosses through the dead center of the graph. • Using 5V inputs and outputs this point is 2.5V in and 2.5V out Lab activity • Find Wp/Wn such that the VTC for an inverter is symmetric. Replace the pulse input by a DC source in the inverter test circuit. Select DC transfer sweep analysis and select sweep 1 DC sweep analysis Choose DC results VTC obtained is not symmetric Insert command=>analysis=>parametric sweep=>sweep1 Defining pMOS width as a parameter In the T-Spice code write the following command .param width=35u And in pMOS properties change W=‘28*l’ to W=‘width’ T-Spice code Parametric sweep analysis waveform Double click on the symmetric VTC to obtain trace characteristics. Designing for symmetric VTC • Record the width of the pMOS corresponding to symmetric operating point. • In this case width = .8u • In S-Edit substitute this width for the pMOS and perform transient analysis. Rise time at symmetric operation Fall time at symmetric operation Power Consumption • Next we will use Tanner Tools to estimate the power consumption of a design. • We will also identify the sources of power consumption. Power Consumption • You already have the following test-bench: Power Consumption • Simulate the circuit over 2 periods with fine resolution (2ns) • Show the waveforms for: – The input and output voltages – The power provided by the power supply – The currents drawn from the power supply and the capacitor Power Consumption 10pF Load & 10ns Rise and Fall Times Power Consumption • Lower the value of the capacitor to 1pF and resimulate Power Consumption 1pF Load & 10ns Rise and Fall Times Power Consumption • Decrease the rise and fall times of the pulse source to 1ns. Power Consumption 1pF Load & 1ns Rise and Fall Times Home work • Revise the work done in all the lab turns till now. • Come prepared to design a half adder and a full adder (using half adder) on next turn. • You will do the schematic design and extract the layout for the above on next turn.