* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lecture 25 circuits applications
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
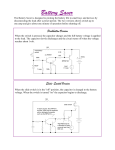
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
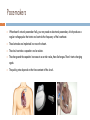
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
LECTURE 25 CIRCUITS APPLICATIONS Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 25 2 ¤ Circuits applications Can you start a car? 3 ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ If the car battery (12 V) is dead, can you start a car using eight D-cell 1.5-V “flashlight” batteries? NO! They do not provide enough current to start a car (a several hundred amps). A flashlight batteries normally has an internal resistance of ~0.1 Ω. The terminal voltage of a battery decreases as the current through it increases since 𝑉 = ℇ − 𝐼𝑟. The maximum current a flashlight battery can supply can be estimated by ℇ +.- / setting the terminal voltage to be zero: 𝐼'() = = = 15 A. * ¨ 0.+ 1 DO NOT TRY THIS AT HOME! If the car battery is not completely flat, it could send a large current through the flashlight batteries, causing them to explode! Example: 1 4 ¨ The equivalent resistance between points A and B of the resistors shown is Req = 26 Ω. An ideal battery with a terminal voltage of V = 12 V is connected to terminals A and B. a) Find the value of resistance R3. b) Find the current in each resistor. c) Find the power dissipated in each of the resistors. d) If R3 is increased, state whether the current through each resistor increases or decreases. R1 = 12 Ω R2 = 55 Ω R3 Clicker question: 1 through 3 5 Example: 2 6 ¨ Three different circuits, each containing a switch and two capacitors, initially charged as shown. The switches are then closed, allowing charge to move freely between the capacitors. Rank the circuits in order of increasing final charge of the left plate of a) the upper capacitor and b) the lower capacitor. Example: 3 7 ¨ A flash unit for a camera has a capacitance of C = 1500 µF. What resistance is needed in this RC circuit if the flash is to charge to 90 % of its full charge in t = 21 s? Demo: 1 8 ¨ Relaxation oscillator (RC circuit) ¤ A capacitor, resistor, and 90V battery are hooked in series with a neon bulb in parallel with the capacitor. ¤ The capacitor charges to about 80V (the breakdown voltage of the neon bulb), then discharges through the bulb and begins the cycle again. Pacemakers 9 ¨ When heart’s natural pacemaker fails, you may need an electronic pacemaker, which produces a regular voltage pulse that starts and controls the frequency of the heartbeat. ¨ The electrodes are implanted in or near the heart. ¨ The circuit contains a capacitor and a resistor. ¨ ¨ The charge and the capacitor increases to a certain value, then discharges. Then it starts charging again. The pulsing rate depends on the time constant of the circuit.