* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
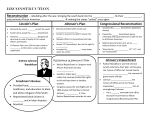
RECONSTRUCTION Rebuilding after the Civil War Era 6 AFRICAN AMERICANS Life was not suddenly better for A. Americans after the Civil War as they had hoped. In the South, they were terrorized, robbed and murdered. In order to escape this, many fled to Kansas where they hoped a new life would be possible without the problems. These people fleeing were nicknamed the “Exodusters” because they left homes to make better lives in the dusty new land, just as the Israelites had done centuries earlier in their exodus from Egypt to Canaan. RECONSTRUCTION What is reconstruction? It is the process of restoring relations with the Confederate states. It was a plan to bring the states back into the Union. It also was to involve how to rebuild the devastated South. It lasted about 10 years after the end of the Civil War. LINCOLN’S RECONSTRUCTION PLAN Before the war had even ended, Lincoln had begun plans to reestablish state governments in the South. He thought these governments would be loyal to the North after the end of the war and make reconstruction easier. For a state to be recognized as legitimate, 10 percent of the men eligible to vote in 1860 had to swear allegiance to the Union. This plan become known as Lincoln’s 10% plan. ANDREW JOHNSON Andrew Johnson became president upon Lincoln’s assassination. Johnson had stayed with the Union as Vice President even though he was a Southerner. During the war, he had called those of the Confederacy “traitors”. Many Northerners were surprised when he became president and seemed to continue Lincoln’s plan of tolerance toward the South. JOHNSON’S RECONSTRUCTION PLAN Johnson issued a Reconstruction proclamation in May of 1865. 1. This proclamation granted amnesty (a pardon) to Confederates who would sign an oath of loyalty to the Union. 2.Political and military leaders and landowners whose property was worth more than $20,000 had to apply for special pardons. Johnson granted such pardons regularly. 3.He appointed provisional governors and set forth minimal requirements for reorganizing Southern state governments. JOHNSON’S PLAN COMPLETE By December 1865, all former Confederate states except Texas had fulfilled the requirements for reentering the Union. Each had elected representatives to Congress. Johnson announced that the Union had been restored. But was it? CONGRESS V JOHNSON When Congress reconvened in December, it refused to seat the newly elected Southern representatives. Many members felt Johnson had been too easy on the South. They said he had not stopped the Southern states from issuing “black codes”. Congress and Johnson battled over Reconstruction throughout 1866. BLACK CODES The purpose of these laws was to define the legal status and civil rights of the former slaves. In reality the laws severely restricted the rights of newly freed African Americans. In some cases, it continued white supremacy by requiring blacks to become in effect, landless indentured servants. In most cases, the law granted new rights while it maintained the old restrictions of slave days at the same time. CONGRESS’S RECONSTRUCTION PLAN In 1867 Congress passed a series of Reconstruction Acts over Johnson’s veto. They abolished the state governments set up by Johnson’s Plan. Divided the South into 5 military districts, each under the command of a general. Federal troops were stationed in each district to carry out the process of readmitting states to the Union. The South was now under military occupation this changed the tone of Reconstruction. THE SUPREME COURT GETS INVOLVED Congress had political control, therefore the army administered Congress’s plan. The battle between the legislative and executive branches took the cause to the Supreme Court. At first it seemed the SC would side with the president. The Court soon sided with Congress and recognized their authority to reconstruct the South. RADICAL REPUBLICANS A group of Congress men that were strongly antislavery and were not willing to forgive the Confederates. Wanted sweeping changes in the South and felt Union troops had to be present to accomplish this. Passed the Wade-Davis Bill in 1864 which Lincoln vetoed. Would have required a majority of a state’s white male citizens to swear both past and future loyalty to the Union. RECONSTRUCTION UNDER RADICAL REPUBLICAN CONGRESS Set about issuing legislation to punish the former Confederate states, increase Republican power in the South, and create conditions that would promote economic development and racial equality in the South. It increased the rights and freedoms of African Americans. Made the Republicans popular with a large new pool of voters Diminished white Southerners’ ability to dominate the South politically and economically. LEGISLATION DURING RECONSTRUCTION Civil Rights Act (1866) 14th Amendment (1868) Granted citizenship to African Am and prohibited states from diminishing the rights accompanying this citizenship. Defined who a U.S. citizen was and prevented states from denying rights and privileges to any American citizen (if citizen of U.S. then citizen of state) 15th Amendment (1870) <suffrage> (right to vote) guaranteed that no citizen could be denied the right to vote based on race, color or former servitude Nor can you be denied the right to vote based on literacy. (whether or not a person can read and write) KU KLUX KLAN White supremacist organization that used intimidation and violence to prevent African Americans from voting or holding positions of power. Helped increase the environment of violence and hatred. Mobs of Southern whites periodically lashed out against the newly freed citizens Also terrorized carpetbaggers and scalawags. (Southerners who cooperated with Republican reconstruction governments.) IMPEACHMENT (BRINGING FORMAL CHARGES AGAINST) Congress impeached Johnson inn 1868 Attempts to veto and undermine congressional legislation Inability of lack of desire to control terrorist organizations Defied the Tenure of Office Act by firing Sec. of War Edwin Stanton House voted to impeach Johnson on 11 charges of misconduct. Trial lasted 8 weeks, Johnson did not attend. Senate failed to convict by 1 vote 35 v 19 Requires 2/3rd vote to convict FREEDMEN’S BUREAU Set up by Congress as part of the office of the War Department Established to provide freed African Am. With food, teachers, legal aid and other assistance. Distributed horses, mules and land that had been confiscated during the war. Helped 40,000 African Am. To establish their own farms. At first paid the cost of education, but later education was turned over to the states’ control. VOTING African American males began to vote for the first time. Between 1869 and 1876, 2 African Americans served in the U. S. Senate and 14 served in the House of Rep. Many of these men had been enslaved or were born of enslaved parents. Hiram Revels 1st black elected to Senate, 1870 Robert Smalls, served in the House. Longest serving black in Congress until 20th century SHARECROPPING A system in which a wealthy patron would give seeds, supplies and a small parcel of land to a farmer in exchange for a portion of the crop. The sharecropper might not be able to survive on what remained. If the crop failed, the sharecropper usually wound up hopelessly in debt to the patron. ULYSSES S. GRANT In 1868 the Republican Ulysses S. Grant, former lead Union General, became president. During his two terms in office, the government began paying less and less attention to the problems of prejudice, discrimination and racial harassment. Scandal and corruption plagued Grant’s administration. CORRUPTION IN GRANT’S ADMINISTRATION The Whiskey Ring Scandal = Whiskey distillers and tax officials were stealing excise taxes from the government and a member of Grant’s staff was part of it. Grant’s secretary of war was accused of accepting bribes. Even Grant wrongly accepted personal gifts. Grant appointed a number of personal friends, relatives and fellow army officers to positions that lacked the skills and experience necessary to do the jobs. Many were greedy and dishonest. GRANT’S BLACK FRIDAY Collapse of the U.S. gold market on Sept. 24, 1869 Jay Gould and Jim Fisk were behind it. Starting on September 20, Gould and Fisk had started to buy as much gold as they could. Just as they planned, the price went higher. At its highest point on September 24, the price of an ounce of gold reached more than 30 dollars above what it was when Grant took office. Grant decided to sell government owned gold into the market to try to stop this rise. Grant’s brother -in-law had been involved, his job was to let the other two men know when Grant planned to put gold on the market so they could sell first. Grant had no knowledge of the scam at first. When he did find out he removed his bother in law from office and put the gold on the market. The effect on the economy was disastrous. When the government gold hit the market, so did panic. CORRUPTION IN SOUTHERN GOVERNMENTS Many Republican appointed government official in the South were inexperienced and even corrupt. Southerners called them carpetbaggers, because they had arrived in the South with only the possessions they had been able to stuff in their luggage. White Southerners believed the carpetbaggers wanted only to turn a profit or rise to power at the expense of the South African Americans newly elected to political positions were often blamed for government wastefulness and dishonesty. DEMOCRATIC SUCCESS Democrats begin to regain control of the South due to the corruption of the carpetbag governments. They also used some underhanded tactics to neutralize the issues of equality that had begun to affect the election process. Gerrymandering – redividing voting districts to decrease African American representation in areas Poll tax – a fee paid to vote, it excluded poor citizens from voting By 1875 the Democrats had regained control of the government in the South PANIC OF 1873 In 1873 a economic panic was begun when a banker closed his Philadelphia bank. Prompted a panic in which 5,000 businesses closed and thousands lost jobs. In North demands of unemployed workers for economic relief replaced the demands for racial equality. In the South the sharecropping system cheated many African Am farmers out of owning land or reaping profits from their labors. White farmers in the South suffered devastating losses during this time and blamed the newly freed blacks. African Americans in the North were trapped in lowpaying, unskilled jobs. They lived in poor housing and had little or no say in government. In North they made up less that 2% of the population. All of this turned the countries attention from racial equality to economic relief. END OF RECONSTRUCTION In the mist of all the social and economic crisis, government scandals, and outbreaks of violence, the Radical Republicans lost their political power. The Radical Republican program of Reconstruction came to and end as it was no longer supported by a majority of voters. They attempted to regain a foot hold in government in the election of 1876. ELECTION OF 1876 Republicans backed Rutherford B. Hayes A moderate that appealed to both the North South and Democrats backed Samuel Tilden Possibly the closest race in U.S. history. 4 states’ returns were disputed (must have a majority of electoral votes to win) Democrats insisted that the majority of the people in the disputed states favored Tilden but had been prevented from voting A special electoral commission was set up to decide the disputed votes. To get Hayes elected, Republicans made many concessions to the Democrats. All 20 votes were given to Hayes as a result of the Compromise of 1877. Hayes won the election. COMPROMISE OF 1877 The compromise essentially stated that Southern Democrats would acknowledge Hayes as president, but only on the understanding that Republicans would meet certain demands. The following elements are generally said to be the points of the compromise: The removal of all federal troops from the former Confederate States. Troops remained in only Louisiana, South Carolina, and Florida, but the Compromise finalized the process. The appointment of at least one Southern Democrat to Hayes's cabinet. (David M. Key of Tennessee became Postmaster General.) The construction of another transcontinental railroad using the Texas and Pacific in the South Legislation to help industrialize the South and get them back on their feet after the terrible loss during the Civil War. In exchange, Democrats would: Peacefully accept Hayes's presidency. RECONSTRUCTION APPRAISED Most of the legal decisions that had advanced African American rights during Reconstruction had been overturned. Radical Republican governments had failed to correct the problem of unequal land distribution in the South African Americans felt as if their needs had been forgotten. Many African Am. left the South by the thousands either for the North or West