* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Communication Objectives
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Targeted advertising wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Michael Aldrich wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Elaboration likelihood model wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
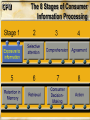
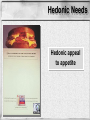
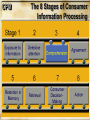
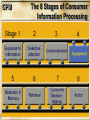
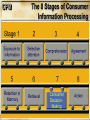
Communication Objectives 1. Creating Brand Awareness 2. Building Brand Image 3. Enhancing attitudes and influencing intentions 4.Facilitating Purchase Behavior Behavioral Foundations of Marketing Communications • How consumers process and respond to marketing communications stimuli and make choices among brands • Two models of consumer behavior » CPM and HEM • Consumer behavior is too complex and diverse to be explained by two extreme models Behavioral Foundations of Marketing Communications Consumer Processing Model (CPM) Behavior is seen as rational, highly cognitive, systematic,and reasoned Behavioral Foundations of Marketing Communications Hedonic, Experiential Model (HEM) Consumer behavior is driven by emotions in pursuit of “fun, fantasies, and feelings” CPM The 8 Stages of Consumer Information Processing Consumer Information Processing: Stage 1 Exposure to information • Consumers come in contact with the marketer’s message • Gaining exposure is a necessary but insufficient for communication success • A function of key managerial decisions regarding the size of the budget and the choice of media and vehicles CPM The 8 Stages of Consumer Information Processing Selective Attention: Stage 2 How to attract consumers attention: Selective Attention: Stage 2 Illustration of attention-getting advertising Selective Attention: Stage 2 Plays on selective attention Appeals to Cognitive and Hedonic Needs Cognitive Needs Immediate functional needs of the consumer Hedonic Needs Needs that make one feel good and bring pleasure Hedonic Needs Hedonic appeal to appetite Hedonic Needs Hedonic sex appeal Hedonic Appeal Virginia Power Company The Martin Agency Use of Novel Stimuli Illustration of novelty in advertising Use of Novel Stimuli Illustration of novelty in advertising Use of Novel Stimuli Here milk is used as a novel stimulus Use of Novel Stimuli Maytag Leo Burnett Company, Inc. Use of Intense Stimuli Use of intensity Use of Intense Stimuli Use of intensity to attract attention CPM The 8 Stages of Consumer Information Processing CPM The 8 Stages of Consumer Information Processing Consumer Information Processing: Stage 4 Agreement with what is comprehended Whether consumers yield to (that is, agree with) what they have comprehended Agreement: Stage 4 • Comprehension by itself does not ensure that the message influences consumers’ behavior • Agreement depends on: CPM The 8 Stages of Consumer Information Processing CPM The 8 Stages of Consumer Information Processing Retention and Search/Retrieval of Stored Information These two information processing stages, retention and information search and retrieval, both involve memory factors related to consumer choice When does Memory Matter? When information in memory is used as: When information in memory is useful for: When information in memory is not: A Consumer’s Knowledge Structure for the Mini Couper Little luggage space Two-Seater Small Cute Economical Sports car Fun to drive Nostalgic British Reliable Mini Couper Sophisticated Sexy British racing green Women CPM The 8 Stages of Consumer Information Processing Consumer Decision Making: Stage 7 Decision heuristics for decision making: The 8 Stages of Consumer Information Processing Action: Stage 8 Action on the basis of the decision • People do not always behave in a manner consistent with their preferences due to the presence of events, or situational factors • Situational factors are especially prevalent in low-involvement consumer behavior