* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation - U of L Class Index
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Speed of sound wikipedia , lookup
Sensorineural hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sound from ultrasound wikipedia , lookup
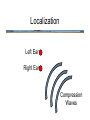
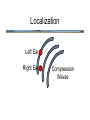
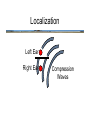
Hearing • • • • • • Detection Loudness Localization Scene Analysis Music Speech Detection and Loudness • Sound level is measured in decibels (dB) - a measure of the amplitude of air pressure fluctuations Detection and Loudness • Sound level is measured in decibels (dB) - a measure of the amplitude of air pressure fluctuations • dB is a log scale - small increases in dB mean large increases in sound energy Detection and Loudness • Sound level is measured in decibels (dB) - a measure of the amplitude of air pressure fluctuations • dB is a log scale - small increases in dB mean large increases in sound energy • We have a dynamic range that is a factor of 7.5 million! Detection and Loudness • minimum sound level necessary to be heard is the detection threshold Detection and Loudness • detection threshold depends on frequency of sound: • very high and very low frequencies must have more energy (higher dB) to be heard • greatest sensitivity (lowest detection threshold) is between 1000 hz to 5000hz Detection and Loudness • Detection can be compromised by a masking sound • even masking sounds that are not simultaneous with the target can cause masking (forward and backward masking) Detection and Loudness • Loudness is the subjective impression of sound level (and not identical to it!) Detection and Loudness • For example, tones of different frequencies that are judged to be equally loud have different SPLs (dB) Detection and Loudness • Hearing loss due to exposure to high-intensity sounds (greater than 100 dB) can last many hours Detection and Loudness • • • Incidence of noise-related hearing loss is increasing dramatically iPods and other “earbud” music players are thought to be partly responsible How loud is an iPod? – maximum volume is approximate but is somewhere between 100 dB (hearing damage in about 2 hours) to 115 dB (hearing damage in about 15 minutes) • • Consequences: difficulty understanding speech, tinnitus, deafness Your perception of loudness adapts so it’s hard to tell how loud your iPod is LOCK THE VOLUME ON YOUR iPOD! Localization • recall the lake analogy: task is to localize the positions of the boats on a lake using the pattern of ripples at two points on the shore Localization • All you have is a pair of instruments (basilar membranes) that measure air pressure fluctuations over time Localization • There are several clues you could use: Localization Left Ear Right Ear Compression Waves Localization • 1 There are several clues you could use: arrival time - sound arrives first at ear closest to source Localization Left Ear Right Ear Compression Waves Localization • 1. 2. There are several clues you could use: arrival time phase lag (waves are out of sync) wave at ear farthest from sound source lags wave at ear nearest to source Localization Left Ear Right Ear Compression Waves