* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SenProbe: Path Capacity Estimation in Wireless Sensor Networks
Wireless USB wikipedia , lookup
Asynchronous Transfer Mode wikipedia , lookup
TCP congestion control wikipedia , lookup
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Serial digital interface wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Policies promoting wireless broadband in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
SenProbe: Path Capacity Estimation
in Wireless Sensor Networks
Tony Sun, Ling-Jyh Chen, Guang Yang
M. Y. Sanadidi, Mario Gerla
Outline
Motivation
Background
Design Consideration
What do we want to measure?
Effective Capacity
Previous Method
Proposed Approach: SenProbe
Simulation Results
Conclusion
SenMetrics05
2
Motivation
Mobile computing platforms may interact with
ambient sensor environment establishing
“Opportunistic wireless networks”
Evaluation and measurement of wireless path
capacity in sensor network is of realistic interest
(i.e. Capacity planning, protocol design, performance
analysis, system deployment, assess applicability of
deployment)
Need a tool that can monitor and measure
opportunistic path capacity in wireless sensor
networks
SenMetrics05
3
Outline
Motivation
Background
Design Consideration
What does SenProbe actually measure?
Effective Capacity
Previous Method
Proposed Approach: SenProbe
Simulation Results
Conclusion
SenMetrics05
4
Design Consideration
CSMA-CA and variant schemes still popularly
used in sensor network for its simplicity
(IEEE 802.15.4 beaconless mode, Berkeley motes,
etc)
Basic CSMA-CA doesn’t incorporate
RTS/CTS mechanisms
Send packet when an idle channel is detected
Smaller packet overhead if idle channel can be
detected quickly
Suffers from hidden terminal problem
SenMetrics05
5
What do we want to measure? (1)
The effective end-to-end rate is defined as
the maximum achievable data rate in the
absence of any cross traffic connection.
It is smaller than the raw data rate at the
physical layer due to
Packet Overhead
Interference between multiple packets in the
pipeline
SenMetrics05
7
What do we want to measure? (2)
In fact, path capacity in wireless net also
varies with:
MAC protocol and link scheduling
Link interference
S/N ratio;
Tx power
Encoding/modulation scheme
Number of antennas (eg MIMO)
Antenna directionality
etc
SenMetrics05
8
Neighborhood Example
If Dr=Di=250m , nodes {3,4,5} are within the same n-hood, C’=C/3
If Dr=250m, Di=500m, nodes {2,3,4,5,6} are in n-hood, C’=C/4
Dr= effective receive range from node 4
(solid-line circle)
Di = interference range caused by node
4 (dotted-line circle)
Distance between nodes: 200m
SenMetrics05
9
Effective Capacity of CSMA-CA
Enabled Wireless Channel
The effective capacity of a one-hop link can
be calculated as
C
TPacket
TPacket
CP
TACK TOverhead
TPacket
S Packet
CP
TACK
S ACK
CP
For the CSMA environment in our study (if
ACKs are used)
C
6ms
2Mbps 1.89Mbps
6ms 0.156ms 0.188ms
SenMetrics05
10
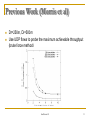
Previous Work (Morris et al)
Dr=250m, Di=500m
Use UDP flows to probe the maximum achievable throughput
(brute force method)
SenMetrics05
11
Outline
Motivation
Background
Design Consideration
What does SenProbe actually measure?
Effective Capacity
Previous Method
Proposed Approach: SenProbe
Simulation Results
Conclusion
SenMetrics05
12
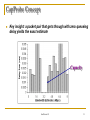
CapProbe Concept
Key insight: a packet pair that gets through with zero queueing
delay yields the exact estimate
Capacity
SenMetrics05
13
Issues: Compression and Expansion
• Queueing delay on the first packet => compression
• Queueing delay on the second packet => expansion
SenMetrics05
14
SenProbe
Path capacity estimation tool specially designed for the multi-hop
CSMA based wireless networks.
One-way estimation technique, based on CapProbe concepts
Aimed to simplify the path capacity estimation process
A back-to-back packet train technique designed to overcome the
hidden terminal effects in CSMA environment
SenProbe measures end-to-end effective capacity in wireless ad hoc
networks.
SenProbe is simple, fast and less intrusive to comparative
techniques.
SenMetrics05
15
SenProbe Algorithm(1)
Instead of using back-to-back packet pairs, SenProbe
relies on back-to-back packet train to overcome the
effect of hidden terminal in CSMA-CA
The length of this back-to-back packet train depends on
the interference range and the transmission range of the
specific radio technology under question
InterferenceRange
NTRAIN
2
Tranmissio
nRange
SenMetrics05
16
SenProbe Algorithm(2)
The receiver measures the OWD of
every packet in kth packet train
received as the difference between
time received and time sent
OWD[k , i] Trcv [k , i] Tsend [k , i], 1 i NTRAIN
the minimum OWDSUM is kept for
OWDSUM [k ] min OWD [k , i] OWD [k , j ]
the kth packet train. The “good”
1i j N
dispersion sample r (i.e. samples
r arg min OWDSUM [k ]
encountering no cross traffic) is the
k
sample with the minimum OWD
sum
TRAIN
Dispersion of the good sample
calculated, and used to estimation
capacity
SenMetrics05
T OWD [r , v] OWD [r , u ]
P
C
T
17
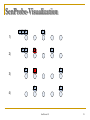
SenProbe-Visualization
4 3 2
1
1)
4 3
2
1
4
3
1
4
1
2)
3)
4)
SenMetrics05
18
Outline
Motivation
Background
Design Consideration
What does SenProbe actually measure?
Effective Capacity
Previous Method
Proposed Approach: SenProbe
Simulation Results
Conclusion
SenMetrics05
19
Simulation Results (1)
End-to-End Capacity (Mbps)
2.5
Packet-pair technique
FTP
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Number of hops
Path Capacity measured via FTP connection and Packet-Pair
technique (one way CapProbe)
SenMetrics05
20
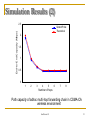
Simulation Results (2)
End-to-End Capacity (Mbps)
2.5
SensorProbe
Theoretical
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Number of hops
Path capacity of adhoc multi-hop forwarding chain in CSMA-CA
wireless environment
SenMetrics05
21
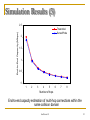
Simulation Results (3)
End-to-End Capacity (Mbps)
2.5
Theoretical
SensorProbe
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Number of hops
End-to-end capacity estimation of multi-hop connections within the
same collision domain
SenMetrics05
22
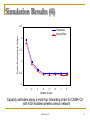
Simulation Results (4)
End-to-End Capacity (Mbps)
2.5
Theoretical
SensorProbe
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
1
2
3
4
5
Number of hops
6
7
8
Capacity estimates along a multi-hop forwarding chain for CSMA-CA
with ACK enabled wireless sensor network
SenMetrics05
23
Conclusion
SenProbe uses back-to-back packet trains, and
relies on packet dispersion between the packet
trains to measure the path capacities in a one-way
fashion.
SenProbe estimates e2e path capacity in CSMA
enabled wireless sensor networks.
SenProbe is a simple and non-intrusive technique
that can accurately reflects the effective path
capacity
SenMetrics05
25
Thanks!
SenMetrics05
26