* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download state-space analysis of
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
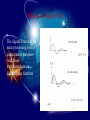
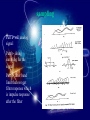
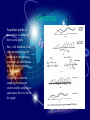
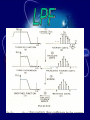
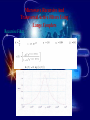
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Supervised by Prof. Dr . ADNAN AFFANDI INTRODUCTION FILTERING • Filtering in communication systems ,stands as a basic • signal process it cover operation such as ,channeling ,demodulating , detecting ,decoding , phase splitting and others . But until recently ,analog filters where in use.Sometime • after the appearance of digital system,the digital filter appeared. It is now used in various fields such as biomedical • engineering , acoustics, sonar, radar and others . What is a Digital filter The digital filters are the main processing tool of quantization samples . And linear transformations on discreat time function Continue NOTE DIGITAL FILTER IS LARGE AND IMPORTANT BRANCH OF DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Analog Signal In a transmitter the information modulates the carrier ,i .e , is impressed on a high -frequancy sine wave ADVANTAGE -Filter duration impulse response are achievable. -Linear phase filter are realizable. -Some realization problems such as negative elements values,and practical problems such as large components at low frequencies do not arise. -Greater accuracy is achieved. -Environmental conditions such as temperature , humidity and pressure have little effect on the filters response. DIGITAL SIGNAL Digital filters are still limited by being an active system it requires power its performance is limited by quantization of the input samples and filter cofficients the use of finite arithmatic in the coputions Digital Filter Types CONTINUE sampling Part a- still analog signal Part b- doing sampling for the signal Part c- filter band limit then we get filter response which is impulse response after the filter CONTINUE Amplitude points at same points of sampling here is zero points Part - d all functions in the same position of impulse sampling at zero position to prevent any interferance which is happened when (b.w) decrease . Correct filter when the sampling positions are correct and the sampling at equal space then we detect the signal Microwave Recursive And Transversal Active Filters Using Lange Couplers The main purpose of this chapter is to analyse the methodology of using lange couplers in recursive and transvesal filters designs,in keeping with the strict interpretations of low frequancy principles . The design approach has been outlined for both transversal and recursive type circuits . By using lange couplers with various coupling values , and than calculating the corresponding filters parameters,we have readily compared theoretical results with computer-simulated ones. Expermental filter examples, comprising one of each kind , further illustrates the validity of our approach . The last step in the design has been to include an active device , to help in the realization of highly selective response . Microwave Recursive And Transversal Active Filters Using Lange Couplers Transversal Active Filter Microwave Recursive And Transversal Active Filters Using Lange Couplers Recursive Filter STATE-SPACE ANALYSIS OF -D IIR FILTERS Abstract Two computer programs for the design of the filters are written . The first solves the stability problem by imposing some constraints on the filters coefficients . The second has no constraints, and the stability of the resulting filter is guaranteed by approximating an implse response that obeys the basic stability theory in the bounded input bounded output sense . STATE-SPACE ANALYSIS OF -D IIR FILTERS FREQUENCY RESPONSE This program obtains the frequency response of an IIR filter . The input: A,B,C,D matrices N1,N2: The no. of point on the Z1,Z2 axies. The output: T transfer function. The equation: (processing) T=C/(Z12-A)*[B]+[D] Z12=[Z1:Z2]t[I} STATE-SPACE ANALYSIS OF -D IIR FILTERS TIME RESPONSE This program obtains the time response of a digital filter . The input : A,B,C,D matrices. Q011,Q012,Q021,Q022 initial conditions. N1,N2 the no.of points on the n1,n2 axes . The output: Q1,Q2 the state space equations. Y the time response. The equations: Q1(n1,n2)=A11Q1(n1-1,n2)+A12Q2(n1-2,n2)+B1X(n1,n2) Q2(n1,n2)=A21Q1(n1,n2-1)+A22Q2(n1,n2-1)+B2X(n1,n2) y(n1,n2)=CQ(n1,n2)+DX(n1,n2). The Global Positioning System (GPS)is a new satellite navigation system that is currently being devloped by the United State. It is scheduled to become fully operational in the medel of 1990s. The GPS is ,by far,the most ambitions navigation project ever undertaken by the United State, or by any nation for that matter ,and its application go beyond the usual positioning of aircraft and ships. The central problem for the GPS receiver is the precise estimation of position, velocity ,and time based on noisy on noisy observations of the satellite signals .